What are the Key Facts of Russia?
| Official Name | Russian Federation |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Moscow |
| Largest City | Moscow |
| Coordinates | 60.000000, 90.000000 |
| Area | 6,612,073 sq. mi (17,125,191 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 13,923 mi (22,408 km) |
| Coastline | 23,397 mi (37,654 km) |
| Currency | Russian ruble (RUB) |
| Neighboring Countries | Norway, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia, North Korea. Maritime neighbors: Japan (by the Sea of Okhotsk), United States (by the Bering Strait) |
| Population | 146,793,744 (2019 est.) |
| Official Languages | Russian |
| Major Religion | Christianity |
| National Day | 12 June, Russia Day |
| National Anthem | “Gimn Rossiyskoy Federatsii” |
| Form of Government | Semi-presidential federation |
| President | Vladimir Putin |
| Prime Minister | Mikhail Mishustin |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $25,763.3 (World Bank, 2017) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $10,749.1 (World Bank, 2017) |
| HDI | 0.816 (2017), Rank: 49 |
| Literacy Rate | NA |
| Space Agency | Roscosmos State Corporation for Space Activities |
| Military Expenditure Ranking | 5 (SIPRI, 2017) |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 546 (as of 2018), 1,204 (as Soviet Union) |
| Driving Side | Right |
| Calling Code | +7 |
| Time Zone | UTC+2 to +12 |
| Internet TLD | .ru, .su, .рф |
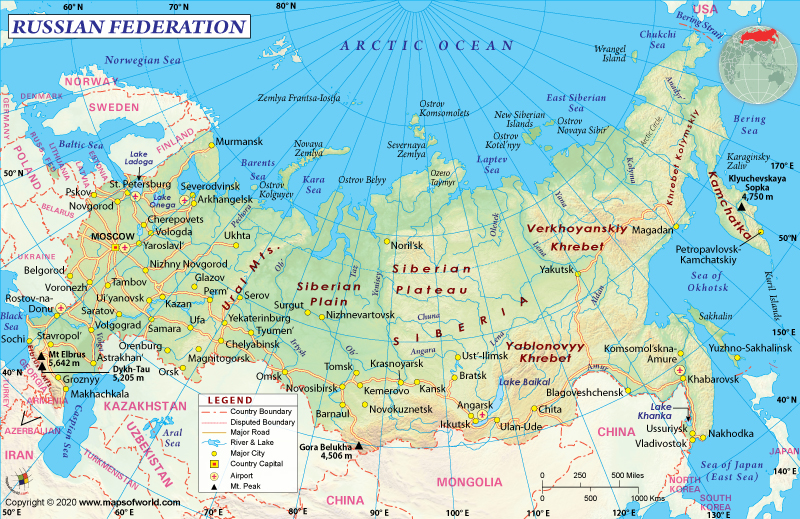
Where is Russia?
Russia is the largest country in the world. It extends from northeastern Europe to northern Asia. Its area is approximately 1/8 of the earth’s inhabited land.
What is the Geography of Russia?
Russian territory is so vast that it covers 11 time zones. Moreover, the land mass of Russia is divided into five natural zones.
The tundra zone lies in the northern area and is comparatively a treeless zone due to the extremely cold weather. Covering almost 50 percent of Russia, it is also home to the oil and gas fields. The taiga is the world’s largest forest zone; it abounds in coniferous trees like cedar and fir and houses 33 percent of the country’s population. The steppe, or plains zone comprises grasslands and provides conducive conditions for agricultural activities, such as moderate temperatures, and sunshine and humidity. However, this area is also prone to occasional droughts owing to the shortfall in rains. Particularly the region along the Lower Volga and Caspian Sea coast, as well as some areas of southernmost Siberia, experience low rainfall due to the semi-arid climate (the arid zone). All in all, Russian landscape comprises two plains (the East European Plain and the West Siberian Plain), two lowlands (the North Siberian and the Kolyma, in far northeastern Siberia), two plateaus (the Central Siberian Plateau and the Lena Plateau to its east), and a series of mountainous areas situated in the extreme northeast or spanning the southern border intermittently.
The last and fifth zone in Russia is the mountain zone. There are nine major mountain ranges in Russia, including the Ural, the Caucasus, the Sayan and the Altay ranges. The Urals are famous for major mineral deposits. The Yenisey Valley can be viewed as a dividing line between the eastern and the western parts of Russia. The eastern part has more mountainous territory than the western part, which is dominated by low plains in the interiors. Mount Elbrus in Caucasus is the highest peak in Europe, at 5,642 meters.
In addition, Russia is home to Europe’s longest river, the Volga, the deepest lake, Baikal, and the largest lake, Ladoga. Moreover, the long Kamchatka peninsula located in the far east of Russia contains many volcanic peaks, some of which are still active.
The part of Russia falling in Europe experiences Continental climate, with warm to hot summers and severely cold winters. Rainfall takes place throughout the year. However, the winters are drier compared to summers in Eastern Siberia and the Far East. Most of the country witnesses snowfall in winters, whereas some areas adjoining the Black Sea witness winter rains. Additionally, the areas around the Arctic Ocean experience polar climate. The inner regions of northeast Siberia have recorded lowest temperatures of -69 degree celsius (or 92.2 F) till date.
What is the Economy of Russia?
After the disintegration of the erstwhile USSR, Russia has undergone significant changes, moving steadily from a centrally planned model towards a market-based system. Economic reforms in the 1990s privatized a lot of industries. However, energy, banking, transportation, and defense-related sectors still have substantial state control. Russia’s major industries are petroleum, natural gas, mining, coal, chemicals, metals, engineering goods, aircrafts, space and defense equipment, shipbuilding, construction/ medical/ scientific/ electrical equipments.
Being a leading producer in the world of oil and natural gas, and a substantial exporter of metals such as steel and primary aluminum, Russia is heavily influenced by the movement of world commodity prices. Moreover, being dependent on commodity exports makes it vulnerable to business cycles that follow the global price swings. Russian economy witnessed an average 7 percent growth during 1998-2008 when the oil prices rose rapidly. Since then, growth rates have diminished. Due to the combined effect of falling oil prices, international sanctions, and structural problems, Russia went into a deep recession in 2015, with GDP falling by close to 2.8%. The downturn continued through 2016, when GDP contracted another 0.2%. The trend got reversed in 2017 as its GDP touched I.579 trillion dollars. Services sector accounted for 62.3% of the GDP, followed by industry: 32.4%, and primary sector: 4.7%. Its major trading partners are European Union, China, US, Belarus and Turkey. Unemployment is relatively low, and stands at 4.7% (World Bank, 2018).
What is the Transportation System of Russia?
Russia had 32 registered air carriers in 2015, and 1218 airports. In addition, it has 49 heliports. Its railway network is strong, with 1,283,387 km of total length. Its 102,000 km of waterways include the 72,000-km system that links the Baltic Sea, White Sea, Caspian Sea, Sea of Azov, and the Black Sea. It has a strong fleet of 2625 merchant ships, comprising a large number of general cargo carriers and oil tankers. Kaliningrad, Nakhodka, Novorossiysk, Primorsk, and Vostochnyy are its major seaports.
What International Organizations is Russia part of?
APEC, Arctic Council, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), BIS, BRICS, BSEC, CBSS, CD, CE, CERN (observer), CICA, CIS, CSTO, EAEC, EAEU, EAPC, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, G-20, GCTU, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), LAIA (observer), MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OPCW, OSCE, Paris Club, PCA, PFP, SCO, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNSC (permanent), UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Related Links:

![]()
