Map of Brazil – States, Cities, Rivers, and Roads
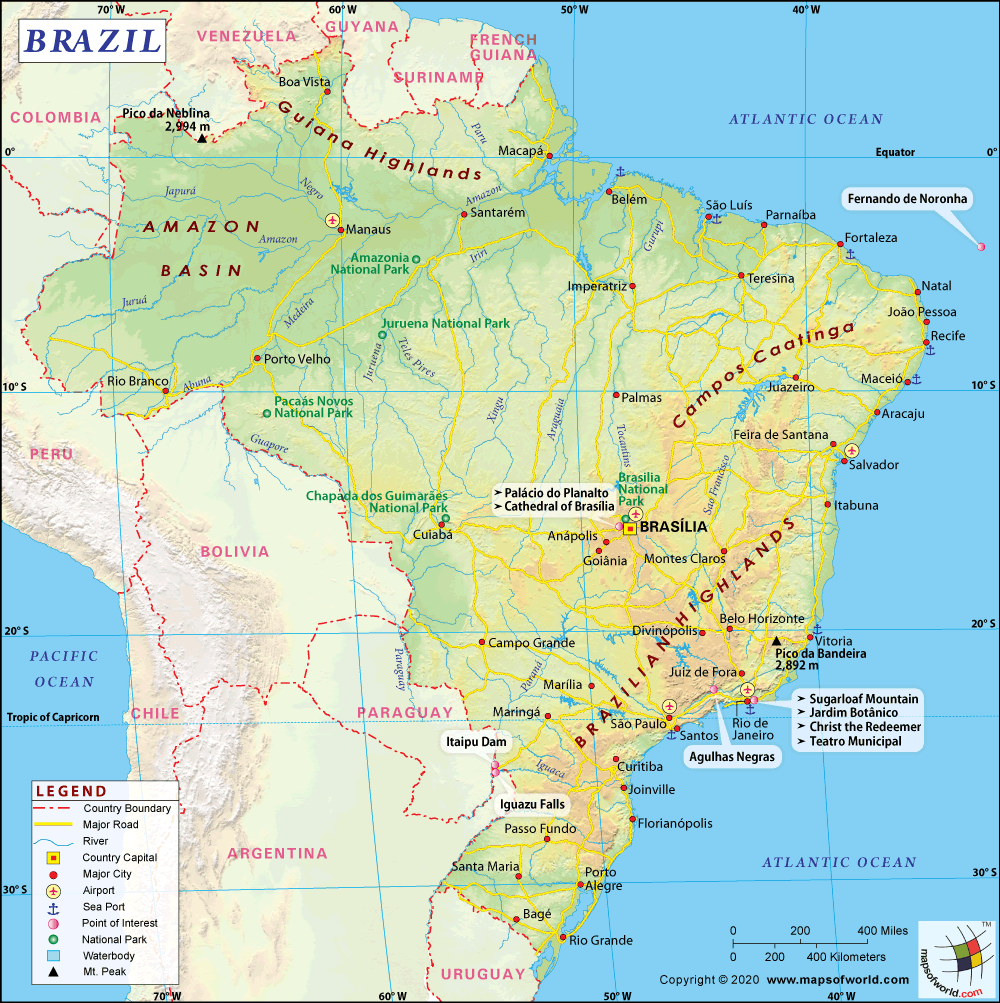
- Brazil States - Acre, Alagoas, Amapa, Amazonas, Bahia, Ceara, Distrito Federal, Espirito Santo, Goias, Maranhao, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Minas Gerais, Para State, Paraiba, Parana, Pernambuco, Piaui, Rio de Janeiro, Rondonia, Roraima, Santa Catarina, Sao Paulo, Sergipe, State of Rio Grande do Norte, State of Rio Grande do Sul, Tocantins
- Brazil Cities - Aracaju, Belem, Belo Horizonte, Boa Vista, Brasilia, Campo Grande, Cuiaba, Curitiba, Florianopolis, Fortaleza, Goiania, Joao Pessoa, Macapa, Maceió, Manaus, Natal, Palmas, Porto Alegre, Porto Velho, Recife, Rio Branco, Salvador, Sao Luis, Sao Paulo, Teresina, Vitoria
- Brazil Regions - Central West Region of Brazil, North Region of Brazil, Northeast Region of Brazil, South Region of Brazil, Southeast Region of Brazil
- Neighbouring Countries - Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela
- Continent And Regional Maps - South America Map, Americas Map
- Other Brazil Maps - Where is Brazil, Brazil Blank Map, Brazil Political Map, Brazil Railway Map, Brazil River Map, Brazil Road Map, Brazil Physical Map, Brazil Flag
Welcome to MapsOfWorld’s Brazil Map page! Brazil is the largest country in South America, covering over 8.5 million square kilometers of land. The country has a diverse geography, ranging from the Amazon rainforest to the tropical beaches of Rio de Janeiro.
In addition to the detailed map of Brazil, this page provides useful information about the country’s geography, culture, history, economy, and tourism. Brazil is home to a number of famous landmarks, such as the Christ the Redeemer statue in Rio de Janeiro and the Iguazu Falls on the border of Brazil and Argentina. Brazil is also known for its vibrant culture, including its music, dance, and cuisine.
Brazil History
The history of Brazil dates back to as early as 10,000 years ago, with evidence of pottery from 8,000 years ago. In 1500, the Portuguese arrived and claimed Brazil, eventually gaining control of the export of Brazilwood. In the 1600s, sugarcane plantations on the northeast coast became the major source of revenue for the Brazilian economy, with black slaves imported from Africa to work on these plantations.
The 1800s saw Brazil ruled as a monarchy until a republic was established in a coup d’etat. Between 1893 and 1926, several military and civilian movements shook the nation, and from the 1960s to 1980s, Brazil saw a rise in internal military disturbances which later led to a military dictatorship. Post-1985, democracy was re-established, and in 2010, Dilma Rousseff was elected President, becoming the first woman to hold this office.
State and Polity
Brazil is a federal presidential constitutional republic with three independent branches – executive, legislative, and judicial. The executive power is headed by the President, currently Jair Bolsonaro, advised by a cabinet. The seat of the federal government is in Brasilia.
Brazil Economy
Brazil is the ninth-largest economy in the world and is known for its agricultural, mining, and manufacturing sectors. The country is a member of the BRICS group of major emerging economies and has a diversified economy. In 2020, Brazil’s gross domestic product (GDP) was $1.4 trillion. The country’s major exports include soybeans, coffee, iron ore, and crude petroleum. The Gross National Income (GNI) per capita in Brazil in 2020 in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms was USD 14,480.
Brazil Defense
The Ministry of Defense of Brazil or the Ministerio da Defasa is the organization responsible for managing the military of Brazil, headed and managed by the Minister of Defence. The Ministry of Defense has three major components under its command structure – the Air Force Command, the Army Command and the Navy Command. Other agencies operated by the Ministry of Defense are the Infraero, National Civil Aviation Agency, and the Superior War School.
Tourism in Brazil
Brazil is a popular tourist destination, known for its natural beauty, vibrant culture, and famous landmarks. The country has a number of popular tourist destinations, including the beaches of Rio de Janeiro, the Amazon rainforest, and the Iguazu Falls. Other popular tourist attractions in Brazil include the Christ the Redeemer statue, the city of Salvador, and the Pantanal wetlands. In 2019, Brazil received over 6.6 million international tourists, generating approximately $5.9 billion in revenue.
Health and Education
The life expectancy of a Brazilian is 76.1 years (as of 2020), and the country spent approximately 9.2% of its gross domestic product (GDP) on healthcare in 2019. The literacy rate in Brazil for people aged 15 and above is 93.2% (as of 2019). In terms of education expenditure, Brazil spent approximately 5.3% of its gross domestic product (GDP) on education in 2018.
We hope you find this page useful in your exploration of Brazil. Don’t forget to check out our other pages about South America and other countries around the world!
 Wall Maps
Wall Maps