What are the Key Facts of Malawi?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Malawi |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Lilongwe |
|
Largest City |
Lilongwe |
|
Coordinates |
-13.500000, 34.000000 |
|
Area |
45,747 sq mi ( 118,484 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,775 mi ( 2,857 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km), landlocked |
|
Currency |
Kwacha (D) (MWK) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Zambia, Tanzania, Mozambique |
|
Population |
18,091,575 (2016 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
English, Chichewa |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
6 July (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Mulungu dalitsa Malawi” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary presidential republic |
|
President |
Peter Mutharika |
|
Vice President |
Everton Chimulirenji |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 1,308.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 389.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.477 (2017), Rank: 171 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
62.14 (UNESCO, 2015) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
134 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
0 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+265 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (CAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.mw |
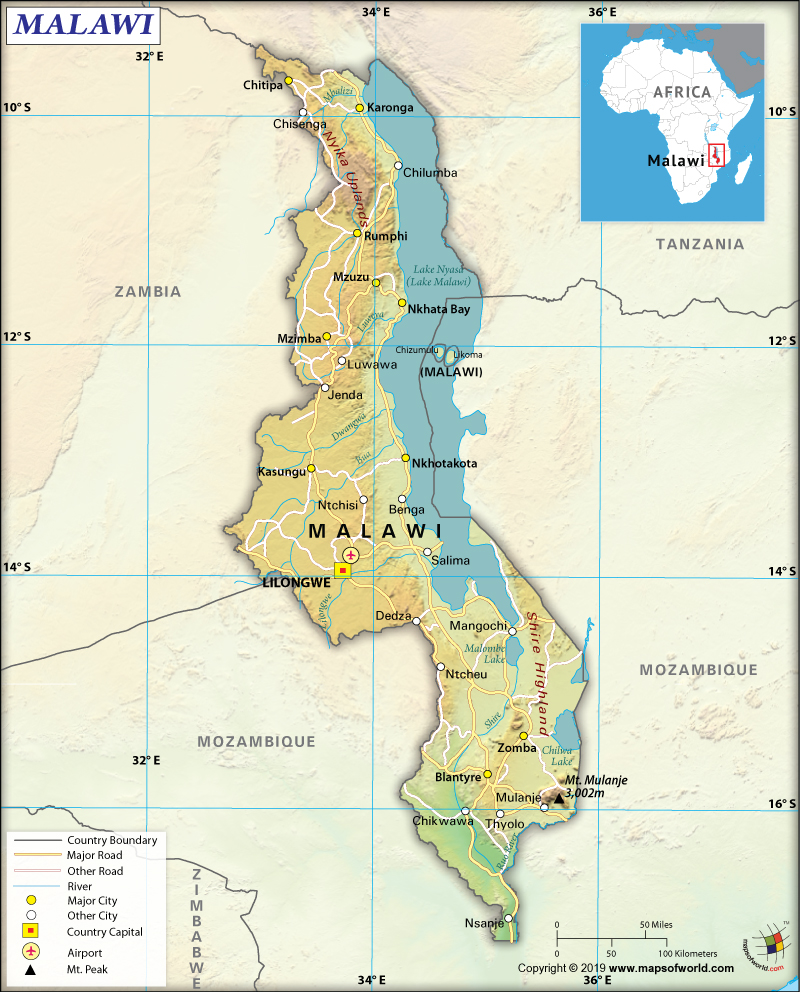
Where is Malawi?
Malawi is a southeast African country that is located fully within the tropics. The country occupies a thin land strip between Mozambique and Zambia. It protrudes in the south along the Shire River into Mozambique.
What is the Geography of Malawi?
Malawi is spread across a total area of 118,484 sq. km (45,747 mi), out of which 94,080 sq. km (36,324 mi) is land and the rest 24,404 sq. km (9,422 mi) is water. The total land boundary of the country is 2,857 km (1,775 mi), out of which 1,498 km (931 mi) is shared with Mozambique, 847 km (526 mi) with Zambia, and 512 km (318 mi) with Tanzania. As Malawi is completely landlocked, there is no coastline.
The Great Rift Valley is spread across the country from north to south. The 3rd largest lake in Africa, Lake Malawi (also known as Lake Nyasa), is located in this deep trough. It is spread over 25% of the total area of the country.
The landforms in the western parts of the Great Rift Valley include high plateaus that generally go up by 914-1,219 m (3,000-4,000 ft) above sea level. The Nyika Uplands is located in the northern parts of Malawi, which go up as high as 2,438 m (8,000 ft). The Central Zambezian Miombo woodlands ecoregion is located in northern and central Malawi, especially to the western parts of the lake.
Shire Highlands (having an elevation of 600-1,600 m or 1,969-5,249 ft) are located in the southern direction of the lake. This highland rises to an elevation of 2,130 m (6,988 ft) at the Zomba Plateau and 3,002 m (9,849 ft) at the Mulanje Massif. At the extreme southern part of Malawi, the elevation is significantly low (varies from 60-to-90 m or 197-to-295 ft) above the sea level.
While Sapitwa (Mount Mlanje) is the highest elevation point of the country at 3,002 m (9,849 ft), the lowest point is the junction of the international boundary with Mozambique and Shire River at 37 m (23 ft). The mean elevation of Malawi is 779 m (2,556 ft). Major mountains of the country are Mulanje (Sapitwa), Nakodzwe, Namasile, Dzole, Chinzama, etc. Major Rivers of Malawi are South Rukuru River, Dwangua River, and Shire River.
The climate in Malawi is generally categorized as tropical. During November-to-April, the country’s temperature remains warm. Equatorial rains and thunderstorms are common during this time. The severity of the storms reaches their peak in late-March. However, the rainfall diminishes rapidly after March. Wet mists start floating from the highlands into the plateaus during May-September. Almost no rainfall takes place during this time.
September-April remains hot and humid along the Shirey Valley. During the daytime, the average temperature revolves within 27-29 °C (80.6-84.2 °F). During June-August, both southern parts and lake areas remain comfortably warm. The maximum daytime temperature reaches around 23 °C (73.4 °F). However, the night time in the rest of the country remains chilly (10-14 °C or 50.0-57.2 °F). During June-July, high altitude areas remain cold at night with temperatures ranging from 6-8 °C (42.8-46.4 °F).
What is the Economy of Malawi?
Malawi is one of the least developed countries of the world, having a nominal GDP of US$ 7.065 billion (2018). The economy of Malawi is mainly agriculture based. 85% of the population lives in rural areas and most of them are involved in agricultural activities. In fact, agriculture contributes more than 1/3rd of GDP and around 90% of the export revenue. The Malawian economy depends mainly on the economic aid from the IMF, World Bank, and other countries. When the IMF stopped aid disbursements in December 2000, Malawi’s development budget dropped by 80%.
T
he services sector contributes 46% to the GDP, followed by agriculture (35%) and industry (19%). The economic growth rate has come down from 4% in 2017 to 3.5% in 2018 because dry spells and infestation of fall armyworm lowered agricultural output significantly. The weak business environment as well as the erratic supply of energy also adversely affected performances of both the industrial and services sector. 1-in-4 people in Malawi live in extreme poverty and around 2.8 million people are fighting hunger.
What is the Transportation System of Malawi?
The transport system in Malawi has not developed properly. There are 39 airports across the country, out of which 6 have paved runways and 33 have unpaved runways. Lilongwe International Airport and Chileka International Airport are the main airports of Malawi.
Malawi has around 15,451 km (9,601 mi) of roads, out of which only 6,956 km (4,322 mi) are paved and remaining 8,496 km (5,279 mi) is unpaved. Only 797 km (495 mi) of narrow gauge railway is present in Malawi.
The waterways in the country are comparatively developed. 700 km (435 mi) of waterways (most of them in Shire River and Lake Malawi) are present in Malawi. In central Malawi, Chipoka port in the Salima district has railhead. Smaller ports are there in Chilumba, Nkhotakota, Nkhata Bay, and Monkey Bay. The mainland is connected with Likoma Island as well as the Mozambican/Malawian sides of the lake by MV Ilala.
What International Organizations is Malawi part of?
WTO, ACP, AfDB, UN, AU, C, CD, IMF, COMESA, FAO, G-77, ILO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, UNESCO, ICCt, ICRM, UNCTAD, IDA, IFAD, UNIDO, IFC, IFRCS, WHO, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, NAM, ITU, MIGA, UNISFA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, UNWTO, OPCW, SADC, UNOCI, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), ISO (correspond)