What are the Key Facts of Grenada?
|
Official Name |
Grenada |
|
Continent |
North America (Caribbean) |
|
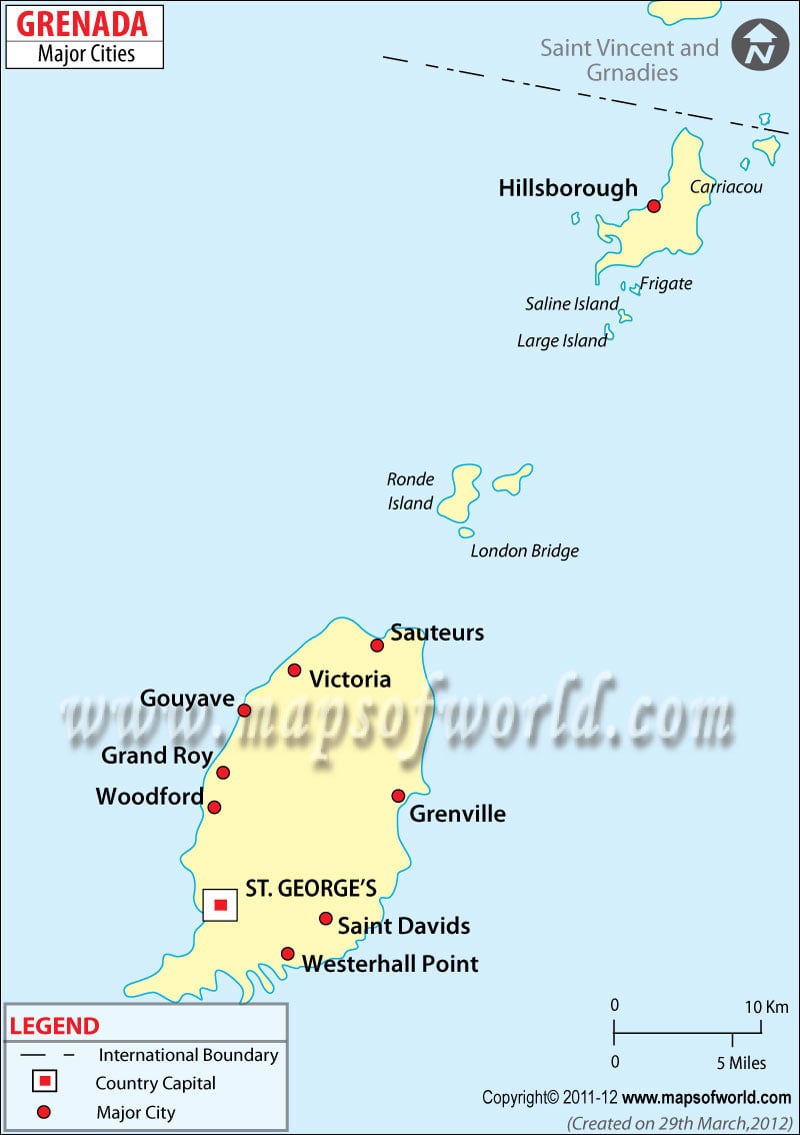
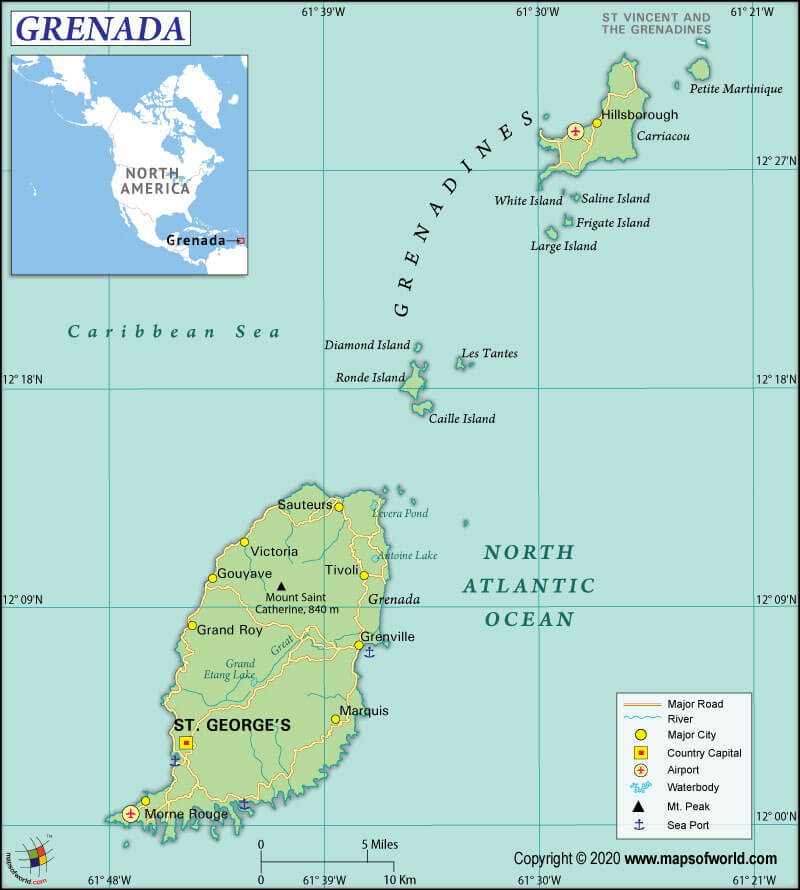
Capital |
St. George’s |
|
Largest City |
St. George’s |
|
Coordinates |
12.116667, -61.666667 |
|
Area |
133 sq. mi (344 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi ( 0 km) Island Country |
|
Coastline |
75 mi (121 km) |
|
Currency |
East Caribbean dollar (XCD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Maritime Neighbor: St. Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, Venezuela |
|
Population |
112,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
English |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
7 February (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Hail Grenada” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary two-party parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Elizabeth II |
|
Prime Minister |
Keith Mitchell |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 17,956.1 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 10,965.5 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.763 (2019), Rank: 78 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
98.60 (UNESCO, 2014) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
2 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+1-473 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC-4 (AST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.gd |
Where is Grenada?
Grenada (whose official name is Grenada and is also known as the “Isle of Spice” or “Island of Spice”) is a West Indian country at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain in the Caribbean Sea. This island nation is situated north of Trinidad and Tobago, between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
What is the Geography of Grenada?
Grenada spreads across a total area of 344 sq. km (133 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 344 sq. km (133 sq. mi) is land and 0 sq. km (0 sq. mi) is water. Grenada has no land boundary but has a 121 km (75.2 mi) long coastline.
While the highest point is Mount Saint Catherine at 840 m (2755.9 ft), the lowest point is the Caribbean Sea at 0 m (0 ft).
Grenada’s terrain is characterized by mountains in the central part of the country and all the islands in the country have a volcanic origin.
Grenada is made up of 3 main islands: Grenada, Carriacou, and Petit Martinique. Numerous other small islands in the Caribbean Sea are also part of the country. The country is located in the south of the Tropic of Cancer. The capital city, St. George’s, is located on the biggest island of the country. All the small islets and cays constituting the country are mostly uninhabited.
The terrain is mostly mountainous in all the three main islands. The highest mountains in Grenada are Mount St. Catherine, Mount Lebanon, and Mount Sinai. Major rivers in the country are the Great River, St. Patrick’s River, and St. John’s River. All of these rivers are present on the main island named Grenada. Carriacou and Petit Martinique islands don’t have rivers.
The most beautiful and vital lakes in the country are Lake Antoine, Levera Pond, Grand Etang Lake, etc. Coral reefs, bays, and white sand beaches (Morne Rouge and Grand Anse) dot Grenada’s coastline.
What is the Climate of Grenada?
A tropical climate is found in Grenada. It remains hot and humid throughout the year. During the rainy season (June-December), it remains hot and humid, along with getting lots of rainfall. From January to mid-April, the season remains relatively cool and dry.
During the Jan-April period, a constant wind (called the northeast trade winds) blows steadily and with moderate intensity.
The temperature and the frequency of rainfall gradually increase during the period starting from mid-April to late May.
During June-December, the winds blow more irregularly. The feeling of sultriness increases as there may be some pauses in between the blow of wind.
The capital city of the country, St. George’s (located on the south-western coast) receives around 2000 mm (78 inches) of annual rainfall.
May-January receives more than 100 mm (4 inches) per month rainfall.
June-November gets more than 200 mm (8 inches) of rainfall.
During March-April, St. George’s receives the least rainfall, which is around 65-70 mm (2.6-2.8 in) on average every month.
The yearly rainfall amount in the southern Grenadines (including flat areas such as the main island’s southwestern tip, Point Salines) is less than 1,500 mm (60 inches), less than that of St. George’s in main Grenada Island.
Hills and low mountains in the main island’s interior get up to 3,500 mm (138 in) yearly rainfall. The temperature remains a bit lower and often cloudy here. Downpours or thunderstorms can be intense in these inland areas, but they are generally short lives.
The average water temperature in Grenada remains warm:
- 27 °C (81 °F) during December-April
- 29 °C (84 °F) during September-October
Tropical storms and cyclones (known as hurricanes in the Caribbean area) are the greatest danger in Grenada. They usually pass through during June-November (most likely during August-October). February-April is the best time to visit the country. However, you can also visit in January.
What is the Economy of Grenada?
Grenada has a small and open economy. It depends mainly on the foreign exchange earned from tourism and a private university, St. George’s University. In 2019, the nominal GDP of Grenada increased by 3.126% to US$1.228 billion.
The country experienced a negative trade balance of -US$163 million in 2018. While the export value was US$36.5 million, the import value was US$200 million. Major exports are Nutmeg, mace and cardamons, Non-fillet Fresh Fish, Cocoa Beans, Other Fruits, and Delivery Trucks. Major imports are Cars, Poultry Meat, Refined Petroleum, Other Furniture, and Other Edible Preparations.
The unemployment rate in Grenada was dropped from 28.2% in 2016 to 24% in 2017. The poverty rate in Grenada was around 32% during 2016-17. Extreme poverty was 13%, which was the highest among the Caribbean countries.
What is the Transportation System of Grenada?
Grenada has three airports, out of which all three have paved runways. Major airports are Maurice Bishop International Airport (St. George’s), Lauriston Airport (Hillsborough), and Pearls Airport (Grenville).
The total roadways in Grenada are 1,127 km (700.3 mi) long, out of which 902 km (560.5 mi) is paved, and 225 km (139.8 mi) is unpaved. Saint George’s is the principal seaport in Grenada. There are six merchant marine vessels in the country, out of which 3 is general cargo and 3 are other types of dishes.
What International Organizations is Grenada Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, UNESCO, NAM, ILO, ACP, AOSIS, C, Caricom, CDB, CELAC, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, Interpol, IOC, ITU, ITUC, LAES, MIGA, OAS, OECS, OPANAL, OPCW, Petrocaribe, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UPU, WHO, WIPO