What are the Key Facts of Tunisia?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Tunisia |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Tunis |
|
Largest City |
Tunis |
|
Coordinates |
34.000000, 9.000000 |
|
Area |
63,170 sq. mi (163,610 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
929 mi (1,495 km) |
|
Coastline |
713 mi (1,148 km) |
|
Currency |
Tunisian dinar (TND) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Algeria, Libya. Maritime neighbors: Italy, Malta. |
|
Population |
11,694,720 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Arabic |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
20 March (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Humat Al Hima” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Kais Saied |
|
Prime Minister |
Elyes Fakhfakh |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 11,201.3 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 3,317.5 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.739 (2019), Rank: 91 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
79.04 (UNESCO, 2014) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
72 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
13 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
216 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (CET) |
|
Internet TLD |
.tn |
Where is Tunisia?
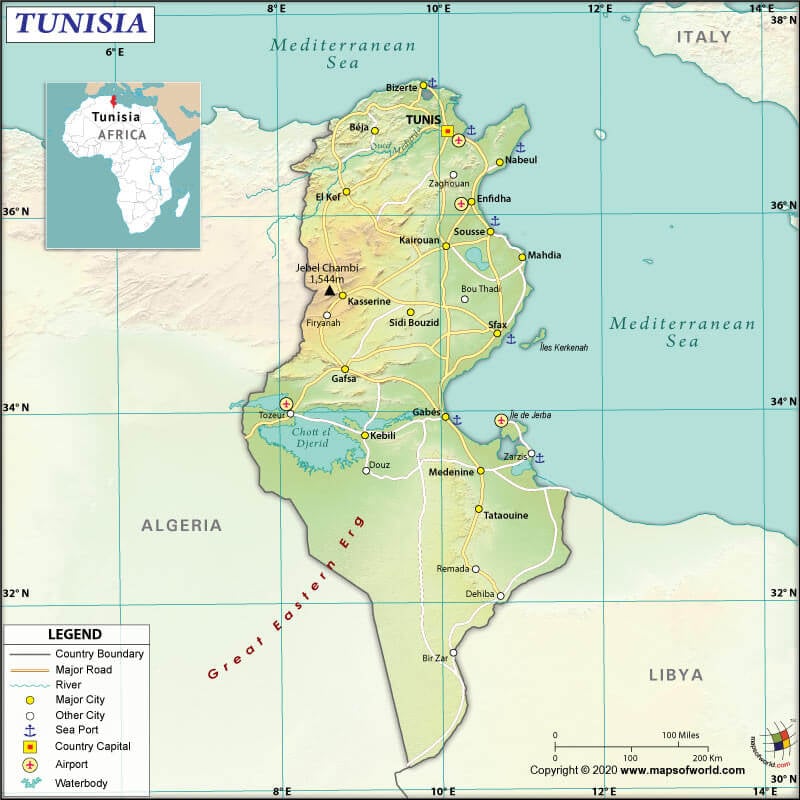
Tunisia (whose official name is the Republic of Tunisia) is a North African country located between Libya and Algeria, bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It is situated in the Maghreb region of North Africa.
What is the Geography of Tunisia?
Tunisia spreads across a total area of 163,610 sq. km (63,170 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 155,360 sq. km (59,985 sq. mi) is land, and 8,250 sq. km (3,185 sq. mi) is water.
The total land boundary of Tunisia is 1,495 km (928.9 mi) long, which is shared with two countries: Algeria (1,034 km or 642.5 mi) to the west and southwest and Libya (461 km or 286.5 mi) to the southeast. Tunisia has a 1,148 km (713.3 mi) long coastline. The Mediterranean Sea borders the country to the north and east.
The mean elevation of the country is 246 m (807.1 ft). While the highest point is Jebel ech Chambi at 1,544 m (5065.6 ft), the lowest point is the Shatt al Gharsah at -17 m (-55.8 ft).
Tunisia’s terrain is characterized by mountains in the northern region, plain in the central region, and desert in the southern part (merging into the Sahara). Tunisia consists of the Atlas Mountain’s eastern-end as well as the Sahara desert’s northern reaches.
The Atlas Mountains are a major landform in this North African country, where the mountain extends from the Algerian border towards the northeast to the Mediterranean Sea. You’ll find low, rolling hills and flat coastal areas as you move towards the northern and eastern directions of the Atlas Mountains.
A small part of Sahara, the largest desert globally, can be found in the southern fringes of Tunisia. You will find a large erg or “field of sand dunes” called the Grand Erg Oriental in central Tunisia.
A low-lying series of islands (having altitude no more than 13 m or 42 ft) called the Kerkennah can be found in Tunisia. Jerba Island, having a size of around 20×20 km, is connected to the mainland with the help of a road.
The highest mountains in Tunisia are Jebel ech Chambi, Jebel Bireno, Jebel el Ajered, Jebel Selloum, Jebel Tiouacha, etc.
Medjerda River is the longest rivers in Tunisia, which is around 450 km (1,476 ft) long. It rises in Algeria, flows through the country, and enters the Mediterranean Sea. It has dozens of small tributaries. Other major rivers in the country are Oued Sejenane, Oued Zeroud, Oued el Melah, etc.
You will find a natural, shallow lagoon called the Lake of Tunis (14 sq mi or 37 sq km in size) between the Gulf of Tunis (Mediterranean Sea) and Tunis. The lowest point of the country (Shatt al Gharsah) is one of the series of salt lakes called the shatts, located in the northern edge of the Sahara’s east-west line.
What is the Climate of Tunisia?
Tunisia’s climate can be characterized as a hot-summer Mediterranean climate in the north. As per Köppen climate classification, the climate is characterized as Csa. While the months of summer remain hot and dry, winter months’ temperature remains mild (having moderate rainfall).
During July-August, the tropical continental air mass of the desert reaches the country. This can increase the temperature above 40 °C (104 °F). During winter months, the weather in Tunisia (except the southwest region) remains mild and rarely exceeds 20 °C (68 °F).
The central region of Tunisia is hot and dry. The climate becomes hotter, drier, and sunnier as you move towards the south. A hot desert climate (classified as BWh as per Köppen climate classification) is found in southern Tunisia. This climatic condition is characterized by scorching summers, warm winters, and very low yearly rainfall.
During summertime, the daytime temperature hovers around 45 °C (113 °F). In the desert areas, the nighttime remains cold. Almost everywhere in Tunisia, the yearly average rainfall remains lower than 500 mm (19.68 in). That’s why the country is characterized as dry and semi-arid. The areas having a pre-Saharan climate get less than 250 mm (9.84 in) of rainfall. However, the regions with a typical Saharan climate get less than 100 mm (3.94 in) yearly average precipitation. The southernmost region in the country (such as El Borma and surrounding areas along the Algerian border) gets 50 mm (1.97 in) of rainfall.
What is the Economy of Tunisia?
Tunisia’s economy has been facing problems since the 2008 global financial crisis followed by the 2011 Arab Spring revolution. Though the country has embraced an open, democratic governance system, the economic transition is not yet seen.
The barriers to economic inclusion remain, and the Tunisian economy is riddled with slow economic growth and high unemployment. Slow economic growth and high unemployment are the main problems of the country.
The nominal GDP of Tunisia grew at an annual rate of 1.043% to US$38.798 billion in 2019. The export and import values of the country in 2018 were US$15.2 billion and US$20.2 billion, respectively.
The major exports are Insulated Wire, Non-Knit Men’s Suits, Pure Olive Oil, Non-Knit Women’s Suits, and Crude Petroleum. Tunisia’s major imports are Refined Petroleum, Low-voltage Protection Equipment, Cars, Insulated Wire, and Wheat.
The unemployment rate (percentage of the total labor force, as per modeled ILO estimate) dropped from 18.334% in 2011 to 15.058% in 2014 but again increased to 16.022% in 2019. The rate of poverty came down from 25.4% to 15.2% during 2000-2015.
What is the Transportation System of Tunisia?
The country has 29 airports, out of which 15 have paved runways, and 14 have unpaved runways. Major airports are Tunis-Carthage International Airport (Tunis), Sfax-Thyna International Airport (Sfax), Monastir-Habib Bourguiba International Airport (Monastir), Enfidha-Hammamet International Airport (Enfidha), Djerba – Zarzis International Airport (Djerba), etc.
The total roadways in the country are 20,000 km (12427.4 mi) long. Tunisia has 2,173 km (1350.2 mi) long railways, out of which 471 km (292.7 mi) is a standard gauge, 1,694 km (1052.6 mi) is a narrow gauge, and 8 km (5 mi) is dual gauge.
Sfax, Gabes, Bizerte, Rades, and Skhira are the major seaports of the country. There are 67 merchant marine vessels in the country, out of which 9 are general cargo, 1 is an oil tanker, and 57 are other types of vessels.
What International Organizations is Tunisia Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, ILO, ABEDA, AfDB, AFESD, AMF, AMU, AU, CAEU, CD, EBRD, FAO, G-11, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, BSEC (observer), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), OSCE (partner), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Links: