What are the Key Facts of Tanzania?
|
Official Name |
United Republic of Tanzania |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Dodoma |
|
Largest City |
Dar es Salaam |
|
Coordinates |
-6.000000, 35.000000 |
|
Area |
365,756 sq. mi ( 947,303 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
2,586 mi ( 4,161 km) |
|
Coastline |
885 mi ( 1,424 km) |
|
Currency |
Tanzanian shilling (TZS) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Zambia, Malawi, Mozambique, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo |
|
Population |
56,313,438 (2018 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Swahili, English |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity, Islam |
|
National Day |
26 April (Union Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Mungu ibariki Afrika” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary dominant party presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
John Magufuli |
|
Prime Minister |
Kassim Majaliwa |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 3,227.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 1,050.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.538 (2017), Rank: 154 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
77.89 (UNESCO, 2015) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
77 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
2 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+255 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+3 (EAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.tz |
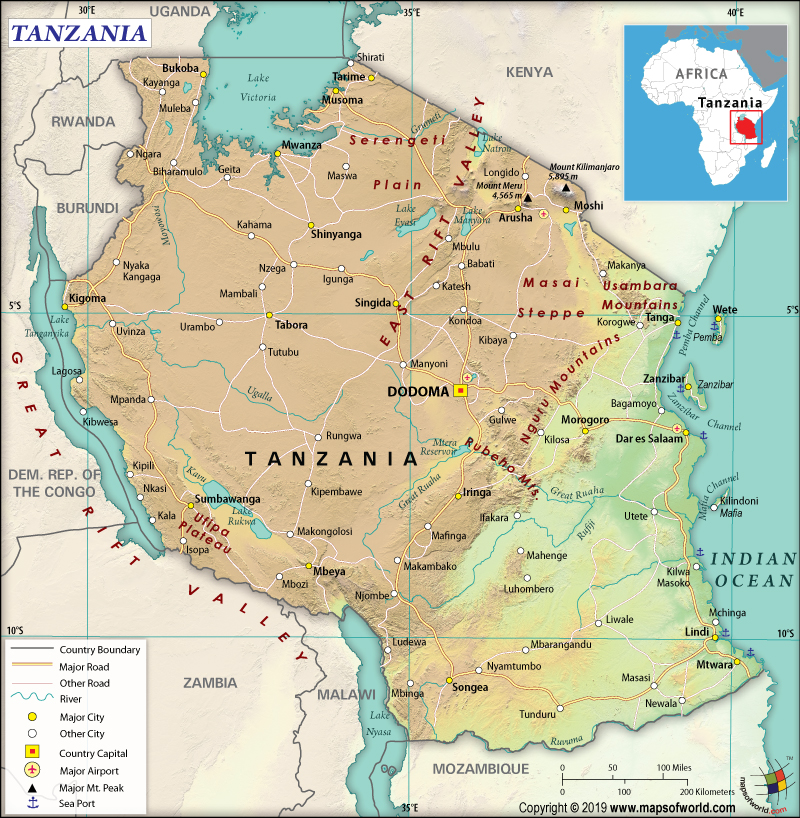
Where is Tanzania?
Tanzania is an East African country that borders the Indian Ocean and is located between Mozambique and Kenya. It is bordered by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, and Rwanda to the west, Zambia to the southwest, Malawi and Mozambique to the south, the Comoro Islands to the east, Kenya to the northeast, and Uganda to the north.
What is the Geography of Tanzania?
Tanzania is spread across a total area of 947,303 sq. km (365,756 sq. mi), out of which 885,800 sq. km (342,009 sq. mi) is land area and 61,500 sq. km (23,745 sq. mi) is water area. The islands of Mafia, Zanzibar, and Pemba are included in the total area of Tanzania.
This country has a 4,161 km (2,586 mi) long land boundary and a 1,424 km (885 mi) long coastline. The land boundary is shared with 8 neighboring countries including Mozambique (840 km or 522 mi), Kenya (775 km or 482 mi), Burundi (589 km or 366 mi), Malawi (512 km or 318 mi), Democratic Republic of the Congo (479 km or 298 mi), Uganda (391 km or 243 mi), Zambia (353 km or 219 mi), and Rwanda (222 km or 138 mi).
The landscape in Tanzania can be divided into three distinct parts. One part is the plains that are present in the coastal areas, the second part is the plateaus located in the central part of Tanzania, and the third part is the highlands in both north and south.
The mean elevation of Tanzania is 1,018 m (3,340 ft). The highest elevation point of the country is Kilimanjaro (located in the far-northeast mountainous region of Tanzania) at 5,895 m (19,341 ft), which is also the highest elevation point in the entire world. The lowest elevation point of Tanzania is the Indian Ocean at 0 m (0 ft).
The elevation of the Rubeho Mountains (having a compact group of connected peaks) is significantly lower. Other major mountains of the country are Mawenzi, Luhombero, Hanang, Klute, Meru, etc.
The coral reefs protect the coastline of the Indian Ocean in Tanzania. These reefs also protect the Mafia, Zanzibar, and Pemba islands. The large central plateau in the mainland consists of the rolling hills, plains, and grasslands. The Serengeti Plain is spread across a total area of 30,000 sq km (12,000 sq mi).
The largest intact caldera of the world, the Ngorongoro Crater, is located in Tanzania. This crater is spread across a total area of 265 sq km (102 sq mi) and its sides are as deep as 600m (1,960 ft), thereby forming a spectacular bowl-like formation.
Some of the major lakes of Africa border Tanzania such as Lake Tanganyika, Lake Victoria, and Lake Nyasa. The major rivers that flow through Tanzania are Nile, Rufiji, Great Ruaha, Wami, Malagarasi, Pangani, Ruvuma, Zambezi, White Nile, Congo, etc.
A tropical climate persists in Tanzania. However, the topography of the country influences climatic variation among different regions.
The average temperature in the highlands in the cold season is 10 °C (50 °F) and in hot season is 20 °C (68 °F). The temperature hardly falls below 20 °C (68 °F) in other parts of Tanzania. The months from November-February is the hottest period of the country when the temperature ranges from 25 °C (77 °F) to 31 °C (87.8 °F). However, from May-August is the coldest period and the temperature ranges within 15 °C (59 °F) and 20 °C (68 °F).
The migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone drives the seasonal rainfall. The migration takes place southwards during October-December, reaches Tanzania’s south during January-February, and returns northwards during March-May.
The migration of Intertropical Convergence Zone causes northern and eastern Tanzania to experience two rainy periods: a short one known as “Vuli” during October-December and a longer rainy period known as “Masika” during March-May. However, the central, western, and southern parts of Tanzania get a single wet season, which starts in October and continues till April/May.
What is the Economy of Tanzania?
The nominal GDP of Tanzania grew at a rate of 5.2% in 2018 to reach a figure of US$57.437 billion. Throughout 2009-17, the Tanzanian economy grew at an average annual rate of 6-7%, mainly because of the availability of huge natural resources coupled with tourism.
The major export items of the economy are gemstones, diamonds, gold, coal, other minerals, cloves, pyrethrum, tobacco, sisal, tea, cashew nuts, cotton, coffee, etc. The items mainly imported by Tanzania are agricultural machinery, machinery/transportation equipment, industrial raw materials, implement/pesticides, consumer goods, construction materials, petroleum/petroleum products, etc. In 2017, the country had a negative balance of trade of US$2.88 billion as the import and export value in that year was US$8.17 billion and US$5.3 billion respectively.
The unemployment rate has come down from 3.26% in 1998 to 1.93% in 2018. The rate of poverty has declined from 34.4% in 2007 to 26.8% in 2016. This means that there are around 13 million people who still live below the poverty line.
What is the Transportation System of Tanzania?
Tanzania has 87,581 km (54,420 mi) long roadway, out of which 10,025 km (6,229 mi) is paved and 77,556 km (48,191 mi) is unpaved. Though the rivers in the country are non-navigable, most of the navigations take place on major lakes such as Nyasa, Victoria, and Tanganyika lakes).
There is 4,567 km (2,838 mi) long railway, out of which 1,860 km (1,156 mi) is 1.067-m gauge and 2,707 km (1,682 mi) is 1.000-m gauge. There are 166 airports in Tanzania, out of which 10 have paved runways and 156 have unpaved runways.
The major airports in this East African country are Kilimanjaro International Airport, Julius Nyerere International Airport, Kigoma Airport, Mwanza Airport, etc.
What International Organizations is Tanzania part of?
WTO, UN, UNESCO, IMF, WHO, ILO, FAO, ACP, AfDB, AU, C, CD, EAC, EADB, EITI, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MONUSCO, NAM, OPCW, SADC, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), ICC (NGOs)
Related Link:

![]()
