Major Recent Earthquakes in the World |
||||
| Date | Location | Coordinates | Deaths | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2/6/2023 | Turkey | 37.166°N, 37.032°E | 57,759 | 7.8 |
| 9/21/2022 | Haiti | 18.784°N,73.159°W | 2,207 | 7.2 |
| 3/4/2022 | Tonga | 20.657°S,174.504°W | 0 | 7.6 |
| 12/30/2021 | Loyalty Islands, New Caledonia | 20.414°S 168.625°E | 0 | 7.6 |
| 11/29/2021 | Loyalty Islands, New Caledonia | 20.941°S 168.340°E | 0 | 7.5 |
| 9/29/2021 | Melamchi, Nepal | 27.764°N 85.790°E | 36 | 6 |
| 2/15/2021 | Off the east coast of Honshu, Japan | 38.297°N 144.715°E | 1 | 7.3 |
| 11/30/2020 | South of Java, Indonesia | 10.732°S 114.957°E | 0 | 6.3 |
| 9/18/2020 | Central Mid-Atlantic Ridge | 0.703°S 24.123°W | 0 | 6.9 |
| 12/5/2019 | Mindanao, Philippines | 6.533°N 125.013°E | 22 | 6.8 |
| 11/26/2019 | Ambon, Indonesia | 2.904°S 129.220°E | 23 | 7.1 |
| 5/26/2019 | Northern Peru | 5.776°S 75.997°W | 2 | 8 |
| 11/30/2018 | Anchorage, Alaska, USA | 61.169°N, 149.990°W | 0 | 7.1 |
| 8/19/2018 | Lombok, Indonesia | 8.277°S 116.142°E | 563 | 6.9 |
| 11/12/2017 | Iraq-Iran border region | 34.799°N 45.987°E | 630 | 7.3 |
| 11/13/2016 | Kaikoura, New Zealand | 42.670°S 173.027°E | 2 | 7.8 |
| 4/16/2016 | Ecuador | 0.371°S 79.940°W | 676 | 7.8 |
| 10/26/2015 | Hindu Kush region, Afghanistan | 36.501°N 70.956°E | 399 | 7.5 |
| 04/25/2015 | East South East of Lamjung, Nepal | 28.147, 84.708 | 6204 | 7.8 |
| 03/11/2011 | Japan | 38.297, 142.373 | 20896 | 9 |
| 04/13/2010 | Southern Qinghai, China | 33.165, 96.548 | 2200 | 6.9 |
| 01/12/2010 | Haiti region | 18.443, -72.571 | 316000 | 7 |
| 09/30/2009 | Southern Sumatra, Indonesia | -0.720, 99.867 | 1117 | 7.5 |
| 05/12/2008 | Eastern Sichuan, China | 31.002, 103.322 | 87587 | 7.9 |
| 05/26/2006 | Indonesia | -7.961, 110.446 | 5749 | 6.3 |
| 10/08/2005 | Pakistan | 34.53N, 73.58E | 86000 | 7.6 |
| 03/28/2005 | Northern Sumatra, Indonesia | 2.07N, 97.01E | 1313 | 8.6 |
| 12/26/2004 | Sumatra | 3.30N, 95.87E | 227898 | 9.1 |
| 12/26/2003 | Southeastern Iran | 28.99N, 58.31E | 31000 | 6.6 |
| 05/21/2003 | Northern Algeria | 36.90N, 3.71E | 2266 | 6.8 |
| 03/25/2002 | Hindu Kush Region, Afghanistan | 35.9N, 69.2E | 1000 | 6.1 |
| 01/26/2001 | Gujarat, India | 23.3N, 70.3E | 20085 | 7.6 |
| 09/20/1999 | Taiwan | 23.7N, 121.0E | 2400 | 7.6 |
| 08/17/1999 | Turkey | 40.7N, 30.0E | 17118 | 7.6 |
| 01/25/1999 | Colombia | 4.46N, 75.82W | 1185 | 6.1 |
| 07/17/1998 | Papua New Guinea | 2.96S, 141.9E | 2183 | 7 |
| 05/30/1998 | Afghanistan-Tajikistan Border Region | 37.1N, 70.1E | 4000 | 6.6 |
| 02/04/1998 | Hindu Kush region, Afghanistan | 37.1N, 70.1E | 2323 | 5.9 |
| 05/10/1997 | Northern Iran | 33.9N, 59.7E | 1567 | 7.3 |
| 05/27/1995 | Sakhalin Island | 52.6N, 142.8E | 1989 | 7.5 |
| 01/16/1995 | Kobe, Japan | 34.6N, 135E | 5502 | 6.9 |
| 09/29/1993 | Latur-Killari, India | 18.1N, 76.5E | 9748 | 6.2 |
| 12/12/1992 | Flores Region, Indonesia | 8.5S, 121.9E | 2500 | 7.5 |
| 10/19/1991 | Northern India | 30.8N, 78.8E | 2000 | 7 |
| 07/16/1990 | Luzon, Philippine Islands | 15.7N, 121.2E | 1621 | 7.7 |
| 06/20/1990 | Western Iran | 37.0N, 49.4E | 50000 | 7.4 |
| 12/07/1988 | Spitak, Armenia | 41.0N, 44.2E | 25000 | 6.8 |
| 08/20/1988 | Nepal-India border region | 26.8N, 86.6E | 1000 | 6.8 |
| 03/06/1987 | Colombia-Ecuador | 0.2N, 77.8W | 1000 | 7 |
| 10/10/1986 | El Salvador | 13.8N, 89.2W | 1000 | 5.5 |
| 09/19/1985 | Mexico, Michoacan | 18.2N, 102.5W | 9500 | 8 |
| 10/30/1983 | Turkey | 40.3N, 42.2E | 1342 | 6.9 |
| 12/13/1982 | Yemen | 14.7N, 44.4E | 2800 | 6 |
| 07/28/1981 | southern Iran | 30.0N, 57.8E | 1500 | 7.3 |
| 06/11/1981 | southern Iran | 29.9N, 57.7E | 3000 | 6.9 |
| 11/23/1980 | southern Italy | 40.9N, 15.3E | 2735 | 6.5 |
| 10/10/1980 | El Asnam, Algeria (formerly Orleansville) | 36.1N, 1.4E | 5000 | 7.7 |
| 09/16/1978 | Iran | 33.2N, 57.4E | 15000 | 7.8 |
| 03/04/1977 | Romania | 45.8N, 26.8E | 1500 | 7.2 |
| 11/24/1976 | Turkey-Iran border region | 39.1N, 44.0E | 5000 | 7.3 |
| 08/16/1976 | Mindanao, Philippines | 6.3N, 124.0E | 8000 | 7.9 |
| 07/27/1976 | Tangshan, China | 39.6N, 118.0E | 242769 | 7.5 |
| 05/06/1976 | northeastern Italy | 46.4N, 13.3E | 1000 | 6.5 |
| 02/04/1976 | Guatemala | 15.3N, 89.1W | 23000 | 7.5 |
| 09/06/1975 | Turkey | 38.5N, 40.7E | 2300 | 6.7 |
| 02/04/1975 | Haicheng, China | 40.6N, 122.5E | 2000 | 7 |
| 12/28/1974 | Pakistan | 35.0N, 72.8E | 5300 | 6.2 |
| 05/10/1974 | China | 28.2N, 104.0E | 20000 | 6.8 |
| 12/23/1972 | Nicaragua, Managua | 12.4N, 86.1W | 5000 | 6.2 |
| 04/10/1972 | southern Iran | 28.4N, 52.8E | 5054 | 7.1 |
| 05/22/1971 | Turkey | 38.83N, 40.52E | 1000 | 6.9 |
| 05/31/1970 | Chimbote, Peru | 9.36S, 78.87W | 70000 | 7.9 |
| 03/28/1970 | Gediz, Turkey | 39.06N, 29.54E | 1086 | 6.9 |
| 01/04/1970 | Tonghai, Yunnan Province, China | 24.12N, 102.49E | 10000 | 7.5 |
| 07/25/1969 | Yangjiang, Guangdong, China | 21.61N, 111.83E | 3000 | 5.9 |
| 08/31/1968 | Dasht-e Bayaz, Iran | 33.9N, 59.02E | 12000 | 7.3 |
| 08/19/1966 | Varto, Turkey | 39.1N, 41.48E | 2529 | 6.8 |
| 03/22/1966 | Southeast of Ningjin, Hebei (Hopeh), China | 37.5 115.1 | 1000 | 6.9 |
| 03/07/1966 | East of Longyao, Hebei (Hopeh), China | 37.35 114.92 | 1000 | 7 |
| 07/26/1963 | Skopje, Former Yugoslav Rep. of Macedonia (Makedonija, Yugoslavia) | 42.1N, 21.4E | 1100 | 6 |
| 09/01/1962 | Bu'in Zahra, Qazvin, Iran | 35.6N, 49.9E | 12225 | 7.1 |
| 05/22/1960 | Temuco-Valdivia, Chile | 38.29S, 73.05W | 1655 | 9.5 |
| 02/29/1960 | Agadir, Morocco | 30.45N, 9.62W | 15000 | 5.7 |
| 12/13/1957 | Sahneh, Iran | 34.35N, 47.67E | 1130 | 7.1 |
| 07/02/1957 | Near Sang Chai, Mazandaran, Iran | 36.14N, 52.70E | 1200 | 7.1 |
| 09/09/1954 | Chlef (Orleansville, El Asnam), Algeria | 36.28N, 1.47E | 1250 | 6.8 |
| 03/18/1953 | Yenice-Gonen, Turkey | 40.01N, 27.49E | 1070 | 7.3 |
| 08/02/1951 | Cosiguina, Nicaragua | 13.0N, 87.5W | 1000 | 5.8 |
| 08/15/1950 | Near Zhamo (Rima), Xizang (Tibet), China "Assam-Tibet" Earthquake | 28.7N, 96.6E | 1526 | 8.6 |
| 08/05/1949 | Ambato, Ecuador | 1.5S, 78.25W | 5050 | 6.8 |
| 07/10/1949 | Khait, Tajikistan (Tadzhikistan, USSR) | 39.2N, 70.8E | 12000 | 7.5 |
| 10/05/1948 | Ashgabat (Ashkhabad), Turkmenistan (Turkmeniya, USSR) | 37.95N, 58.32E | 110000 | 7.3 |
| 06/28/1948 | Fukui, Japan | 36.1N, 136.2E | 3769 | 7.3 |
| 12/20/1946 | Nankaido, Japan | 33.0N, 135.6E | 1362 | 8.1 |
| 11/10/1946 | Ancash, Peru | 8.5S, 77.5W | 1400 | 7.3 |
| 05/31/1946 | Ustukran, Turkey | 39.33N, 41.10E | 1300 | 5.9 |
| 11/27/1945 | Makran Coast, Pakistan (Baluchistan, India) | 24.9N, 63.5E | 4000 | 8 |
| 01/12/1945 | Mikawa, Japan | 34.7N, 137.0E | 1961 | 7.1 |
| 02/01/1944 | Gerede, Turkey | 41.11N, 33.22E | 2790 | 7.4 |
| 01/15/1944 | San Juan, Argentina | 31.5S, 68.6W | 8000 | 7.4 |
| 11/26/1943 | Ladik, Turkey | 40.97N, 33.22E | 4000 | 7.6 |
| 09/10/1943 | Tottori, Japan | 35.5N, 134.2E | 1190 | 7.4 |
| 12/20/1942 | Erbaa, Turkey | 40.9N, 36.5E | 1100 | 7.3 |
| 11/10/1940 | Vrancea, Romania (Rumania) | 45.8N, 26.7E | 1000 | 7.3 |
| 12/26/1939 | Erzincan, Turkey | 39.8N, 39.38E | 32700 | 7.8 |
| 01/25/1939 | Chillan, Chile | 36.25S, 72.25W | 28000 | 7.8 |
| 07/16/1935 | Hsin-chu (Shinchiku), Taiwan (Formosa) | 24.6N, 120.8E | 2740 | 6.5 |
| 05/30/1935 | Quetta, Pakistan (Baluchistan, India) | 29.6N, 66.5E | 30000 | 7.6 |
| 04/20/1935 | Miao-li, Taiwan (Formosa) | 24.3N, 120.8E | 3270 | 7.1 |
| 01/15/1934 | Bihar, India-Nepal | 26.5N, 86.5E | 10700 | 8.1 |
| 08/25/1933 | North of Maowen, Sichuan (Szechwan), China | 32.0N, 103.7E | 9300 | 7.5 |
| 03/02/1933 | Sanriku, Japan | 39.25N, 144.5E | 3000 | 8.4 |
| 08/10/1931 | Near Fuyun (Koktokay), Xinjiang (Sinkiang), China | 46.8N, 89.9E | 10000 | 8 |
| 04/27/1931 | Zangezur Mountains, Armenia-Azerbaijan border (Armeniya-Azerbaydzhan, USSR) | 39.2N, 46.0E | 2800 | 5.7 |
| 03/31/1931 | Managua, Nicaragua | 12.15N, 86.28W | 2500 | 6 |
| 07/23/1930 | Irpinia, Italy | 41.05N, 15.37E | 1404 | 6.5 |
| 05/06/1930 | Salmas, Iran (Persia) | 38.15N, 44.70E | 2500 | 7.2 |
| 05/01/1929 | Koppeh Dagh, Iran (Persia) | 37.85N, 57.75E | 3800 | 7.2 |
| 05/22/1927 | Gulang, Gansu (Kansu), China | 37.5N, 102.7E | 40900 | 7.6 |
| 03/07/1927 | Tango, Japan | 35.8N, 134.8E | 3020 | 7.6 |
| 03/16/1925 | Near Dali (Talifu, Ta-li), Yunnan, China | 25.7N, 100.2E | 5800 | 7 |
| 09/01/1923 | Kanto (Kwanto), Japan | 35.3N, 139.5E | 142800 | 7.9 |
| 05/25/1923 | Torbat-e Heydariyeh, Iran (Persia) | 35.2N, 59.2E | 2200 | 5.7 |
| 03/24/1923 | Near Luhuo, Sichuan (Szechwan), China | 31.3N, 100.8E | 3500 | 7.3 |
| 12/16/1920 | Haiyuan, Ningxia (Ning-hsia), China | 36.5N, 105.7E | 200000 | 7.8 |
| 02/13/1918 | Nan'ao, Guangdong (Kwangtung), China | 23.5N, 117.2E | 1000 | 7.4 |
| 07/30/1917 | North of Daguan, Yunnan, China | 28.0N, 104.0E | 1800 | 7.5 |
| 01/20/1917 | Bali, Indonesia | 9.0S, 115.8E | 1500 | |
| 01/13/1915 | Avezzano, Italy | 41.98N, 13.65E | 32610 | 7 |
| 10/03/1914 | Burdur, Turkey (Ottoman Empire) | 37.82N, 30.27E | 4000 | 7 |
| 08/09/1912 | Murefte, Turkey (Ottoman Empire) | 40.75N, 27.20E | 2800 | 7.4 |
| 01/23/1909 | Silakhor, Iran (Persia) | 33.4N, 49.1E | 6000 | 7.3 |
| 12/28/1908 | Messina, Italy | 38.15N, 15.68E | 72000 | 7.2 |
| 10/21/1907 | Qaratog (Karatag), Tajikistan (Turkestan, Russia) | 38.5N, 67.9E | 12000 | 8 |
| 01/14/1907 | Kingston, Jamaica | 18.2N, 76.7W | 1000 | 6.5 |
| 08/17/1906 | Valparaiso, Chile | 33S, 72W | 3882 | 8.2 |
| 04/18/1906 | San Francisco, California | 37.75N, 122.55W | 3000 | 7.8 |
| 03/16/1906 | Chia-i, Taiwan | 23.6N, 120.5E | 1250 | 6.8 |
| 01/31/1906 | Off coast of Esmeraldas, Ecuador | 1N, 81.5W | 1000 | 8.8 |
| 04/04/1905 | Kangra, India | 33.0N, 76.0E | 19000 | 7.5 |
| 05/28/1903 | Gole, Turkey (Ottoman Empire) | 40.9N, 42.7E | 1000 | 5.8 |
| 04/28/1903 | Malazgirt, Turkey (Ottoman Empire) | 39.1N, 42.6E | 3500 | 7 |
| 12/16/1902 | Andijon (Andizhan), Uzbekistan (Turkestan, Russia) | 40.8N, 72.3E | 4700 | 6.4 |
| 04/19/1902 | Quezaltenango and San Marcos, Guatemala | 14N, 91W | 2000 | 7.5 |
What is an Earthquake
An earthquake is a sudden shaking or vibration of the Earth's surface caused by the movement of tectonic plates or other geological processes. Earthquakes can vary in intensity and duration, and can cause damage to buildings and other structures, as well as triggering landslides and tsunamis.
What Causes Earthquakes
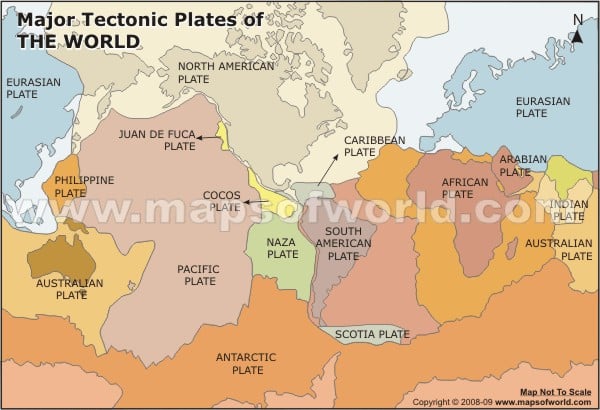
Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates in the Earth's crust. The Earth's crust is made up of several large, solid plates that float on top of the molten mantle layer below. When these plates move against each other, they create friction and stress, which can build up over time. When the stress becomes too great, the plates suddenly shift, causing an earthquake. Earthquakes can also be caused by volcanic activity, landslides, and human activities such as drilling and mining.
Important Terms Related to Earthquake:
- Plates:The underground rocks of earth's surface.
- Fault:Discontinuity along the rock's edge that causes damage to the plates.
- Focus:The point where the rock fault occurs.
- Epicenter:The point on the earth's surface directly above the focus.
- Magnitude:The measure of earthquake energy (expressed in terms of the Richter scale). A unit increase in magnitude corresponds to a ten-fold increase in the earthquake's destructive power.
What to do in an Earthquake
If you are indoors:
a) Drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy desk or table, and hold on until the shaking stops. b) Stay away from windows, mirrors, and anything that could fall, such as shelves or hanging objects. c) If you are in bed, stay there and cover your head with a pillow. d) If you are in a wheelchair or unable to drop to the ground, lock your wheels and cover your head with your arms.
If you are outdoors:
a) Move to an open area away from buildings, trees, and power lines. b) If you are in a car, pull over to a clear location away from buildings, overpasses, and bridges, and stay inside the car until the shaking stops. c) If you are in a high-rise building, stay away from windows and outside walls, and use the stairs to evacuate the building after the shaking stops. d) If you are near the coast and feel an earthquake that lasts longer than 20 seconds or see a noticeable rise or fall in sea level, move immediately to higher ground to avoid the potential danger of a tsunami. Remember to stay calm, and wait for the shaking to stop before attempting to move or evacuate.
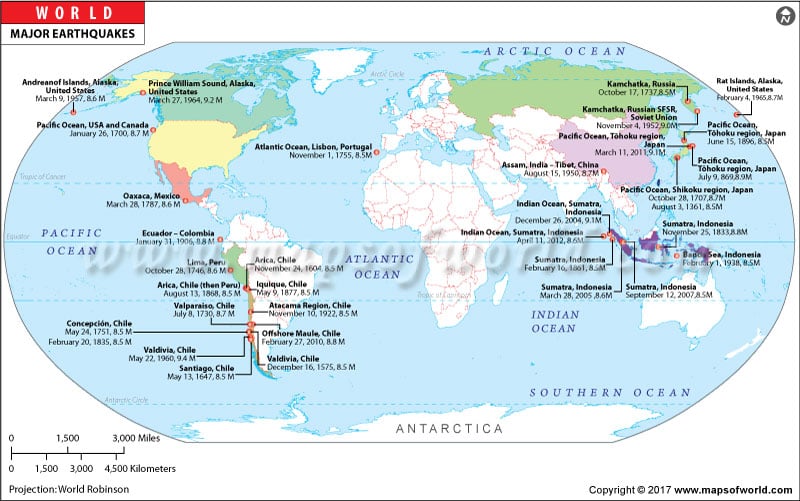
Maps of Earthquakes
Last Updated on: April 21, 2023