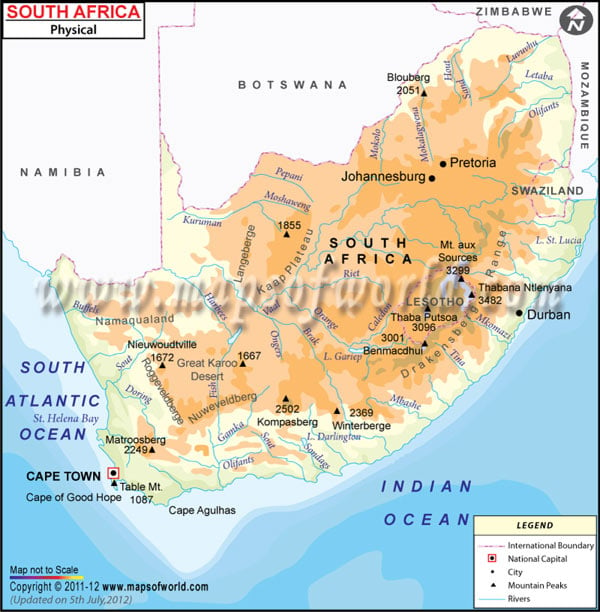
- South Africa Cities - Durban, Pretoria, Soweto, Cape Town
- South Africa Provinces - Eastern Cape, Free State, Gauteng, KwaZulu-Natal, Limpopo, Mpumalanga, North-West, Northern Cape, Western Cape
- Neighboring Countries - Lesotho, Mozambique, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Namibia
- Continent And Regions - Africa Map
- Other South Africa Maps - South Africa Map, Where is South Africa, South Africa Blank Map, South Africa Road Map, South Africa River Map, South Africa Political Map, South Africa Flag
Sudan, known as the Republic of Sudan officially, is located in northeastern Africa. It shares its boundary with Egypt to the north, the Red Sea, Ethiopia and Eritrea to the east, Central African Republic and Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest and South Sudan to the South.
Sudan Physical Features
The country lies between latitudes 8.N. and 23. N. The Somalia Physical Map is beneficial for school presentations and other purposes. A map legend at the bottom helps all the signs, characters, graphics, and symbols used throughout the map.
Sudan covers a total area of 1,886,068 km2 (490,000 sq mi)southwest corner. The capital city of Sudan, Khartoum, located at the confluence of the White Nile River and Blue Nile River, is also marked on the map. The terrain of Sudan is primarily flat plains broken by several mountain ranges. Further, Physiographically, Sudan can be divided into the following geographical regions:
Plains and the Nubian Desert
The Nile-Congo watershed bounds the plains of Sudan on the west and highlands of Darfur, Ethiopian Plateau and the Red Sea on the east. The tables can be further divided into the northern area of rock desert, central south clay plain, and western Plain, a place of undulating dunes that merge into the desert. Northern Sudan is majorly sand or gravel-covered desert. The Nubian Desert lies to the east of the Nile River, with sandy dunes drifting over the landscape. Farther in the northeast are Red Sea Hills. The clay plain in south-central Sudan is covered by inselbergs that form the Nuba Mountains. The western plains are composed of Nubian sandstone, forming a dissected plateau region.
Highlands of Darfur
The Darfur is an area in western Sudan. The region is primarily a semi-desert plateau with Marra Mountains. The Marra Mountains are rugged volcanic chains rising out of the Darfur Plateau farther west. These mountain ranges extend for 100 miles (160 km) west-southwest of Al-Fashir in western Sudan. The mountain’s elevation is 3,000-10,000 feet (900-3,000 m). Marrah Mountains form the west boundary of the clay plain and Nile-Congo Watershed. Deriba Caldera (3,042 m or 9,980 ft) in the Marrah Mountains is the highest point of Sudan. The eastern and southern uplands constitute the Foothills of the Ethiopian highland.
Nile River and water Bodies of Sudan
The Nile River is an important physical feature of the country. Nearly all streams and rivers of Sudan drain either into or towards the Nile. The river enters the country as the White Nile(Bahr Al-Abyad), about 60 miles (100 km) south of Kusti in the southeast. The river maintains a shallow gradient until it is joined by the Blue Nile (Bahr Al-Azraq) at Khartoum. The Blue Nile rises in the Ethiopian Plateau and the confluence with White Nile at Khartoum and then the Nile River (Nahr Al-Nil). The Blur River is joined by Rahad and Dinder Rivers between Sennar and Khartoum. The major Dams located on the White Nile and the Blue Nile are Jebel Aulia Dam and Roseires and Sennar Dams on the Blue Nile. Lake Nubia is situated on the Sudan-Egypt border.