What are the Key Facts of Dominican Republic?
|
Official Name |
Dominican Republic |
|
Continent |
North America (Caribbean) |
|
Capital |
Santo Domingo |
|
Largest City |
Santo Domingo |
|
Coordinates |
19.000000, -70.666667 |
|
Area |
18,792 sq mi (48,671 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
234 mi ( 376 km) |
|
Coastline |
800 mi ( 1,288 km) |
|
Currency |
Peso (DOP) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Haiti, Puerto Rico, Turks and Caicos Islands |
|
Population |
10,735,896 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
27 February (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Himno Nacional” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential republic[ |
|
President |
Danilo Medina |
|
Vice President |
Margarita Cedeño de Fernández |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 17,798.8 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 7,650.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.736 (2017), Rank: 94 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
93.78 (UNESCO, 2016) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
79 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
7 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+1-809, +1-829, +1-849 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC-4 (AST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.do |
Where is the Dominican Republic?
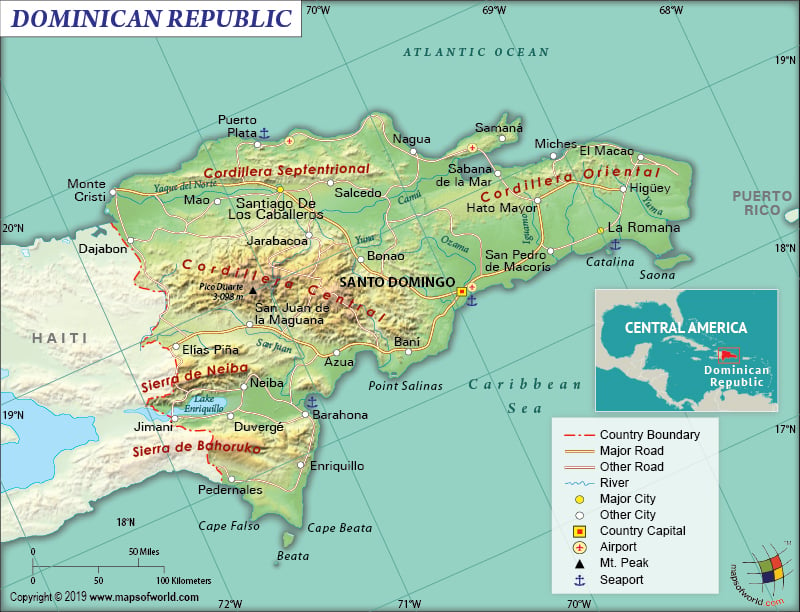
The Dominican Republic is located in the Caribbean region’s Greater Antilles archipelago, where it shares the island of Hispaniola with Haiti. It occupies around 2/3rd of the Hispaniola island in the Central American region and is situated in the eastern direction of Haiti. The concerned island itself is located between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean.
What is the Geography of the Dominican Republic?
The Dominican Republic is one of the largest Caribbean islands. It is spread across an area of 48,670 sq. km (18.792 sq. mi), out of which 48,320 sq km (18,656 sq mi) is land area and 350 sq km (135 sq mi) is water area. This country shares its 376 km (234 mi) long land boundary with Haiti. This country has a long coastline, which is 1,288 km (800 mi) in length.
As a matter of fact, the terrain of the Dominican Republic includes rugged highlands as well as mountains, interspersed with fertile valleys. The mean elevation of the country is 424 m (1,391 ft). While Pico Duarte is the highest elevation at 3,098 m (10,164 ft), Lago Enriquillo is the lowest elevation at -46 m (-151 ft) below sea level. Another major mountain is lto de la Bandera.
Moreover, the central and western parts of the Dominican Republic are mountainous. The southeast parts are dominated by extensive lowlands. This country has 4 major mountain ranges and the largest one is the rugged Cordillera Central. It is also the highest range of the four. The highest elevation point of the country, Pico Duarte, is located in this region. There are many peaks in the Cordillera Central range whose elevation is more than 5,000 ft (1,524 m).
Further, the lesser-known mountain ranges run along the southwest border with Haiti as well as the northern coastlines. The territory of the Dominican Republic includes many small offshore islands as well as cays. Two such large islands that are located near the shores are Saona (towards the southwest direction) and Beata (towards the southeast direction). Yaque del Norte is the largest river in the country.
The Dominican Republic has a tropical maritime climate, which is characterized by little seasonal temperature variation. The hot and tropical temperature prevails throughout the year. However, temperature variation can be found in accordance with regional changes. While May-to-October gets a hotter and muggy season, December-to-March gets a relatively cooler temperature. November-to-April is the intermediate months.
During summer (May-to-October), the plains experience sweltering heat. In the winter season, the Dominican Republic generally experiences more pleasant climate. However, it remains humid during the winter season too. From late April to October, the eastern and southern coast of the country receives significant rainfall due to the rainy season. The northern coast remains rainy round the year, thanks to its exposure to the trade winds. During June-to-September, a fall in temperature is experienced on the north-western coast.
The effect of trade winds increases or decreases the trade winds’ effects, thereby influencing the extent of rainfall. That’s why the Azua (on the coast of the Ocoa Bay) receives just 640 mm (25 in) of rainfall every year and Santo Domingo (on the southern coast) receives around 1,450 mm (57 in) rainfall per year.
What is the Economy of the Dominican Republic?
To begin with, in the Caribbean and Central American region, the Dominican Republic is the largest economy. This upper-middle-income developing economy had a nominal GDP of US$81.299 billion in 2018 and it grew by 7% in the same year.
Additionally, the services sector and the industrial sector employ over 60% and 20% of the labor force. The contributions of these sectors to GDP are 60.8% and 33.8% respectively. While agriculture employs around 15% of the workforce, its contribution to the GDP is merely 5.5%.
Main industries of the Dominican Republic are ferronickel and gold mining, tobacco, cement, textiles, tourism, and sugar production. The USA is the largest trading partner. While around 50% of its exports and 40% of its total imports are traded with the US, remittances (accounting for 7% of the GDP) also play an important part in the economy.
The unemployment rate is over 12% and over 2/3rd of the total population is still under poverty. More than 20% of the population is living in extreme poverty.
What is the Transportation System of the Dominican Republic?
The Dominican Republic has 19,705 km (12,244 mi) of roadways, out of which 9,872 km (6,134 mi) are paved and 9,833 km (6,110 mi) are unpaved. There are 36 airports present in the country, out of which 16 have paved runways and 20 have unpaved runways. One heliport is also there. Out of the 496 km (308 mi) long railways, 354 km (220 mi) are standard gauge and the rest 142 km (88 mi) are narrow gauge. There are 3 major seaports present in the country and they are Puerto Haina, Santo Domingo, and Puerto Plata. 23 merchant marine ships are also there in the Dominican Republic.
What International Organizations is the Dominican Republic part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, Interpol, WHO, ACP, AOSIS, BCIE, Union Latina, CD, UNESCO, CELAC, UNIDO, FAO, Petrocaribe, G-77, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, MIGA, MINUSMA, NAM, OAS, OPANAL, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), ISO (correspondent), OIF (observer), Caricom (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), ITUC (NGOs), SICA (associated member)