What are the Key Facts of Belgium?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Belgium |
|
Continent |
Europe |
|
Capital |
Brussels |
|
Largest City |
Brussels |
|
Coordinates |
50.833333, 4.000000 |
|
Area |
11,849 sq mi ( 30,688 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
806 mi ( 1,297 km) |
|
Coastline |
41.3 mi ( 66.5 km) |
|
Currency |
Euro (€) (EUR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Netherlands, Germany, Luxembourg, France |
|
Population |
11,420,163 (2018 census ) |
|
Official Languages |
Dutch, French, German |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
21 July |
|
National Anthem |
“La Brabanconne” |
|
Form of Government |
Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Philippe |
|
Prime Minister |
Charles Michel |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 50,774.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 46,556.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.916 (2017), Rank: 17 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
39 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
154 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+32 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+1 (CET), Summer (DST) UTC+2 (CEST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.be |
Where is Belgium?
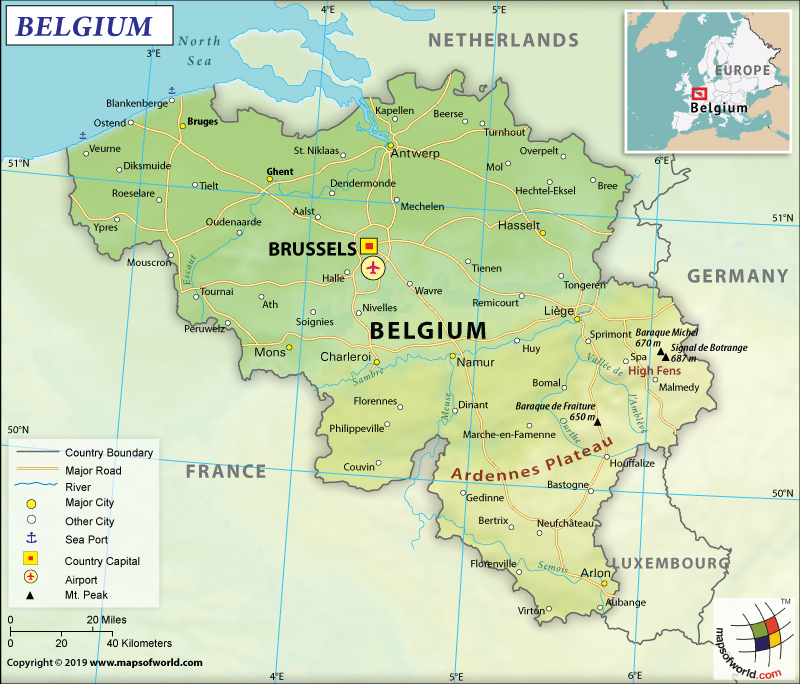
Belgium is a western European country. It shares borders with the Netherlands (478 km or 297 mi) to the north, Germany (133 km or 83 mi) to the east, Luxembourg (130 km or 81 mi) to the southeast, France (556 km or 345 mi) to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest.
What is the Geography of Belgium?
Belgium is spread over a total area of 30,528 sq. km (11,787 sq mi), out of which 30,278 sq. km (107 sq mi) is land area and 250 sq. km (97 sq mi) is water area. There are three regions in Belgium: the Walloon Region, the Flemish Region, and the Brussels-Capital Region. The country has a total land border of 1,297 km (806 mi) and a coastline of 66.5 km (41.32 mi).
In terms of geographical regions, there are 3 main regions and they are the Anglo-Belgian Basin, the Hercynian orogenic belt, and the Belgian Lorraine. The Anglo-Belgian Basin consists of the central plateau as well as the northwest coastal plain. The Hercynian orogenic belt includes the Ardennes uplands in the southeast. Belgian Lorraine is located in the southernmost tip of Belgium and borders the Ardennes to the north.
Sand dunes and polders are mainly present in the coastal plain. As you further go inland, the land rises gently and the area is irrigated by numerous waterways. That’s why you will find both fertile valleys as well as the Campine sandy plain (in the northeastern parts of Belgium). The Ardennes consists of thickly forested hills as well as plateaus, which are more rugged, and caves. This place is characterized by caves as well as small gorges.
The mean elevation of Belgium is 181 m (594 ft). While the highest elevation point of the country is Botrange at 694 m (2,277 ft), the lowest point is the North Sea level. Other major mountains of the country are Baraque Michel, Baraque de Fraiture, Hochtumsknopf, Schwirzbierg, and Spiebig. The main rivers of Belgium are the Meuse, Scheldt, Oise, Leie, Semois, Sambre, and many more.
Belgium has a maritime temperate climate that is characterized by a significant amount of rainfall throughout all seasons. In January, the average temperature revolves around 3 °C (37.4 °F) and the average rainfall is around 65 mm (2.6 in). In July, the average temperature revolves around 18 °C (64.4 °F) and the average rainfall is around 78 mm (3.1 in). The winters are generally cooler and the temperature can go as low as -16 °C (3 °F). Summers are comfortable but sometimes they can go up to 30 °C (86 °F).
What is the Economy of Belgium?
The Belgian economy is a well-diversified economy having a broad mixture of manufacturing, transport, high-tech, and services. In 2018, the nominal GDP was US$531.767 billion and the annual GDP growth rate was 1.4%. 3/4th of the Belgian trade takes place with the European Union countries. Belgium has become a regional logistical hub and that’s why shifts in foreign demand adversely affect the economy.
Belgium imports entire fossil fuels from other countries and its dependence will increase in the coming years, as it has planned to shut down all its 7 nuclear plants by 2025. The unemployment rate is decreasing in the country in recent years. It was 5.21% in 2015 and 2016 and decreased to 5.05% in 2017 and 4.95% in 2018. However, around 19.8% of the population is at risk of poverty.
The public debt level has reduced from a peak of 140% of GDP in the 1990s to around 103% of GDP in 2017 (World Bank). The government has pledged to carry out a reform program (including welfare benefits, labor market rules, and tax policy) so that the competitiveness of the economy improves. The wages in Belgium have become more competitive regionally but the risks of trade union tensions and extended strikes have increased.
What is the Transportation System of Belgium?
Belgium has well-developed roadways, airways, railways, and water networks. 3,592 km (2,232 mi) of railway tracks are there in the country and all of them are standard gauges. In fact, Belgium has 2,950 km (1,830 mi) of electrified tracks.
The total length of roadways present in the country is 118,414 km (73,579 mi), out of which 13,892 km (8,632 mi) are main roads, 1,747 km (1,086 mi) of motorways, and 102,775 km (63,861 mi) other paved roads. The urban railway network is also highly developed in urban areas including Brussels, Charleroi, and Antwerp. There are 41 airports in Belgium, out of which 26 have paved and 15 have unpaved runways. 1 heliport is also there. Brussels Airport is the largest airport in the country.
The waterways in the country are also very developed. 2,043 km of waterways are there in Belgium, out of which 1,528 km are commercially used regularly. 192 merchant marines are present. While 18 are bulk carriers, 18 are general cargo, 20 are oil tankers, and 136 are other kinds of marine ships. Antwerp, Zeebrugge, and Oostende are the major ports.
What International Organizations is Belgium part of?
WTO, Australia Group, Schengen Convention, NATO, UNESCO, Benelux, NSG, BIS, UN, CD, UNHCR, CE, CERN, UNIDO, EAPC, UNTSO, EBRD, ECB, UNCTAD, EIB, EMU, ESA, EU, UNIFIL, FAO, IMF, FATF, G-9, G-10, ILO, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, Paris Club, ICRM, IDA, OECD, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, WHO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MONUSCO, NEA, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, UNRWA, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, ICC (national committees), ADB (nonregional members), AfDB (nonregional members), EITI (implementing country), IGAD (partners), OAS (observer), Pacific Alliance (observer), SELEC (observer), ITUC (NGOs)
Related Links: