What are the Key Facts of Venezuela?
|
Official Name |
Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela |
|
Continent |
South America |
|
Capital |
Caracas |
|
Largest City |
Caracas |
|
Coordinates |
8.000000, -66.000000 |
|
Area |
353,841 sq mi ( 916,445 sq km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
3,273 mi ( 5,267 km) |
|
Coastline |
1,740 mi ( 2,800 km) |
|
Currency |
Petro Bolívar Soberano (VES) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Brazil, Colombia, Guyana |
|
Population |
31,568,179 (2016 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Spanish |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
5 July (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Gloria al bravo pueblo” |
|
Form of Government |
Federal presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Nicolás Maduro |
|
Vice President |
Delcy Rodríguez |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 18,102.5 (World Bank, 2014) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 16,054.5 (World Bank, 2014) |
|
HDI |
0.761 (2017), Rank: 78 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
97.13 (UNESCO, 2016) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
NA (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
15 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+58 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC−4 (VET) |
|
Internet TLD |
.ve |
Where is Venezuela?
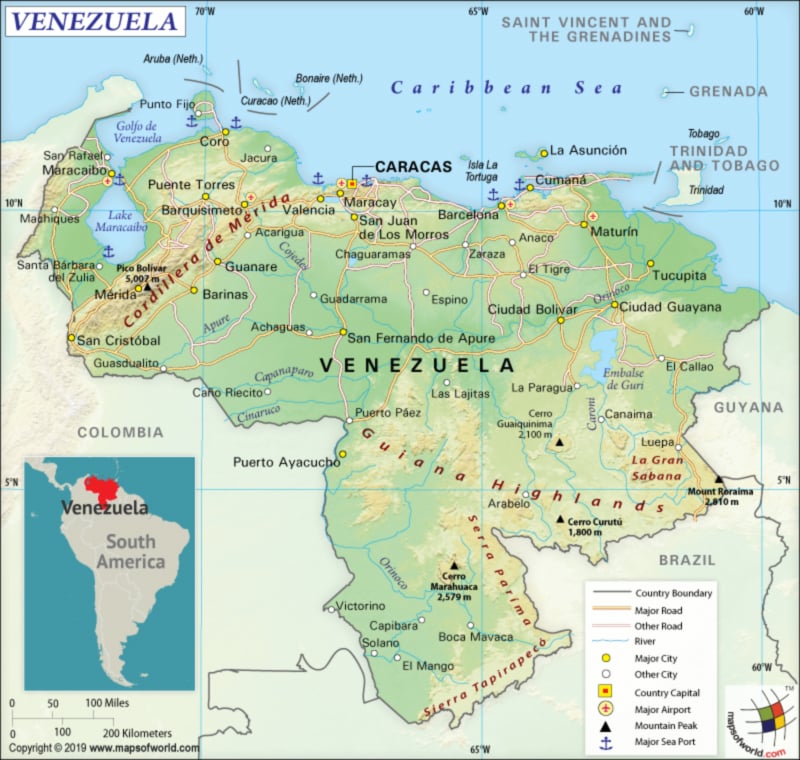
Venezuela is located in the Northern Hemisphere that sits closer to the equator. Therefore, it comes within the tropics. Venezuela is situated in South America’s northern coast. It consists of both a continental mainland and many islands in the Caribbean Sea.
The country shares its borders with Colombia (2341 km or 1,455 mi) to the west, Brazil (2137 km or 1,328 mi) to the south, and Guyana (789 km or 490 mi) to the east. Other neighbors in the Caribbean Sea off the northern coast are Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, Aruba, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Bonaire, Curaçao, and the Leeward Antilles.
What is the Geography of Venezuela?
Venezuela has a triangular look and is spread over a total area of 912,050 sq km (352,144 sq mi), out of which 882,050 sq km (340,561 sq mi) is land and 30,000 sq km (11,583 sq mi) is water. While the total land boundary is 5,267 km (3,273 mi), the coastline (to the north) is 2,800 km (1,740 mi) long.
There are 4 well-defined topographical regions of Venezuela. They are the wide plains in the central parts of the country, the mountains in the north that extend along the northern Caribbean coast from the Colombian border, the Guiana Highlands in the southeastern part of Venezuela, and the wide plains in central parts of the country.
The extreme northeastern extensions of the Andes Mountain range of South America form the northern mountains of Venezuela. The Amazon Basin’s northern fringes and the highest waterfall of the world, Angel Falls, are situated in the Guiana Highlands. In fact, a large table-top like mountain such as tepuis can also be found in the Guiana Highlands. Extensive plains (known as llanos), extending from the Colombian border (in the far western parts of Venezuela) to the Orinoco River delta (in the eastern parts of Venezuela), is there in central Venezuela.
The mean elevation of Venezuela is 450 m (1,476 ft). While the highest elevation point of the country is Pico Bolivar at 4,978 m (16,332 ft), the lowest point is the Caribbean Sea level. The other mountains in Venezuela are Pico Humboldt which is the second highest peak at 4,940, Pico La Concha at 4,922 metres, Pico Bonpland at 4,883 m, Pico Espejo at 4,880 m, Cerro Pintado at 3,660 m, Cerro Marahuaca at 2,832 m etc. The major rivers of the country are Orinoco River (having rich alluvial soils), Apure, and Caroní.
Venezuela’s climate depends upon the elevation. The average annual temperature remains around 35 °C (95.0 °F) in the plains because of low elevation. The highland and glaciers have an average annual temperature of 8°C (46.4°F).
In the northwestern semiarid portions, the average annual rainfall hovers around 430 mm (16.9 in). The Amazonian Jungle in the southern part and the Orinoco Delta in the far eastern part of Venezuela get more rainfall (more than 1,000 mm or 39.4 in). The level of rainfall remains lowest during August-April.
What is the Economy of Venezuela?
The GDP (Gross Domestic Product) of Venezuela is at US$482.359 billion (World Bank, 2014). The economy of Venezuela is mainly based on the petroleum sector, followed by manufacturing. Trade and export account for 48.1% and 16.7% of the GDP respectively. Petroleum products account for around 95% of the total Venezuelan exports.
Heavy industries of Venezuela manufacture products such as aluminum, steel, and cement. Other products manufactured in the country are electronics, automobiles, foodstuffs, and beverages. 3/4th of the electricity in Venezuela is produced from the Guri Dam.
Though 1/4th of the land area in Venezuela is used for agriculture, it employs just 7.3% of the labor force and contributes just 4.7% to the GDP. Venezuela is not self-reliant in food and needs to import food items in large amounts. The agricultural products exported by the country include rice, coffee, tropical fruits, corn, pork, fish, and beef.
The lower global prices of petroleum, the US sanctions, and hyperinflation have adversely affected Venezuela. The nominal GDP of Venezuela has come down from US$279.249 Billion in 2016 to US$143.841 Billion in 2017 and further to an estimated US$98.468 Billion in 2018. It is expected to reach US$76.458 Billion in 2019.
While the unemployment rate has reached an estimated 35% of the total labor force in 2018, over 94% of the population (in 2018) lives in poverty. A survey conducted by three universities in Caracas has found out that 60% of the population lives in extreme poverty.
In early June, the UN has published a report saying that the ongoing political and economic crisis in the country has led 4 million Venezuelans to move out of Venezuela (in just 7 months) and take shelter in other neighboring countries such as Colombia, Peru, Brazil, Argentina, Ecuador, and Chile. Special Representatives of UNHCR and IOM called for international help in dealing with the unprecedented crisis.
An internal UN report said that 7 million Venezuelans (24% of the total population) need immediate humanitarian aid as they suffer from malnutrition and disease. The consumption of meat, vegetables, and milk dropped significantly in Venezuela. Consumption of milk has dropped by 77%. UN estimates also show that the number of Venezuelans suffering from undernourishment currently has increased three folds since 2010-12 to around 3.7 million. Around 22% of the children (below 5-years of age) in Venezuela suffer from chronic malnutrition.
What is the Transportation System of Venezuela?
Venezuela has around 100,000 km (62,000 mi) of road network, out of which 1/3rd are paved. The airway is the main transport with which Venezuela is primarily connected with the rest of the world. There are 444 airports in the country, out of which 127 have paved runways and 317 have unpaved runways. Simón Bolívar International Airport at Maiquetia and La Chinita International Airport at Maracaibo are the main airports in Venezuela. 3 heliports are also there in the country.
There is 7,100 km (4412 mi) of waterways transport in Venezuela. Oceangoing vessels are used to navigate on Orinoco River (connecting Ciudad Guayana to the Atlantic Ocean) and Lake de Maracaibo. 4 major seaports are there including La Guaira, Punta Cardon, Puerto Cabello, and Maracaibo.
Railway system is very limited in the country. There is just 447 km (278 mi) of 1.435-m gauge railway available, out of which just 41.4 km (26 mi) has electric train services. Metro networks are mainly concentrated in the major cities. Most important metros are Caracas Metro, Valencia Metro, and Maracaibo Metro.
What International Organizations is Venezuela part of?
WTO, CD, CDB, IMF, Petrocaribe, CELAC, OPCW, OPEC, UN, FAO, G-15, G-24, G-77, Interpol, IADB, IAEA, WHO, ILO, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, NAM, Union Latina, IMO, IMSO, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITSO, ITU, LAES, LAIA, MIGA, UNESCO, UNHCR, OAS, OPANAL, PCA, UNASUR, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), ICCt (signatory), ITUC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs), Caricom (observer), LAS (observer)
Related Links: