Germany Map
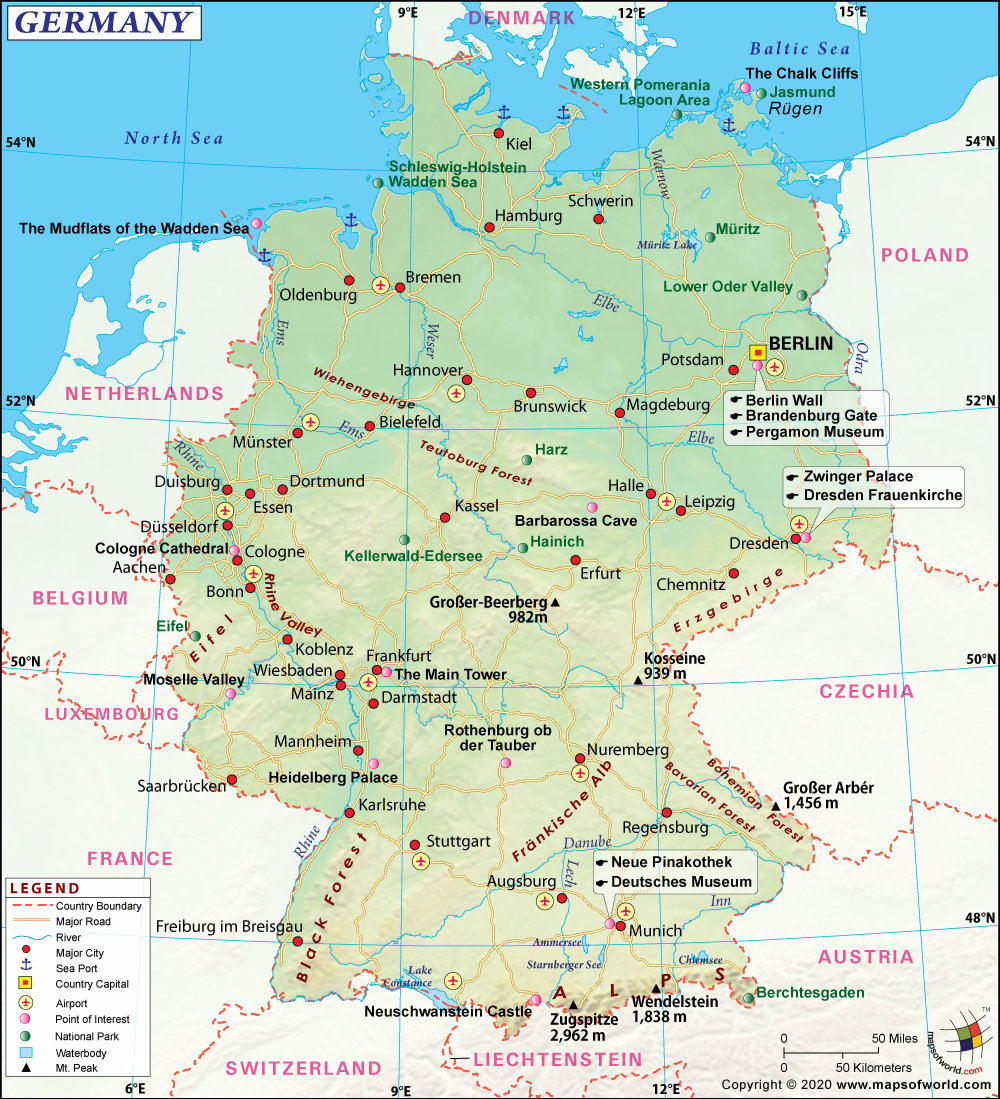
- Germany Cities - Aachen, Augsburg, Bad Oeynhausen, Baden-Baden, Bamberg, Baumholder, Daun, Dortmund, Dresden, Dusseldorf, Essen, Freiburg, Gelsenkirchen, Heidelberg, Hofheim, Kaiserslautern, Karlsruhe, Landstuhl, Münster, Nuremberg, Oberstdorf, Regensburg, Trier, Cologne
- Germany States - Baden-Wurttemberg, Bavaria (Bayern), Brandenburg, Hessen, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Niedersachsen, Nordrhein-Westfalen, Rheinland-Pfalz, Saarland, Sachsen, Sachsen-Anhalt, Schleswig Holstein, Thuringia
- Neighboring Countries - Luxembourg, Netherlands, Denmark, Poland, Belgium, Austria
- Continent And Regions - Europe Map
- Other Germany Maps - Where is Germany, Germany Blank Map, Germany Road Map, Germany River Map, Germany Political Map, Germany Physical Map, Germany Flag
About Germany Map
Explore this Germany map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Germany location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Germany history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Official Name | (Federal Republic of Germany) Bundersrepublik Deutschland |
| Capital | Berlin |
| Population | 82 million |
| Area | 357,020 sq km or 137,846 sq mi |
| Currency | Euro ($1=1.08) |
| Religion | Christianity |
| Literacy | 100% |
| Languages | German Language |
| Major Cities | Berlin, Hamburg, Munich, Colonge, Frankfurt, Leipzig |
| Climate | Mainly moderate climate |
The Federal Republic of Germany (Deutschlandkarte) is a 357,022 square kilometers large country located in Central Europe. Germany measures 876 kilometers from North to South and 640 kilometers from East to West and is a parliamentary federal democracy. With a teeming population of over 82.2 million people and a density of over 231 people per square kilometer, Germany has the largest population among the European Union member countries. It is also the 15th most populous country in the world. Germany is home to an immigrant population of over 7.3 million and about 88% of the country’s population lives in the cities. But that’s just statistics. Germany is an experience to be cherished. Life in Germany is incomplete without mentioning the spunky street carnivals, dressing in flamboyant outfits, eating out at quaint eateries and sampling the flowing beer of the country’s pubs, indulging in heated debates about the latest FIFA or Formula I stars, and trying your hand at car racing.
Berlin, Bremen, Dresden, Dusseldorf, Frankfurt, Hamburg, Hannover, Kiel, Cologne, Magdeburg, Munich, Stuttgart, Leipzig are largest among the 82 cities in Germany. The adjoining map of Germany shows that the country is bound by the Baltic Sea, North Sea, and Denmark in the north, Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and France to the west, Switzerland and Austria to the south, and the Czech Republic and Poland to the east. The culture of Germany is classic, rich, and evolving. Tourists are awed by the multifaceted life here.
Germany is a federation of the 16 states of Baden Wurttemberg, Bavaria, Berlin, Brandenburg, Bremen, Hamburg, Hessen, Lower Saxony, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania , North Rhine-Westphalia, Rhineland-Palatinate , Saarland, Saxony , Sachsen-Anhalt, Schleswig Holstein, and Thuringia. The country has grown to be Europe’s largest economy and a key player in international politics. Germany has survived and thrived despite a long history of political unrest and the two World Wars. In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic were formed. In 1990, the two states united with the ‘Fall of the Wall’ and ever since the consolidated state has strengthened its trade and defenses.
Germany adopted the Euro as its currency in 1999. As a nonpermanent member of the UN Security Council, a founding member of the EU, the G8, and NATO, Germany’s claim to being a major power is substantiated by the country’s advances in the fields of science, technology, and biotech and automobile engineering. The high standard of living and a high level of social security have made Germany a favorite with immigrants. German is the official language and is commonly spoken; however, the presence of a high ratio of immigrant population also makes English, Polish, and Turkish other languages commonly spoken in the cities. German brands such as Adidas have redefined the ‘hip and happening’ across the globe.
The country’s multinational enterprises have taken the world by storm. 500 of the world’s largest corporations are German. The government spends a substantial amount of the budget on military and developmental research. Berlin, the capital city, houses the Federal Foreign Office. Germany has diplomatic missions in over 191 countries of the world. With a GDP of over 2,400 billion Euros and a per capita GNP of over 29,000 Euros, Germany is the world’s largest exporter.
History – surviving the World Wars:
Early Germany: The earliest recorded history of Germany is of the Germanic tribes who were the early settlers of the land. The rule of Augustus Caesar in the 2nd century BC saw the beginnings of a power struggle with the Germanic tribes and the Roman monarchy. The tribes had occupied central and southern Germany by 100 BC. The Rhine defined the boundaries of the Roman expansion for over 100 years. The Romans then made an attempt to conquer the Rhine valley but were halted by the victory of the German general Arminius in the Battle of Teutoburg.
Holy Roman Empire: In the first century AD, the Romans recaptured German towns and villages on the banks of the Rhine. The Germanic tribes started to move to various parts of Europe in the 5th century. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting large areas of Germany and France in the 8th century. Charlemagne fought long battles with the native Saxons and succeeded in converting them to Christianity and in annexing the territory. He established the Holy Roman Empire in the 9th century. Charlemagne was known for his effective administration but the Germanic tribes never ceased to trouble him. After Charlemagne’s death his kingdom saw a period of bitter power struggle. Feuding dukes ruled fiefdoms that broke away from what was Charlemagne’s empire.
Power Struggles: The Holy Roman Empire was re-established by Otto I in the 10th century. The united nation did not survive Otto’s death. The country again dissolved into small feudal states. Through the 11th to the 14th century, Germany saw a period of dissent, power struggles, and supremacy of the Pope and Roman Church.
Protestant Reformation Movement: The Renaissance movement that swept across Europe in the 14th and 15th century, translated into Martin Luther King’s Protestant Reformation Movement in Germany. At the end of the Thirty Years’ War in 1648, a number of independent nation-states replaced the Holy Roman Empire.
World War I: Germany saw a quick growth in the economy and culture with the advent of the Industrial Revolution. Otto von Bismarck took advantage of Berlin’s emergence and made a successful bid at unifying these states into the German Empire in the year 1871.By early 1900s Germany had entered into a Triple Alliance with Hungary and Italy and led them against Great Britain, France, Russia and USA in the World War I. Losing the war cost the country its political and economic strength. A period of uncertainty and political instability ensued in the Weimar Republic as it was then called.
The Great Depression: The Treaty of Versailles in 1919 greatly weakened the country’s economic prowess and poverty and unemployment was rampant. The subsequent years saw the rise of the Deutsche Arbeiterpartei, DAP, a political party with a radical totalitarian ideology. By 1929, Germany was steeped in the throes of the economic dejection. Economic conditions hit rock bottom very soon as the Great Depression ravaged the country.
The Rise of Hitler: It is at such a time that the DAP, as the National Socialist German Workers’ Party (Nazi Party) came to be known through its leader, Adolf Hitler. Hitler was a determined man, an excellent orator, and an exceptionally ambitious leader. Hitler was appointed the Chancellor of Germany in the year 1933. Hitler popularized his socio-political ideology by advocating racial purity and declaring the German Aryans a superior race. Jews, Roma gypsy tribes, physically challenged individuals, communist, and people from the gay and lesbian community were deemed ‘unfit to live’ by Hitler and the Nazi Party. The ensuing Holocaust saw the extermination of over 6 million Jews and over 1 million people from the other groups. The Third Reich, as the rule was called, was an era of expansion and anti-Semitism. Hitler styled himself Führer, leader, of Germany, organized the country’s social, economic, and military forces in keeping with the party’s visions. He seized all legislative and administrative powers of Germany; Hitler had become a force unto himself. The SA and the SS were established to organize Germany into a Nazi state.
World War II: By 1939, Hitler’s conquest of Poland led to a conflict with France and Britain. In 1940, Germany had entered into an agreement with Italy and Japan and the World War II raged between the Axis powers as they were called, and the Allied nations including the Britain, USSR and USA. By 1945, Hitler had committed suicide and Germany had been ravaged by a complete defeat. German borders were redrawn.
Independent and united Germany: In 1949, the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the German Democratic Republic (GDR) emerged as separate states with an emergence of great disparity in the socioeconomic conditions. A wall was built in Berlin between the two and the borders were sealed. Economic conditions worsened in the GDR necessitating a break down of the strict sanctions and barriers and the Berlin Wall was demolished in 1990. The country slowly worked its way through economic and social reforms, providing healthcare and welfare to erstwhile GDR. Germany as a country revived and flourished with greater enterprise.
State and Politics – creation of a superpower:
The German legislature is bicameral and the 16 states of Germany abide by their individual constitutions. The government is elected by universal suffrage. In Germany, the state is headed by the President and the government by the Chancellor. The President, elected by the Bundesversammlung, has representative powers whereas executive powers are vested in the Chancellor. The Bundestag and the Bundesrat are the legislative councils of the German parliament. The unique feature of the German legislature is that while the Bundestag has members who are elected by direct elections, members of the Bundesrat are state government representatives. Both these councils, together, are responsible for the legislative function of the country. The judicial functions are taken up by the state and federal courts with separation of jurisdiction.
The German army, the Bundeswehr, is an awe-inspiring force with the army, navy, air force, and the support functions employing over 200,000 people. Women serve the Bundeswehr in all capacities. Germany’s contribution to the UN peacekeeping forces has necessitated the posting of a number of troops in various countries as well. By enacting the Nuclear Exit Law, the government has agreed to phase out all nuclear power plants in the next decade and the anti-nuclear sentiments in the country are strong.
Geography – Rugged Land, Rivers and Rolling Plains:
The landscape of Germany is dominated by the tall rugged Alps in the south. Zugspitze, at 2,962 meters, is the highest elevation in the country. The forested central plains are made up of the Rhine, Danube, Elbe, and Oder river valleys. Northern Germany is a stretch of coastal land on shores of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea. The Bavarian plateau in southwest Germany completes the myriad range of land relief found in the country.
The country experiences temperate climate with the exception of the higher elevations of the south where Christmas tends to get white. Temperate climate and summer rains keep the land fertile and make the various national parks such as the Wadden Sea National Park, the Jasmund National Park, the Müritz National Park, the Lower Oder Valley National Park, and the Bavarian Forest National Park, home to some colorful biolife. Deer, boars, foxes, and a number of migratory birds can be spotted in Germany. The spruce, aspen, and fir trees of southern Germany seem right out of a Grimm’s fairy tale. The country attracts most tourists in spring (March – May) and in fall (September-November).
Art and Culture of Germany:
Education: Germany is recognized as the seat of erudite European culture and has been home to leading philosophers, poets, artists, and musicians. Germany’s contribution to Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque architecture and artistry is recognized the world over. The country has 32 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The castles and cathedrals that dot the landscape stand testimony to the genius of architects such as Ludwig Mies van der Rohe. Popular interest in art and architecture is actively promoted by the presence of over 5000 museums. German authors of influence include Walther von der Vogelweide, Friedrich Schiller, Bertolt Brecht, and Heinrich Boll. 7,500 libraries and over 95,000 publications a year make Germany a booklovers’ paradise. The Frankfurt Book Fair is a festival of sorts and one of the major events awaited by domestic and international publishers alike. The country has over 103 universities and centers of higher education which attract a large number of foreign students. The subjects of interest range from Philosophy to Music. Friedrich Nietzsche is considered an authority on existentialism and Gottfried Leibniz’s theories form the fundamentals of those studying rationalism. German philosophers, Kant and Hegel are pioneers of modern western philosophy and musicians such as Bach, Beethoven, Mendelssohn and Bramhs define classical music. Music and drama are actively promoted by the festivals hosted here and infrastructure support is provided by the 300 theaters and a multitude of opera houses. The European music scene is dominated by the German pop and jazz musicians and orchestras.
Germany – the land of carnivals: Germany is a land of fun loving people. Carnivals and fairs dominate the German calendar. Every year in February, the country gears up to host a series of carnivals and fairs. These carnivals and fetes last till fall. The cities of Mainz, Cologne, Dusseldorf and Bonn and all the adjoining villages hold food and entertainment events. The locals dressed in colorful attire participate in the musical shows and street carnivals. The country’s best vineyards are located on the banks of the Rhine and also hold a number of wine and beer festivals intended at promoting their produce. Christmas, is when Germany resumes festivities, with over 60% of the population practicing Christianity.
German Media and Communications: With a strong focus on the education, the growth of press and publications in Germany was a natural outcome. Over 350 daily newspapers keep the politically conscious masses engaged, and magazines such as Der Spiegel and Stern cater to a niche audience. The internet penetration of the country is high by global standards with over 60% households connected to the World Wide Web. Radio and communication networks connect the country to the rest of the world. German broadcasting station ZDF boasts of being the largest in all of Europe.
Football, Formula I and famous sportspersons: Speaking of sports in Germany, football is the first sport that comes to the mind. The German Football Association alone boasts of over 6.3 million members. The national football team is a strong one and won the FIFA World Cup trophies of 1954, 1974 and 1990. The country’s stadiums are iconic in terms of their infrastructure, and have hosted the FIFA World Cup in the years 1974 and 2006. The country has an equally strong Woman’s football team which bagged the FIFA Women’s World Cup in 2003 and 2007. Germany is now set to host the FIFA Women’s World Cup in 2011. Besides football, Germans actively follow foosball, tennis, golf, and car-racing. Among the German sports icons, Franz Beckenbauer, Steffi Graf, Boris Becker, and Michael Schumacher are well known. The German Sport University of Cologne is the largest sports university in the world and has been instrumental in securing a stronghold for German participants in the Olympic Games. The country has hosted the Summer Olympic Games twice and the Winter Olympic Games once.
Travel and Cuisine:
German Tours remain an ever popular option with those fascinated by the country’s political and cultural history and those who are intrigued by its geographic diversity. The tall, rugged mountains of south Germany, the northern plains, the urban west and the fertile eastern plains are home to the 300 year-old world of porcelain manufacture and trade. Germany travel received a boost in recent years with a renewed interest in the country’s haute cuisine, Rhine River cruises, and adventure tourism. While the country’s rugged landscapes are perfect for adventure sports such as hiking, walking, and cycling, the spas resorts at Wiesbaden, Baden-Baden, Bad Dürkheim, and Bad Elster make leisure tourism an attractive option.
Getting there and getting around: The infrastructure of the country supports the booming tourism industry. The high speed and regular rail networks crisscrosses the country and the network covers over 36,000 km. Germany has over 540 airports to manage the influx of tourists. Aviation industry in Germany took off as early as the 1920’s with a number of small companies being set up. Deutsche Luft Hansa AG was set up in 1926 and as Lufthansa is recognized till date as one of the best commercial fleets of the world. Lufthansa’s long and short haul fleets consist almost entirely of Boeing and Airbus crafts. Frankfurt airport is one of the major airports of Europe and is regarded by many as one of the major gateways to the continent. Going by 2009 statistics, Frankfurt is the 3rd largest airport in Europe and 9th in the world in terms of traffic.
Familiar Names and Fun Vacations: With international trade and commerce on the rise, the hospitality industry in Germany has flourished well. The Berlin Hotel Management School and the Hotel Management Schools of Hamburg and Dusseldorf accept many international students. Many international hotel chains including the Marriott, Hilton and Best Western have properties in different German cities. While the scenic natural settings and wilderness attract leisure travelers, business and budget travel to Germany is on the rise recently.
Germany is a very friendly country for ‘Europe on a shoestring’ travelers offering budget options for accommodation, travel, food and entertainment. The castle hotels of Colmberg, Hugenpoet, Sababurg, and Auf Schonburg remind tourists of the reason most Grimm’s fairy tales were set in the locales of Germany. Rhine river cruises remain the favorite option of honeymoon couples.
Food and Fiesta: German cuisine is reflective of the country’s geographic diversity. The local restaurants of the northern coastal region serve an amazing variety of seafood. A great lunch in Germany would typically include herbed and baked or charred salmon, fish soups and chowder, and pickled herrings and sardines. The Rhine valley offers a plentitude of freshwater fishes including carp and trout. Pike is considered a gourmet’s delight in this area.
Most German dishes are stewed, and meat and potatoes are common ingredients in most recipes. The restaurants in the forested areas of Germany serve meats of game animals such as the boar and the venison. The Schnitzel and the Gulasch remain particular favorites through the reason. Lamb, turkey, pork, and poultry remain part of the standard German food. The cosmopolitan cities have many restaurants serving international fare and the country is known for its haute cuisine.
Cheese and Wine or Beer Country? : A visit to Germany remains incomplete without tasting the different varieties of cheese and wines manufactured indigenously. Riesling, Silvaner Spätburgunder, and Dornfelder are commonly served white and red wines and go well with the local cuisine. Germany is popularly known as ‘Beer Country’. The local breweries around the Rhine valley and Cologne area produce an interesting variety of beer and ales. Malt Korn is a ‘must-try’ for those in the country.
MapsofWorld Trivia: Leica and Rolleiflex, world famous cameras, were produced in Germany. Most of these are now collector’s items. Germany binoculars and precision microscopes are known for their accuracy, the world over.
Enterprises such as Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Audi, Porsche, Volkswagen, Lufthansa, and SAP have put Germany on the map of international trade and commerce. The country’s rich and colorful history adds on to the growing interest in German tourism.
You haven’t been to Germany if you haven’t:
- Seen the Rache des Papstes on Fernsehturm Berlin. Berlin’s TV tower is an imposing 368 meters tall structure, the tallest in Germany. The Rache des Papstes or Pope’s Revenge, is a natural sign of the Cross formed by the sun’s reflection on the Fernsehturm Berlin’s steel dome.
- Visited Hiddestorf and heard tales of witchcraft and the witch trials from the locals. The witch trials that swept across Europe were particularly detrimental to the Germany people and over 26,000 men and women were accused of being witches. The trial, condemnation, and witch-hunts that followed are horror tales in Germany.
- Heard Bach compositions in his motherland. Johann Sebastian Bach is one of the most recognized composers in the world and the best proponent of the Baroque style of music. Music festivals of Bach compositions are held across Germany, particularly in cities where he lived. Leipzig, Luneburg, Arnstadt and Kothen are visited by artists wanting to pay their regards to the maestro. Nothing can be as enthralling as listening to Bach compositions in one of these concerts.
- Visit at least 3 of the 9 cities hosting the 2011 FIFA Women’s World Cup. Impuls Arena (Augsburg), Olympic Stadium (Berlin), Ruhrstadion (Bochum), Rudolf – Harbig – Stadium (Dresden), Commerzbank – Arena (Frankfurt), BayArena (Leverkusen), Borussia-Park (Mönchengladbach), Rhein-Neckar-Arena (Sinsheim), and Volkswagen-Arena (Wolfsburg) are the 9 stadiums that shall roar with cheering audience this 2011 as the FIFA Women’s World Cup is hosted by Germany. If you are in Germany make sure you cheer the local team and remain popular.
- Been a part of the Cologne Carnival or at the least been to the Cologne Carnival Museum. The carnival is declared open on the November 11, every year at 11 minutes past 11 and lasts till Ash Wednesday. ‘Kölle Alaaf’ (Cologne Alive) rents the air and the festivities reach a crescendo by Rose Monday. Dancing, merrymaking and feasting at the carnival make a visit well worth it.
The Germans are proud of their rich, erudite culture. Over forty- two Nobel Prize laureates were part of the academic fraternity at the Georg-Augut University of Gottingen. Germany was the very first country to adopt Daylight Saving Time in the year 1916. The Goseck Circle in Saxony-Anhalt, built over 7000 years ago, is the oldest known sun observatory in Europe. Germany is a land of skilled architects and engineers. The country established the world’s oldest savings bank in Lower Saxony in the 18th century. Germany is also a land of fun and fiesta. Baden -Wurttemberg houses the world’s two largest cuckoo clocks. The beauty of the country and the interesting history make Germany the center of tourist and entrepreneurial attraction.
 Wall Maps
Wall Maps