What are the Key Facts of Thailand?
|
Official Name |
Kingdom of Thailand |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Bangkok |
|
Largest City |
Bangkok |
|
Coordinates |
15.000000, 100.000000 |
|
Area |
198,120 sq. mi (513,120 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
3,535 mi ( 5,673 km) |
|
Coastline |
2,000 mi ( 3,219 km) |
|
Currency |
Baht (฿) (THB) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), Malaysia |
|
Population |
69,428,453 (2018 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Thai |
|
Major Religion |
Buddhism |
|
National Day |
28 July |
|
National Anthem |
“Phleng Chat Thai” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch |
Maha Vajiralongkorn |
|
Prime Minister |
Prayut Chan-o-cha |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 19,017.7 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 7,273.6 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.755 (2017), Rank: 83 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
92.87 % (UNESCO, 2015) |
|
Space Agency |
Geo-Informatics and Space Technology Development Agency |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
30 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
33 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+66 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+07:00 (ICT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.th |
Where is Thailand?
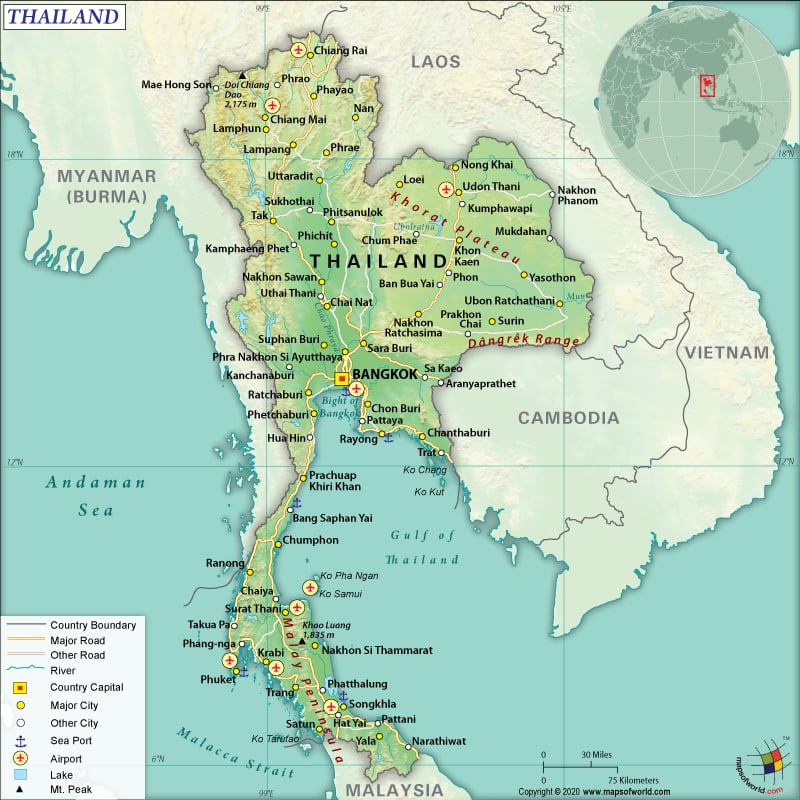
Thailand is a Southeast Asian country that borders the Gulf of Thailand (to the south) as well as the Andaman Sea (to the west). It is bordered by Myanmar to the north, Laos to the north and the east, Malaysia to the south, and Cambodia to the east. Thailand partly occupies the Indo-Chinese peninsula and Malay peninsula. Check out this – Map of Thailand and Other 89 Related Thai Maps for more maps and info about Thailand.
What is the Geography of Thailand?
Thailand is spread across a total area of 513,120 sq. km (198,120 sq. mi), out of which 510,890 sq. km (197,256 sq. mi) is land area and 2,230 sq. km (861 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 5,673 km (3,525 mi) long land boundary and a 3,219 km (2,000 mi) long coastline.
The land boundary is shared with four countries: Myanmar (Burma) (2,416 km or 1,501 mi), Laos (1,845 km or 1,146 mi), Cambodia (817 km or 508 mi), and Malaysia (595 km or 370 mi).
There are 3 distinct landforms present in Thailand. The plain is located in the central parts of the country, Khorat Plateau is situated in the east, and mountains in other parts of Thailand. 287 m () is the mean elevation of this Southeast Asian country. While Doi Inthanon (also called Doi Luang) at 2,565 m (1,594 ft) is the highest elevation point in Thailand, the Gulf of Thailand at 0 m (0 ft) is the lowest elevation point in the country.
Besides Doi Inthanon, the other major mountains of the country are Doi Pha Hom Pok, Phu Khe, Phu Soi Dao, Khao Kacheu La, Doi Chiang Dao, etc. There are two main river systems in Thailand and they are the Mekong and Chao Phraya. The major rivers here are Mekong, Salween, Nan, Mun, Tha Chin, Chi, etc.
The relatively high mountains are mainly located in the northern parts. These high mountains continue extending in a narrow strip southward along the Myanmar border to Malaysia’s northern edges. The fertile lands are located on the central plain, which is dominated by the Chao Phraya River.
The Khorat Plateau consists of an area that includes rolling low hills as well as small and shallow lakes. These lakes drain into the Mekong River system, running along the Laos border. The land fades into the mangrove swamps along the southern peninsula (known as the Isthmus of Kra). Many off-the-coastline islands are there in Thailand and the most popular one is in Phuket.
Thailand has a tropical climate, having three distinct seasons. The first one is a hot season, which starts in March and continues till mid-May. The second season is the rainy season that lasts from mid-May to October. The third one is the dry and cool season. It starts when the northeast monsoon starts blowing from the Asian continent. The southern parts of the country remain hot even during the winter season. However, the inland areas and the northern region remain relatively cool. The average annual temperature revolves around 27.8 °C (82 °F).
If you want to visit the continental parts of Thailand, December-mid-February is the best time. If it is Bangkok or the southwestern coast, try visiting the place during late December-March. For visiting the eastern coast of the Gulf of Thailand, late January-April is the best time for a visit.
What is the Economy of Thailand?
The nominal GDP of Thailand increased at a rate of 4.129% to reach a figure of US$504.993 billion in 2018. In 2017, this Southeast Asian country had a positive balance of trade of US$54.8 billion as it exported US$215 billion value of goods and imported US$160 billion of goods.
The major export items of Thailand are integrated circuits, office machine parts, broadcasting equipment, cars, delivery trucks, etc. Its major import items are office machine parts, crude petroleum, integrated circuits, vehicle parts, gold, etc.
The rate of unemployment is just frictional, which hovered around 0.67% in 2018. The poverty rate (defined by the poverty headcount ratio at US$5.50 per day) was 7.80% in 2017, a decline of 0.6% since 8.40% in 2016.
What is the Transportation System of Thailand?
Thailand has a significantly developed transportation infrastructure. There are 180,053 km (111,880 mi) long roadways, out of which 450 km are expressways. The country has 101 airports, out of which 63 have paved runways and 38 unpaved runways. Over seven heliports are also there.
Some of the major airports in the Kingdom of Thailand are Suvarnabhumi Airport, Udon Thani International Airport, U-Tapao International Airport, Surat Thani International Airport, Krabi International Airport, Samui International Airport, Phuket International Airport, Hat Yai International Airport, Mae Fah Luang Chiang Rai International Airport, Chiang Mai International Airport, and Don Mueang International Airport.
Over 4,127 km (2,564 mi) long railways are also available, out of which 4,043 km (2,512 mi) is narrow-gauge and just 84 km (52 mi) is standard-gauge. There is 4,000 km (2,485 mi) of navigable waterways in Thailand, out of which 3,701 km (2,300 mi) can be navigated by boats with drafts up to 0.9 m (3 ft).
The major seaports of Thailand are Bangkok, Si Racha, Prachuap Port, Map Ta Phut, and Laem Chabang. Laem Chabang is a container port having 7,227,431 TEU in 2017. Map Ta Phut is the LNG terminal of the country. Thailand has 807 merchant marine vessels, out of which 241 are oil tankers, 91 general cargo, 25 container ships, 27 bulk carriers, and 423 others.
What International Organizations is Thailand part of?
WTO, IMF, WHO, UN, ILO, UNESCO, NAM, ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIMSTEC, BIS, CD, CICA, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, OPCW, PCA, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMOGIP, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), OSCE (partner), PIF (partner), WFTU (NGOs), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), OIC (observer), OIF (observer)
Related Link:

![]()
