- Neighboring Countries - Malawi, Zimbabwe, Zambia, Tanzania, South Africa
- Continent And Regions - Africa Map
- Other Mozambique Maps - Mozambique Map, Where is Mozambique, Mozambique Blank Map, Mozambique Road Map, Mozambique River Map, Mozambique Cities Map, Mozambique Political Map, Mozambique Flag
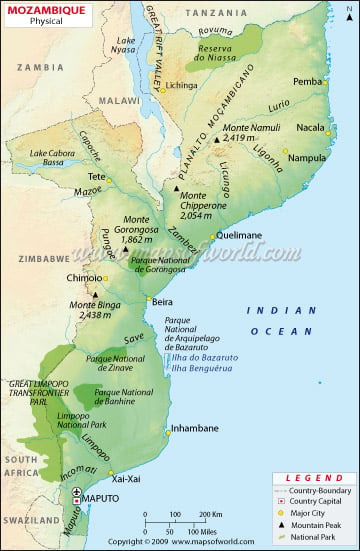
Mozambique, known as the Republic of Mozambique, is officially located in southeastern Africa. It shares the boundary with the Indian Ocean to the east, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Tanzania to the north, Zimbabwe to the west, South Africa and Swaziland to the southwest.
One can point out the Latitudes and Longitudes of Mozambique on the map along with international boundaries. The country is located between spaces 10. S and 27.S and longitudes 30. E and 41. E. Map legend at the bottom helps all the signs, characters, and symbols used throughout the map. The map can be used for school work, presentation and other purposes.
Mozambique Physical Features
The country covers a total area of 309,475 sq mi (802,437 km2). Mozambique is divided into two geographic regions by the Zambezi River.
North of Zambezi River
The region is a narrow coastal strip that gives way to plateaus and inland hills. Further west is rugged highlands, including Niassa highlands, shire or Namuli Highlands, Tete Highlands, Angonia Highlands, and the Makonde Plateau, covered with miombo woodlands. The country’s highest point, Mount Binga at 2,438, is a part of Chimoio Highlands.
South of Zambezi River
In this region, lowlands are broader, with the Lebombo Mountains and Mashonaland Plateau located in the deep south. The Lebombo Mountains are a narrow range of mountains in southern Africa. The Zambezi valley is the most prominent feature of Mozambique; the lower section of the Zambezi Valley is a part of (Great) East Rift Valley. Maputo is the capital and the most populous city of Mozambique. Maputo city is located near the southern end of the country is also marked on the map.
The Coast
The country’s coast has a length of 2,300 kilometres (1,430 mi). Sandy beaches backed by coastal dunes define the southern coastline. Behind the Coastal dunes are river estuaries, salt lakes and closed saline lagoons. There is Maputo Bay, an inlet of the Indian Ocean on the coast of Mozambique. The central coast of Mozambique extends from Bazaruto Island in the north to Angoche Island, which is known as Sofala Bay or Bight of Sofala. The beach is swamp and characterised by coastal wetlands and extensive mangrove swamps. In contrast, the northern coast is indented with rugged cliffs and rocky headlands with the continuous fringe of the island. The north has Conducia Bay, Fernao Veloso Bay and Memba Bay.
Significant Rivers and lakes in Mozambique
Mozambique is drained by five major rivers and several smaller ones. The most extensive river in the country is the Zambezi, and tributaries dominate the central region. Other important rivers are the Ruvuma River in the north, Maputo River, Limpopo River in the south and Komati, Save(Sabi), Lurio and Ligonha rivers defining the country’s local political boundaries. The country has four significant lakes: Lake Chiuta, Lake Cahora Bassa, Lake Shirwa and Lake Niassa.
 Mozambique Population
Mozambique Population