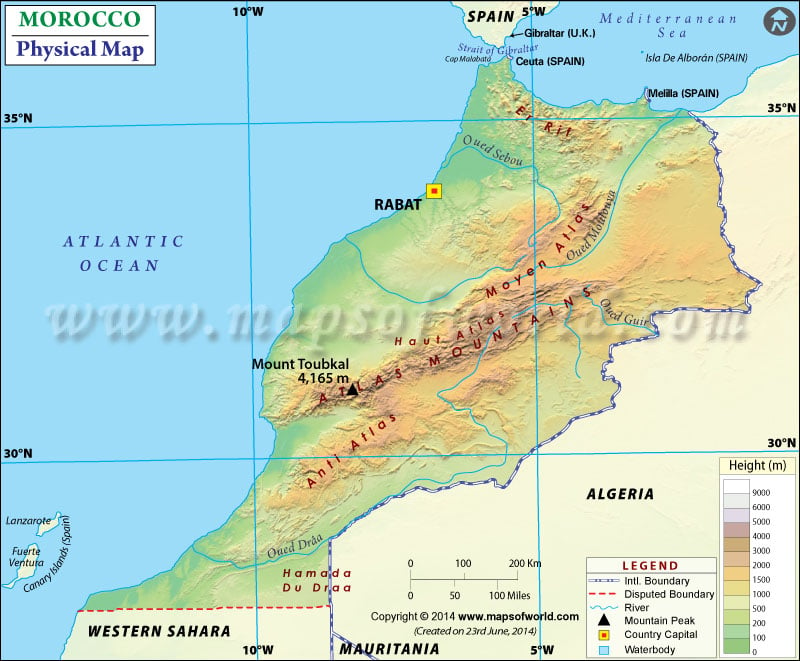
- Neighboring Countries - Western Sahara, Algeria, Spain
- Continent And Regions - Africa Map
- Other Morocco Maps - Morocco Map, Where is Morocco, Morocco Blank Map, Morocco Road Map, Morocco Rail Map, Morocco River Map, Morocco Cities Map, Morocco Political Map, Morocco Flag
Morocco is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is a northwestern-most country bordering the Mediterranean sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Morocco shares its boundary with Algeria to the east and Western Sahara to the south. The country is separated from Spain by the Strait of Gibraltar with 13 kilometres of water.
The map also shows the International and disputed boundaries of the country. The capital city of Rabat is also marked on the map. This physical map depicts the latitudinal extent 27. N to 36. N and the longitudinal area between 1. W to 14.W. Map legend featured at the bottom helps all the signs, characters, and symbols used throughout the map. The map can be used for school work, presentation and other purposes.
Morocco Physical Features
The country covers a total area of 446,550 km2(172,410 sq mi), excluding western Sahara. The geography of Morocco is wide-ranging, from mountains to the Atlantic Ocean to the Sahara Desert. Based on dominant topographic features, the country is divided into the following geographic regions:
Atlas and Rif Mountains
The terrain of the country is primarily mountainous. Two mountain ranges divide Atlantic Morocco from the eastern region. The Atlas Mountains extend from the central north to the southwest. The mountain range stretches about 1,350 kilometres (840 mi). This mountain range creates a barrier across the centre. The three distinct ranges of atlas mountains are the High Atlas, the Middle Atlas and Anti-Atlas. Another is Rif Mountain extending from Tangier to the Moulouya River Valley in northern Morocco near the Moroccan-Algerian Frontier. These mountain ranges form a buffer along the Mediterranean coastline.
Atlantic Morocco and Moroccan Plateau
This region consists of plains formed of fine sediments and plateaus of coarser deposits. The Sebou River basin is a large alluvial plain located northwest of the Rif Mountains and runs roughly from Rabat to Fes. The central agricultural part of the region is the Gharb basin extending about 50 miles along the Atlantic coast and reaching 70 miles (110 km) inland. Rif Mountains border the Gharb basin to the northeast. Between the Atlantic Ocean and Atlas, South of the Rabat-Fes line, lies a series of high Plains known as the Moroccan plateau.
Moulouya Basin and Arid Region
The semiarid lowland is located east of the Rif, and Atlas ranges formed by erosion force of the Moulouya river known as Moulouya Basin. In eastern Morocco lies high plateaus having an elevation between 3,900-4250 feet (1,200-1,300 meters). The arid region lies to the southeast east of Atlas mountains, constituting the northwestern limit of Sahara.
Important Rivers in Morocco
Morocco has the most-extensive stream network in North Africa. The Sebou River is the most significant river of Morocco that constitutes half of Morocco’s surface water resources along with its tributaries. The river is 280 miles (450 km). Another river that rises in High Atlas at the confluence of Dades and the Immi is the Draa, and it is the longest river in the country with 685 miles (1,100 km) in length. Oum er-Rabia is another major river flowing from the Middle Atlas to the Atlantic.