What are the Key Facts of Japan?
|
Official Name |
Japan |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Tokyo |
|
Largest City |
Tokyo |
|
Coordinates |
36.000000, 138.000000 |
|
Area |
145,937 sq. mi ( 377,975 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
0 mi (0 km), Island country |
|
Coastline |
18,486 mi (29,751 km) |
|
Currency |
Japanese yen (¥) (JPY) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Maritime neighbors: China, South Korea, Palau, Philippines, Russia, Northern Mariana Is. (US), Taiwan |
|
Population |
126,529,100 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
Official Languages |
Japanese |
|
Major Religion |
Shintoism, Buddhism |
|
National Day |
11 February (National Foundation Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Kimigayo” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Emperor |
Naruhito |
|
Prime Minister |
Fumio Kishida |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 41,473.3 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 39,290.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.915 (2018), Rank: 19 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
9 (SIPRI, 2018) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
497 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
81 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+09:00 (JST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.jp |
Where is Japan?
Japan is an Eastern Asian country. It is a chain of islands that is towards the east of the Korean Peninsula, especially between the Sea of Japan and the North Pacific Ocean. Check out this – Japan Map and Other 59 Related Japanese Maps for more maps and info about Japan.
What is the Geography of Japan?
The total area of Japan is 145,937 sq. mi (377,975 sq. km), out of which land area is 140,728 sq. mi (364,485 sq. km) and water area is 5,185.4 sq. mi (13,430 sq. km). The total area consists of the Bonin Islands (Ogasawara-gunto), Volcano Islands (Kazan-retto), Ryukyu Islands (Nansei-Shoto), Okino-tori-Shima, Minami-Jima, and Daito-shoto. Japan has a 1,623 mi (29,751 km) long coastline, making it the 6th longest coastline in the world.
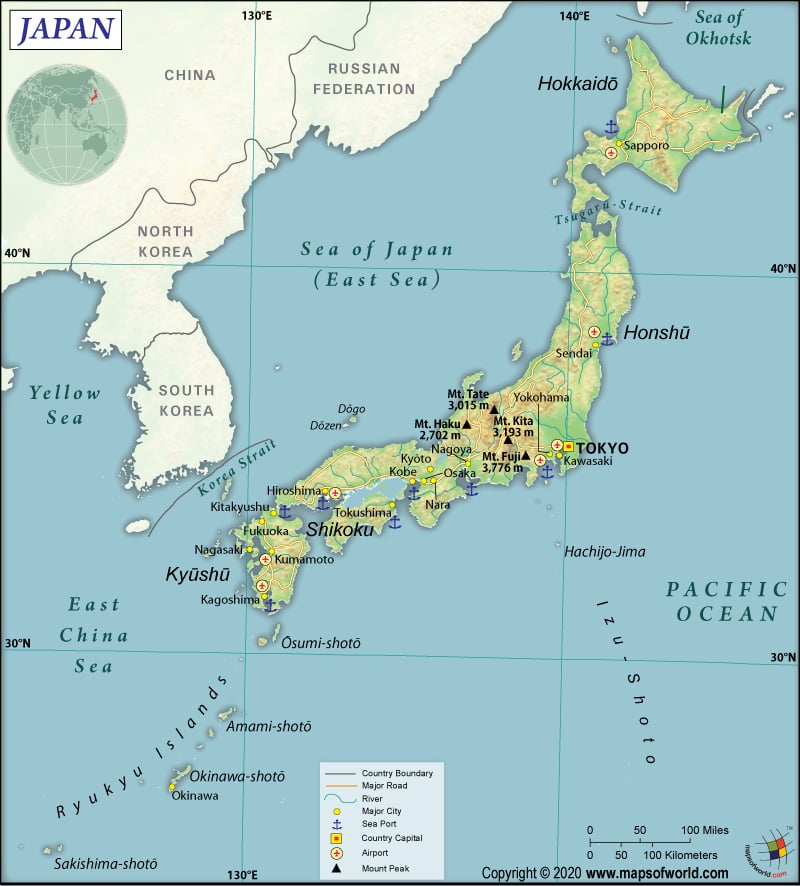
Here is Japan’s Physical Map showing all the physical features of the country.
From northeast to southwest, Japan stretches more than 1,900 mi (3,000 km), which starts from the Sea of Okhotsk and continues to East China and the Philippine Seas. This East Asian country is a part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, comprising an archipelago of 6,852 islands. The five largest islands of the country are Hokkaido, Okinawa, Kyushu, Honshu, and Shikoku.
Japan mostly consists of rugged and mountainous terrain. Around 3/4th of the landform in this island nation is made up of mountains and forested. They are not arable and, at the same time, cannot be used for either industrial or residential purposes. Most of the population of the country lives on the narrow coastal plains, making the country one of the most densely populated countries globally.
2011 estimate shows that just 12.5% is agricultural land, and forests cover around 68.5%. Irrigation happens in only about 9,532.9 sq mi (24,690 sq km) of the area.
Japan is adversely affected by tsunamis, earthquakes, and volcanoes regularly because of its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire. As per the Global Climate Risk Index 2020, Japan was the most adversely affected country in the world due to climate change. The most active volcanoes in the country are Aso, Fuji, Asama, Bandai, Kirishima, Iwo-Jima, Usu, Kikai, Yake-dake, Komaga-take, Tokachi, Suwanosejima, and Oshima.
Mount Fuji is the highest elevation point in Japan at 12,388.5 ft (3,776 m), and Hachiro-gata is the lowest point at -13.12 ft (-4 m). The mean elevation of the country is 1,437 ft (438 m).
The highest mountains of Japan are Mount Fuji, Kenga-mine (Shizuoka), Azumaya San (Gunma), Kita-dake (Nagano), Mount Hotakadake (Nagano), Mount Aino (Shizuoka), Yariga Take (Nagano), Arakawa-dake, and Mount Akaishi (Shizuoka).
Japan’s longest rivers are Shinano (or Chikuma), Tone, Ishikari, Teshio, Kitakami, Abukuma, Mogami, Tenryu, Agano, and Shimanto. The major lakes in Japan are Biwa, Kasumigaura, Saroma, Inawashiro, Nakaumi, Kussharo, Shinji, Shikotsu, Tōya, and Hamana.
What is the Climate of Japan?
There are three main climatic conditions in Japan. During the winter, there is a cold climate in the northern parts, dominated by snow and ice. While the central regions in Japan have a temperate climate, the small southern islands have an almost tropical climatic condition. Rainfall is abundant in nearly all the places in the country. Torrential rains and typhoons are prevalent mainly between summer and autumn.
The monsoon circulation influences Japan’s climatic conditions significantly. While the cold current from the northwest affects the climate in winter, wet and humid currents of tropical origin affect the environment during summer.
There are significant seasonal changes in different parts of Japan due to various factors, which include the presence of mountains, ocean currents, the length of the country, and the influence of the vast Asian continent. However, two climatic features are prevalent throughout this East Asian country high rainfall during the summer season and the absence of a real dry season.
The rainiest areas in Japan receive more than 80 inches (2,000 mm) of annual precipitation. The regions that get maximum rainfall are the Kii Peninsula, the central-western part of Honshu Island, Kyushu’s central-southern part, and Shikoku’s inland and southern areas. Hokkaido’s northernmost part receives the least amount of precipitation, which is generally less than 40 inches (1,000 mm) per year. Summer monsoons, as well as the cold winter, are the main reason behind this reduced influence. Summertime is the rainiest period of the year throughout Japan.
The country gets two types of rain: “Baiu rains” (also called “plum rains”) and Typhoons. The Baiu rains are heavy rainfall that takes place from June 15 to July 15 every year. They are most substantial in the south. This rainfall is suitable for rice cultivation.
The second type of rainfall takes place along with typhoons. They mostly take place in the second half of summer, around August every year. Cyclones mostly take place in the southern part of Japan and may also take place in the Japanese capital, Tokyo. Gale-force winds and torrential rains during the most intense typhoons cause extensive damage. Osaka and Kyoto are hardly affected by cyclones as mountains surround them.
In most of the country, summertime starts in mid-June. However, in Hokkaido and Honshu’s northern part, the temperature remains typically more pleasant during this time. August is the hottest month of the year on the main islands. On the small southern islands, both July and August are the hottest months. The average daily temperature in August revolves ranges from 71 °F (22 °C) to 81 °F (27 °C) in Tokyo. In northern Honshu, the average temperature remains around 76 °F (24.5 °C) in August.
During autumn, the month of September remains hot and humid, especially in the central and southern parts of Japan. The month of September is the rainiest in both Tokyo and Sapporo. Though the summer season is already over in these Japanese cities by September, mid-summer prevails in the southern island of Okinawa. On the south of the island, the temperature sometimes reaches 95 °F (35 °C) or above.
What is the Economy of Japan?
Japan is an economic powerhouse, and in terms of nominal GDP, it is the 3rd largest economy. The nominal GDP of Japan increased at a rate of 0.79% in 2018 (lower than 1.93% in 2017) to reach US$4.971 trillion. It is one of the largest wealth creators globally, ranking 3rd currently.
The leading growth accelerators of this highly developed, free-market economy are motor vehicles, electronic goods, high-tech precision goods (such as robotics, hybrid cars, optical instruments, etc.), steel, machine tools, ships, chemicals, non-ferrous metals, processed foods, and textiles. Japan boasts of having the largest electronics goods industry and 3rd largest automobile manufacturing in the world. Kansai region has come up as the leading industrial cluster and manufacturing center of Japan.
Japan is a significant financial hub and boasts of having the 2nd largest foreign-exchange reserves globally. On the Global Competitiveness Report, Japan ranks 5th on the list and is going to maintain its rank even in 2021. It has the 3rd largest consumer market in the world. The country had an estimated $13.5 trillion of private financial assets in 2010, accounting for around 13.7% of the total individual financial assets of the world.
Japan generally maintains a positive trade balance. In 2017, it had a surplus trade balance of around US$62.4 billion. In 2017, it exported US$694 billion value of goods and imported US$632 billion worth of goods. While the main export items were cars, vehicle parts, integrated circuits, machinery having individual functions, and industrial printers, the major import items were crude petroleum, petroleum gas, broadcasting equipment, integrated circuits, and coal briquettes.
The unemployment rate in Japan has been sliding downwards continuously since 2010 (at that time, it was 5.1%). In 2019, the unemployment rate came down to 2.41% from 2.45% in 2018. The best thing was that Japan’s unemployment rate is lower than most of the leading and emerging economies globally.
However, after the COVID-19 pandemic, the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate again shot up 2.6% in April 2020. There were 1.89 million unemployed persons in Japan in April 2020, an increase of 130,000 from last year.
The rate of poverty in Japan was 15.6% in 2015, which was significantly higher than in other advanced economies (especially OECD countries). The child poverty rate in Japan was 13.9%.
What is the Transportation System of Japan?
Japan has a 757,309.8 mi (1,218,772 km) long road network, out of which 616,919.1 mi (992,835 km) is paved and 140,390.7 mi (225,937 km) is unpaved. Out of the total paved roadways, 5,236.9 mi (8,428 km) of them are expressways.
There are 175 airports in the country, out of which 142 are paved, and the rest 33 are unpaved airports. Sixteen heliports are also present. Some of the busiest airports in Japan are Haneda Airport (Kantō, serving Tōkyō), Narita International Airport (Kantō, serving Tōkyō/Narita), Kansai International Airport (Kansai, serving Ōsaka), Fukuoka Airport (Kyūshū, serving Fukuoka), New Chitose Airport (Hokkaidō, serving Sapporo), Naha Airport (Okinawa, serving Naha), Osaka International Airport (Kansai, serving Ōsaka), Chubu Centrair International Airport (Chūbu, serving Nagoya), Kagoshima Airport (Kyūshū, serving Kagoshima), Sendai Airport (Tōhoku, serving Sendai), and many more.
There is a 16,970 mi (27,311 km) long total railway network available in Japan. 13,798.8 mi (22,207 km) is the 1.067-m gauge (out of which 15,430 km or 9,587.8 mi is electrified), 2,982.6 mi (4,800 km) is standard gauge, 77 mi (124 km) is narrow gauge, 82 mi (132 km) is the dual gauge (electrified), 29.8 mi (48 km) is the 0.762-m gauge (electrified).
1099.8 mi (1,770 km) long waterway is also present in Japan. The seagoing vessels use inland seas. There are 5,017 merchant marine ships in the country, out of which 1,767 are general cargo, 158 are bulk carriers, 37 are container ships, 661 are oil tankers, and 2,394 are other vessels.
The main seaports of Japan are Tokyo, Yokohama, Tomakomai, Osaka, Nagoya, Moji, Mizushima, Kobe, Kawasaki, and Chiba. The primary container ports are Tokyo, Kobe, Yokohama, Osaka, and Nagoya.
What International Organizations is Japan part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, Paris Club, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, G-20, ADB, APEC, ARF, Australia Group, BIS, CD, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NEA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, PCA, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNRWA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ZC, AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), CE (observer), CERN (observer), CICA (observer), ASEAN (dialogue partner), CPLP (associate), EITI (implementing country), ICC (national committees), IGAD (partners), LAIA (observer), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), OAS (observer), OSCE (partner), Pacific Alliance (observer), PIF (partner), SAARC (observer), SELEC (observer), and SICA (observer).
Related Links: