What are the Key Facts of Rwanda?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Rwanda |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Kigali |
|
Largest City |
Kigali |
|
Coordinates |
-2.000000, 30.000000 |
|
Area |
10,169 sq. mi ( 26,338 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
578 mi ( 930 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Rwandan franc (RWF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Uganda, Tanzania, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo |
|
Population |
11,262,564 (2015 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
English, French, Kinyarwanda, Swahili |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
1 July (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Rwanda nziza” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary dominant-party presidential republic |
|
President |
Paul Kagame |
|
Prime Minister |
Édouard Ngirente |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 2,253.5 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 773.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.524 (2017), Rank: 158 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
119 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+250 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (CAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.rw |
Where is Rwanda?
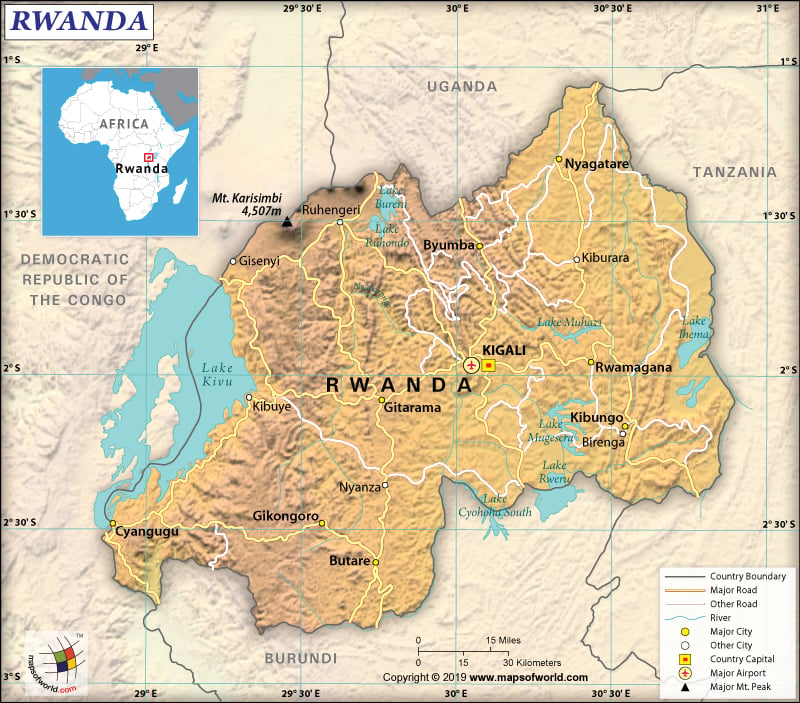
Rwanda is situated in the African Great Lakes region. It is located in the central and eastern parts of Africa, just a few degrees south of the equator. The country shares its borders with 4 countries – the Democratic Republic of the Congo (221 km or 137 mi), Burundi (315 km or 196 mi), Tanzania (222 km or 138 mi), and Uganda (172 km or 107 mi).
What is the Geography of Rwanda?
Rwanda (the 4th smallest country in the African mainland) is spread over a total area of 26,338 sq. km (10,169 sq. mi), out of which 24,668 sq. km (9,524 sq. mi) is land and 1,670 sq. km (645 sq. mi) is water. The total land boundary of this African country is 930 km (578 mi).
As it is landlocked, Rwanda doesn’t have any coastline. Rolling hills can be found in the central parts of Rwanda. Savanna, plains, and swamps are predominantly there in the eastern border region. Rwanda is located at a high altitude in the African Great Lakes region.
The lowest elevation point of Rwanda is Rusizi River at 950 m (3,116 ft). The highest elevation point is Mount Karisimbi at 4,519 m (14,826 ft). Therefore, the mean elevation is 1,598 m (5,243 ft). The major mountains of this African country are Mount Karisimbi, Muhavura, Kaserutoki, Rutare, Muhungwe, Mont Muwogo, Marenga, Kabuye, Ngabwe, Mont Kwiruhelo, etc.
Nyabarongo is the most important river of Rwanda that is 297 km (184 miles) long. There are many lakes in the country, where Lake Kivu (top 20 deepest lakes in the world) is the largest one. Some other important lakes of Rwanda are Muhazi, Ihema, Cyohoha South, Mugesera, Ruhondo, Burera, Rweru, etc.
A temperate tropical highland climate is there in Rwanda. As the country is located at high elevation, the temperatures are significantly lower than that found in the typical equatorial countries. Kigali (the capital city of Rwanda), located at the central part of the country, has a daily average temperature ranging from 12 °C and 27 °C (54 °F and 81 °F). The temperature hardly varies through the year in Kigali.
However, temperature variation can be found as per varying altitudes. As the eastern part of the country is low lying in comparison to the northern and western parts, the temperature in the former is comparatively warmer than the latter.
There are two rainy and dry seasons. While the first rainy season is from February-to-June, the second rainy season is from September-to-December. The two dry seasons are from June-to-September and December-to-February. The west and northwest regions receive more rainfall annually than the eastern and southeastern regions of Rwanda.
What is the Economy of Rwanda?
The economy of Rwanda suffered heavily at the time of the genocide in 1994. It not only affected the gross domestic product of the country but also failed to attract private and external investment.
In the first quarter of 2018, the GDP increased by 10.6% year-on-year basis, thanks to the robust performances by both the industrial and the services sectors. In 2017, the nominal GDP of Rwanda was US$9.135 billion, which increased to an estimated US$9.509 billion in 2018 (World Bank). The economy grew by 5 times during 1994-2017.
In Q1 2018, the best sectoral performers were transport (increased by 28%), retail trade (26%), information and communication (24%), clothing & leather goods activities (24%), public administration (15%), financial services (12%), food processing activities (9%), construction activities (8%), and human health & social work activities (7%). Rwanda’s main export markets are the USA, China, and Germany.
The Rwandan economy is mostly based on subsistence agriculture, contributing 30.9% of the GDP as per latest figures. The country has to import food items to meet its needs. Tea and coffee are the main cash crops of the country. More than 400,000 people work in coffee plantations.
The industrial sector contributes just 17.6% to the GDP. The main constituents of the industrial sector are mineral mining, and manufacturing of products such as cement, small-scale beverages, textiles, plastic goods, shoes, furniture, soap, cigarettes, etc.
The services sector contributes 51.5% to the GDP. The main contributors to the tertiary sector include banking & finance, trade (wholesale & retail), public administration (includes both education and health), hospitality (hotels & restaurants), real estate, insurance, communication, storage, transport, and business services.
The main foreign exchange earner of Rwanda is tourism. The number of tourists has doubled during 2008-2017. In 2017, 1.2 million international tourists visited Rwanda, which is expected to reach 1.7 million by 2028. The tourism sector contributes 12.7% to the GDP and supports 132,000 jobs.
The rate of unemployment is still high in Rwanda. In 2018, it was 15.1%. However, the new labor force survey has found that the unemployment rate has decreased by 3.7% than the previous year. The rate of poverty is still high. Nevertheless, it has decreased from 39.1% in 2014 to 38.1% in 2017.
What is the Transportation System of Rwanda?
The roadway is the main transport system of Rwanda. The total roadway in the country is 4,700 km (2,920 mi), out of which 1,207 km (750 mi) is paved and 3,493 km (2,170 mi) is unpaved. There are 7 airports in Rwanda, out of which 4 are paved and 3 are unpaved. Kigali International Airport is the main airport of the country. Cyangugu, Kibuye, and Gisenyi are the 3 lake ports available in the country. Rwandans also use shallow-draft barges and native crafts for navigating along the Lake Kivu. Imports and exports of products mainly take place through the African Great Lakes. No railways are there in Rwanda.
What International Organizations is Rwanda part of?
UN, WTO, IMF, ACP, AfDB, AU, UNESCO, C, CEPGL, UNIDO, COMESA, UNWTO, EAC, EADB, UNCTAD, FAO, G-77, UNHCR, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, UNISFA, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, UNAMID, IFC, IFRCS, WHO, ILO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, WCO, WIPO, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, UNMISS, UPU, MINUSMA, NAM, OIF, WMO, OPCW, PCA, ITUC (NGOs)