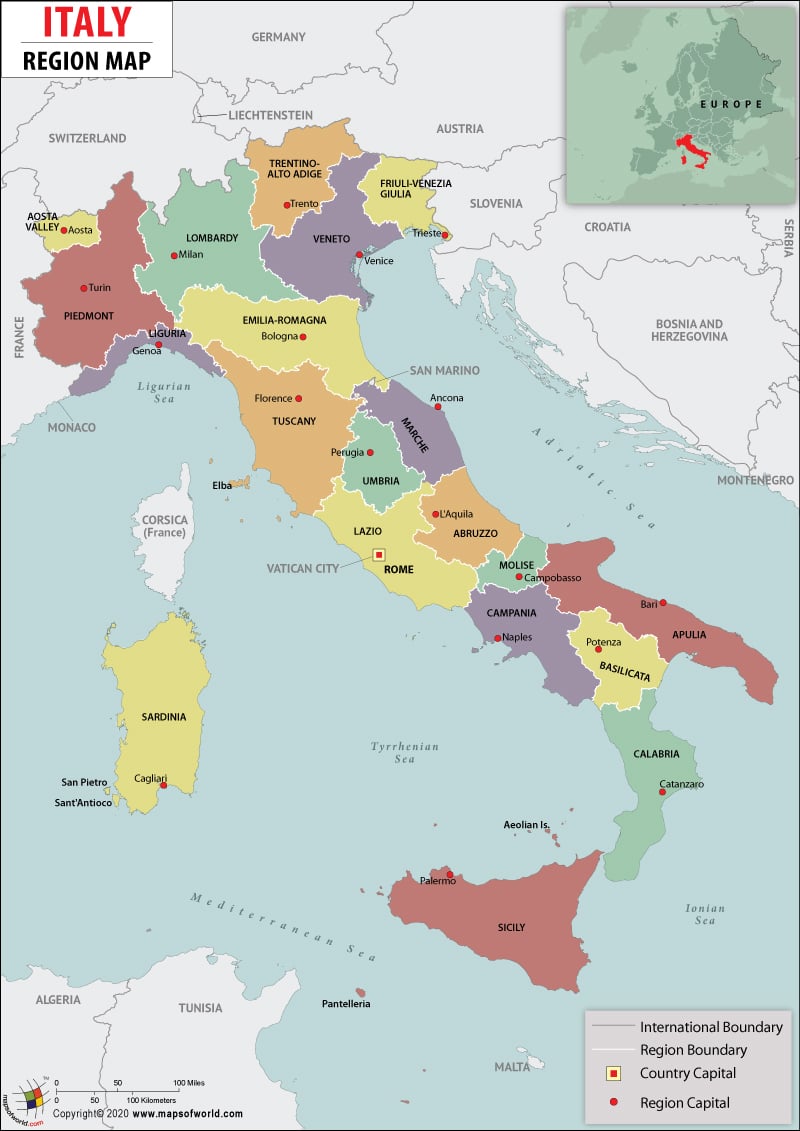
Italy constitutes 20 regions as the administrative divisions, out of which 5 are considered autonomous. The constitution of 1948 granted a certain degree of autonomy to the regions of Italy and specified that the Constitution is supposed to recognize, promote and protect the local autonomy of these regions. This step was taken with the intention of decentralizing services at the State level. The twenty Regions of Italy are:
-
- Abruzzo with L’Aquila as its capital: This place with harsh mountains and a long coastline is a perfect tourist destination
- Apulia with Bari as its Capital:
- Aosta Valley with Aosta as its Capital: Aosta, a region of Italy is located in the North West corner of the Peninsula and is bordered by Mount Blanc, The Grand Pradiso, and Mount Rosa.
- Calabria with Catanzaro as its Capital: One of the most citric fruit-producing regions of Italy, Calabria also forms the basis of all industrial enterprises.
- Campania with Naples as its Capital: The region has been blessed by the best of the Greeks, Romans, Swabians, Bourbons, and Normans all of whom had once settled in this region of Italy.
- Basilicata with Potenza as its Capital: A historical place, it has some very interesting archaeological zone.
- Lazio with Rome as its Capital: It differs a lot from its capital both historically and naturally and is an archive of art and history.
- Emilia-Romangna with bologna as its Capital: With a Cathedral in every Town and Village, this region of Italy runs from the Apennines to the Adriatic.
- Friuli-Venezia Giulia with Trieste as its Capital: Art, culture, and tradition are the marks of identification for this region of Italy.
- Lombardy with Milan as its Capital: Known for its artistic, romantic waterways the region has Milan, a leading commercial center as its Capital.
- Marche with Ancona as its Capital: This region sums up all the beauty of Italy.
- Molise with Campobasso as its Capital: With a number of Seaside resorts this place is a hot favorite among tourists.
- Liguria with Genoa as its Capital: The mildest region of North Italy, this region of Italy is like a Terrace overlooking the Sea.
- Veneto with Venice as its Capital: Its Capital Venice represents the great Civilization of the region.
- Tuscany with Florence as its Capital: The captivating landscape is a true representative of the essence of Italy.
- Trentino-Alto Adige with Trento as its Capital: With the Dolomites standing strong in this region this is one of the most popular regions among mountain lovers.
- Sicily with Palermo as its Capital: A popular holiday spot, its temperate climate, and the resorts make it a hot favorite.
- Sardinia with Cagliari as its Capital: The second largest island in Italy it is a museum of culture and heritage.
- Umbria with Perugia as its Capital: The land of the Saints, as it is commonly known, is known for its mystic character.
- Piedmont with Turin as its Capital: Scenic beauty is best molded by industries in this region of Italy.
Regions of Italy (Administrative divisions) with their capital cities |
|---|
| Region | Population (Jan 2016) | Area (sq km) | Area (sq mi) | Pop. Density (sq mile) |
Capital city | Number of comune |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abruzzo | 1,326,513 | 10,832 | 4,182 | 316 | L’Aquila | 305 |
| Aosta Valley | 127,329 | 3,261 | 1,259 | 101 | Aosta | 74 |
| Apulia | 4,077,166 | 19,541 | 7,545 | 541 | Bari | 258 |
| Basilicata | 573,694 | 10,073 | 3,889 | 148 | Potenza | 131 |
| Calabria | 1,970,521 | 15,222 | 5,877 | 334 | Catanzaro | 405 |
| Campania | 5,850,850 | 13,671 | 5,278 | 1109 | Naples | 550 |
| Emilia-Romagna | 4,448,146 | 22,453 | 8,669 | 513 | Bologna | 333 |
| Friuli-Venezia Giulia | 1,221,218 | 7,862 | 3,036 | 401 | Trieste | 216 |
| Lazio | 5,888,472 | 17,232 | 6,653 | 886 | Rome | 378 |
| Liguria | 1,571,053 | 5,416 | 2,091 | 751 | Genoa | 235 |
| Lombardy | 10,008,349 | 23,864 | 9,214 | 1085 | Milan | 1,523 |
| Marches | 1,543,752 | 9,401 | 3,630 | 425 | Ancona | 229 |
| Molise | 312,027 | 4,461 | 1,722 | 181 | Campobasso | 136 |
| Piedmont | 4,404,246 | 25,387 | 9,802 | 448 | Turin | 1,202 |
| Sardinia | 1,658,138 | 24,100 | 9,305 | 179 | Cagliari | 377 |
| Sicily | 5,074,261 | 25,832 | 9,974 | 508 | Palermo | 390 |
| Trentino-South Tyrol | 1,059,114 | 13,606 | 5,253 | 202 | Trento | 293 |
| Tuscany | 3,744,398 | 22,987 | 8,875 | 422 | Florence | 276 |
| Umbria | 891,181 | 8,464 | 3,268 | 272 | Perugia | 92 |
| Veneto | 4,915,123 | 18,407 | 7,107 | 692 | Venice | 575 |
| ITALY | 60,665,551 | 302,073 | 116,631 | 521 | Rome | 7,978 |
In the time of Ancient Rome, the capital city of Italy was the center of the entire Roman Empire. Today Italy, a founding member of the eurozone and the European Union, is also one of the largest economies in the world, and a major regional power in Europe. Rich Catholic culture has shaped the country’s religious base, even though Judaism has been the longest established religious faith in the country. Home to a number of UNESCO heritage sites, Italy is also a great center of culture, literature, and art. Italy is also known for giving the world the theatrical extravaganza called opera, and its traditional cuisine – pasta and pizzas.
Italy’s Political Timeline |
|---|
| 8th century- 7th Century BC | Greeks settled in the southern part of the Italian peninsula |
| 8th century- 7th century BC | The Roman Republic unified the peninsula |
| 3rd Century BC | Romans captured the neighboring islands |
| 1st century BC | Romans dominated the Mediterranean world |
| 5th Century AD | Roman empire declined |
| 11th century | Northern and central Italy was exposed to the influence of the Renaissance and experienced commercial prosperity. |
| 16th Century | The Renaissance began in Italy and spread throughout Europe |
| 1861 | The nationalist movement reunited Italy with the exception of Rome. |
| 1870 | Rome became part of Italy |
| 1946 | Italy became a Republic |
| 1948 | Constitution was approved |
Location of Italy
Located in southern Europe, Italy is comprised of the Italian Peninsula and a number of islands. Italy shares borders with four countries: Switzerland, France, Austria, and Slovenia. It also surrounds two landlocked countries, San Marino and Vatican City. Italy spans a total area of 116,347 square miles and has a coastline of 4,722 miles.
Economy and Agriculture
Economically, Italy can be divided into two parts – the developed industrial north, which is dominated by private companies, and the less developed agricultural south. Prior to World War II, Italy had an agriculture-based economy, and after the Second World War, Italy rapidly transformed into an industrialized nation. Today, Italy is one of the most developed nations in the world, with a high standard of living. The country has high GDP, but also has a high unemployment rate. Italy’s economy is supported by many small and medium-sized enterprises, which mainly produce high-quality consumer goods.
Italy’s GDP is about $2.05 trillion (2010 United Nations), which is the eighth largest in the world. Italy’s main agricultural products are wheat, rice, citrus fruits, beef, potatoes, and soybeans. Its main industries are the textile industry, tourism industry, and consumer goods manufacturing enterprises. The eurozone crisis has left an indelible mark on the country, though, and unemployment is a major concern.
Political History and Divisions
Prior to June 1946, the monarchy was prevalent in Italy, but the monarchy was abolished in June 1946, and Italy became a parliamentary democratic nation. Italy’s parliament is divided into two houses: the Senate of the Republic (315 seats) and the Chamber of Deputies (630 seats). Italy’s prime minister shares authority with the president of Italy. Fifteen regions of Italy have centralized governments, with the head of the regions reporting to the central government. The twenty regions of Italy have about 110 provinces, each with its own locally elected representatives. One unique feature of Italy’s parliament is that representation is given to permanently non-residing citizens.
Major Cities of Italy
- Venice: Located in northeastern Italy, Venice is the capital of the Veneto region. Venice is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, famous for its beautiful views, works of art, and unique landscapes and architecture. This city attracts many tourists every year.
- Milan: Milan is the commercial, industrial, and business center of Italy. This second largest city in Italy also is the capital of the Lombardy region and can be called the capital of Italian fashion.
- Florence: This famous historical city is the capital of the Tuscany region of Italy. Florence has many monuments and museums that attract visitors to this city on regular basis.
- Rome: The capital of Italy, as well as the Lazio region, Rome, became part of unified Italy in 1870. In ancient times, Rome was the capital of the Roman Empire, which was a powerful empire that spanned the Mediterranean. Rome is also listed as a UNESCO’s World Heritage Site.
Italy – from the Etruscans to the present day
Italy is a peninsular country bounded by the Mediterranean, with the Tyrrhenian Sea in the west and the Adriatic Sea to the east. Italy is a beautiful country with lofty mountains like the Apennine and green valleys like Lombardy. The Po is the longest river in Italy. Italy is home to two great civilizations, namely the Roman and the Etruscan civilizations.
Italy has a population of about 60.3 million people (2022 estimate) and is known for its culture and tradition. Italy is a predominantly Roman Catholic country. The official language of Italy is Italian, but German and French are also spoken by a minority of the population in certain regions. Various dialects are spoken within regions of Italy.