What are the Key Facts of Bulgaria?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Bulgaria |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Sofia |
|
Largest City |
Sofia |
|
Coordinates |
43.000000, 25.000000 |
|
Area |
42,810 sq. mi (110,879 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,122 mi (1,806 km) |
|
Coastline |
220 mi (354 km) |
|
Currency |
Lev (BGN) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Greece, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Turkey |
|
Population |
6,975,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Bulgarian |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
3 March (Liberation Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Mila Rodino” |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Rumen Radev |
|
Prime Minister |
Boyko Borisov |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 24,561.2 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 9,737.6 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.816 (2019), Rank: 52 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
56 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
224 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
359 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (EET), DST: UTC+3 (EEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.bg |
Where is Bulgaria?
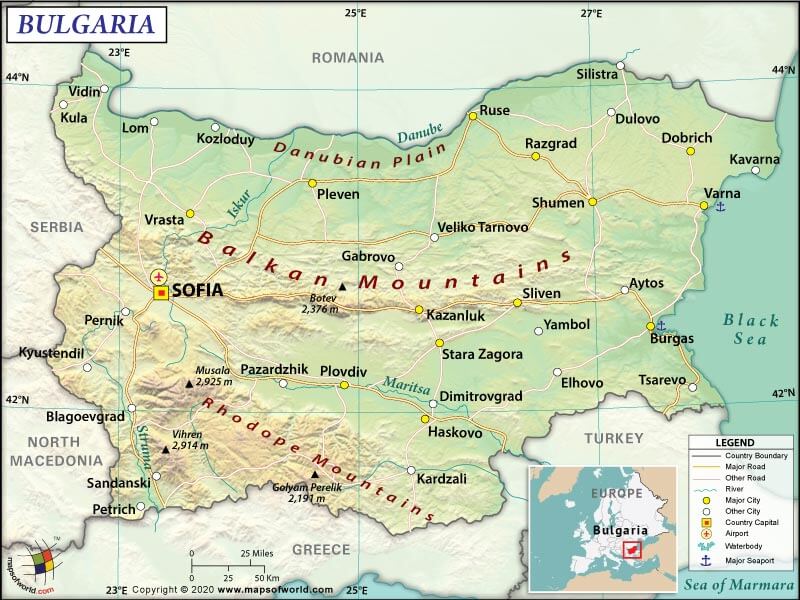
Bulgaria (whose official name is the Republic of Bulgaria) is a Southeast European country that borders the Black Sea between Turkey and Romania.
What is the Geography of Bulgaria?
Bulgaria spreads across a total area of 110,879 sq. km (42,810 sq. mi). Out of the total area, 108,489 sq. km (41,887 sq. mi) is land, and 2,390 sq. km (923 sq. mi) is water.
The Republic of Bulgaria’s total land boundary is 1,806 km (1122.2 mi) long. It shares its border with Romania (605 km or 375.9 mi) to the north, Greece (472 km or 293.3 mi) to the south, Serbia (344 km or 213.8 mi) to the west, Turkey (223 km or 138.6 mi) to the south, and North Macedonia (162 km or 100.7 mi) to the west. The Black Sea is situated to the east of Bulgaria. It has a coastline of 354 km (220 mi) long.
The mean elevation of Bulgaria is 472 m (1548.6 ft). While the highest point is Musala at 2,925 m (9596.5 ft), the lowest point is the Black Sea at 0 m (0 ft).
Bulgaria’s terrain mostly consists of mountains with the lowlands concentrated in the northern and southeastern parts of the country. While 1/3rd of the Bulgarian territory is made up of plains, around 40% of the landform consists of plateaus and hills.
Four most important topographical features of the country include the Rila-Rhodope massif, the Thracian Plain, the Balkan Mountains, and the Danubian Plain.
While the Danube defines the Bulgarian border with Romania, its southern edge slopes upward into the Balkan foothills. The Thracian Plain has a roughly triangular structure, starting from the southeast of Sofia and goes on broadening as it reaches the coast of the Black Sea.
The Balkan Mountains cut through the middle of Bulgaria laterally from west to east. In the mountainous southwest of the country, you will find Rila and Pirin, two major alpine-type ranges. They border the Rhodope Mountains to the east and many other mountains (of varying altitudes) to the south, northwest, and west (such as Belasitsa, Osogovo, and Vitosha).
The highest peaks (mountains) in Bulgaria are Musala (Rila), Vihren (Pirin), Kutelo (Pirin), Malka Musala (Rila), Banski Suhodol (Pirin), etc. The rivers in Bulgaria are usually short and have low levels of water. Major rivers of Bulgaria are Iskar, Struma, Maritsa, and many more. Major lakes are Lake Burgas, Lake Atanasovsko, Lake Varna, etc.
What is the Climate of Bulgaria?
The Republic of Bulgaria has a temperate-continental climate having moderate features that are usually found in Central Europe. It gets very distinct seasons. While the winters are long and cold, summers remain hot. The country (especially in the mountainous areas) gets abundant snowfall during December-mid-March.
As per Koeppen-Geiger classification, the climate in Bulgaria can be classified as Cfa Climate in most regions and Dfb Climate in the mountainous regions.
In the Cfa Climate zone, you’ll find a warm temperated humid Climate. While the temperature in the warmest month remains above 22 °C (71.6 °F) over average, the same in the coldest month in this region hovers within 18 °C (64.4 °F) and -3 °C (26.6 °F).
In the Dfb Climate zone, you’ll find a humid snow climate. While the temperature in the warmest month remains within 10-22 °C (50-71.6 °F), the temperature in the coldest month remains below -3 °C (26.6 °F). In the last four months or more, the temperature remains above 10 °C (50 °F).
The yearly average temperature in the mountainous regions remains around 2.6 °C (36.68 °F), around 8 °C (46.4 °F) in the north, 11 °C (51.8 °F) in the south, and 12 °C (53.6 °F) in the plains.
The nearby Mediterranean Sea influences climate in the southern districts of Bulgaria. That’s why it remains the warmest. In the winter season, the daytime temperature hovers within 0-5 °C (32-41 °F). However, in the summer season, the daytime temperature hovers within 25-30 °C (77-86 °F).
The average yearly rainfall in Bulgaria hovers around 700 mm (27.6 inches). In the mountains, the average yearly rainfall amount remains around 1000 mm and above. In the coastal areas, the average yearly rainfall remains around 400-600 mm (15.7-23.6 inches). While showers and thunderstorms are common during the summer season (especially in the mountainous regions), winter is the driest season.
What is the Economy of Bulgaria?
Bulgaria has an open economy, and over the years, it has demonstrated strong growth. However, the growth rate of the economy is heavily dependent upon external market conditions because of the economy’s reliance on energy imports and foreign demand.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Bulgaria increased by 3.372%, and it grew to US$67.927 billion. Bulgaria’s export and import values in 2018 were US$34 billion and US$38.3 billion, respectively. It has a negative trade balance of -US$4.31 billion.
Major export items are Refined Petroleum, Refined Copper, Raw Copper, Packaged Medicaments, and Wheat. Major imports of Bulgaria are Copper Ore, Crude Petroleum, Cars, Packaged Medicaments, and Petroleum Gas.
The unemployment rate in this Southeast European country has dropped from 12.94% in 2013 to 4.34% in 2019. As per the National Statistical Institute (NSI), the poverty rate in Bulgaria was 22% in 2018.
What is the Transportation System of Bulgaria?
Bulgaria has 68 airports. While 57 are paved, 11 are unpaved. The major airports are Sofia Airport (Sofia), Burgas Airport (Burgas), Varna Airport (Varna), Plovdiv Airport (Plovdiv), Gorna Oryahovitsa Airport (Veliko Tarnovo/Gorna Oryahovitsa), etc.
There are 19,512 km (12,124.2 mi) long roadways available, out of which 19,235 km (11,952.1 mi) are paved (including 458 km or 284.6 mi of expressways), and 277 km (172.1 mi) are unpaved.
5,114 km (3177.7 mi) long railway facility is available across Bulgaria. While 4,989 km (3100 mi) is a standard-gauge railway, 125 km (77.7 mi) is a narrow-gauge railway. An electrified railway facility of around 2,880 km (1789.5 mi) is also available in Bulgaria.
Waterways are around 470 km (292 mi) long. Major seaports are Burgas and Varna. Both of them are located on the Black Sea.
What International Organizations is Bulgaria Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, ILO, Australia Group, BIS, BSEC, CD, CE, CEI, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EU, FAO, G- 9, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITU, MIGA, NATO, NSG, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, SELEC, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WIPO, WMO, ZC, ICC (national committees), IHO (pending member), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer)