What are the Key Facts of Malaysia?
|
Official Name |
Malaysia |
|
Continent |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Largest City |
Kuala Lumpur |
|
Coordinates |
2.500000, 112.500000 |
|
Area |
127,724 sq. mi ( 330,803 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
1,704 mi ( 2,742 km) |
|
Coastline |
33,999 mi ( 54,716 km) |
|
Currency |
Ringgit (RM) (MYR) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Indonesia, Thailand, Brunei, Philippines, Singapore, Vietnam, China |
|
Population |
32,772,100 (2019 est.) |
|
Official Languages |
Malay |
|
Major Religion |
Islam |
|
National Day |
31 August (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Negaraku” |
|
Form of Government |
Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
|
Monarch/King |
Abdullah of Pahang |
|
Prime Minister |
Mahathir Mohamad (Resigned on 02/24/2020) |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 31,698.4 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 11,239.0 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.802 (2017), Rank: 57 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
93.73 (UNESCO, 2016) |
|
Space Agency |
National Space Agency (ANGKASA) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
49 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
11 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
left |
|
Calling Code |
+60 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+8 (MST) |
|
Internet TLD |
.my |
Where is Malaysia?
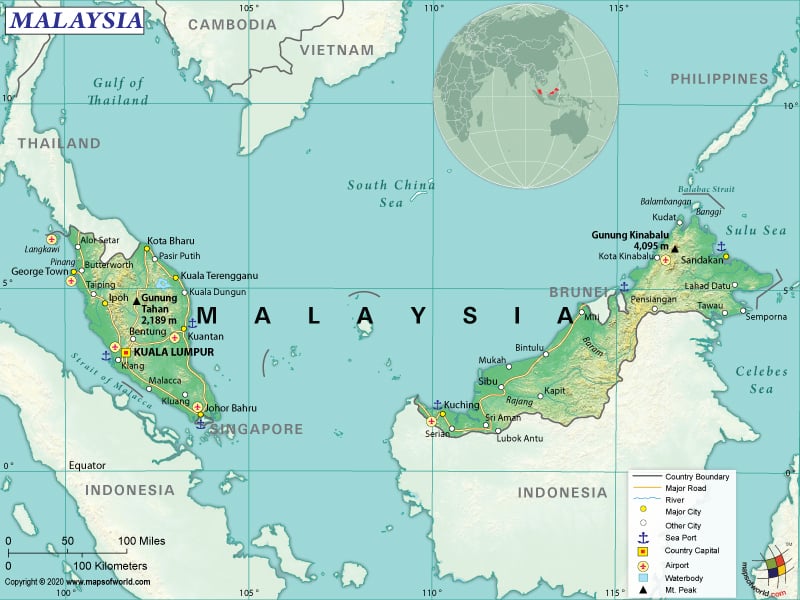
Malaysia is a Southeastern Asian country that is made up of two similarly sized geographical regions: Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia (also called Malaysian Borneo). The South China Sea separates these two regions. The total land boundary shared by Malaysia is 2,742 km (1,704 mi). While Peninsular Malaysia shares 595 km (370 mi) long land boundaries with Thailand, East Malaysia shares its land boundaries with Indonesia (1,881 km or 1,169 mi) and Brunei (266 km or 165 mi). Peninsular Malaysia also shares a maritime border with Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Singapore. The maritime borders shared by East Malaysia include Indonesia, Brunei, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
What is the Geography of Malaysia?
Malaysia is spread across a total area of 330,803 sq. km (127,724 sq. mi), of which 328,657 sq. km (126,895 sq. mi) is land area and 1,190 sq. km (459 sq. mi) is the water area. This country has a 4,675 km (2,905 mi) long coastline. Of this, Peninsular Malaysia has a 2,068 km (1,285 mi) long coastline, and East Malaysia has a 2,607 km (1,620 mi) long coastline.
Generally, the landforms of the country include coastal plains that rise to hills and mountains. The coastal plains ring Peninsular Malaysia’s edge bordering the South China Sea in the eastern direction and the Strait of Malacca in the western direction. The western coast is dominated by mangroves, which are mainly found in marshy, saline, and tropical tidal areas. The eastern coast, on the other hand, has rocky headlands that are interspersed with sandy beaches and a few picturesque lagoons. On offshore, hundreds of tiny islands are there.
Moreover, East Malaysia’s shoreline comes with peat swamps that recede into lowlands, which in turn consist of firmer ground further inland. As you move further into the interior, the coastal plains start rising into the hills that remain covered with rainforest.
Also, the Titiwangsa Mountains form the backbone of the West Malaysian peninsula. In the northwestern direction, the Bintang Mountains are located that extend into southern Thailand. The Tahan Range is located parallel to the Titiwangsa Mountains. It includes Peninsular Malaysia’s highest peak, Mount Tahan (which is mostly barren). The elevation of Mount Tahan is 2,187 m (7,175 ft).
The highest elevation of Malaysia is Gunung Kinabalu at 4,095 m (13,435 ft), and the lowest elevation is sea level at the Indian Ocean. Over 419 m (1,375 ft) is the mean elevation of the country. Malaysia’s highest mountains are Kinabalu, Trusmadi, and Tambuyukon. Some of the major rivers are Rajang, Kinabatangan, Pahang, Perak, and many more. Near the Indonesian border in Sabah, the dormant Bombalai volcano (which last erupted 27,000 years back) is located. This volcano has the potential of erupting again.
What is the Economy of Malaysia?
To begin with, Malaysia is one of the largest economies in Southeast Asia. It is one of the most competitive countries in the world, and its labor productivity is significantly higher than many neighboring economies such as Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines.
The nominal GDP of the country was US$354.348 billion in 2018, with a growth rate of 4.724%. In the last 30 years, the Malaysian economy has been successful in reducing income inequalities and, at the same time, it has decreased high poverty rates successfully. Malaysia wants to keep its economic growth sustainable in the coming years. It is currently considered as an upper-middle-income economy and aims to become a high-income economy by 2024.
From being an agricultural and commodity-based economy, Malaysia has transformed itself into an export-led one that is highly dependent on the manufacturing and services sectors. The country has become a leading exporter of electronic parts/components and electrical appliances. Reports say that 40% of the jobs in the country are export-oriented ones. Extreme poverty in Malaysia is less than 1% of the total number of households. The Malaysian government is now trying to uplift the economic conditions of the poorest 40% of the population.
What is the Transportation System of Malaysia?
Malaysia has an extensive roadway network, which is 144,403 km (89,728 mi) long. This estimate excludes the local roads. While 116,169 km (72,184 mi) of the roadways are paved, 28,234 km (17,544 mi) is unpaved. Over 1,821 km (1,132 mi) of expressways are there within the paved length of roadways.
There is 7,200 km (4,474 mi) of waterways present in this country. Around 3,200 km (1988 mi) of waterways are present in Peninsular Malaysia, 2,500 km (1,553 mi) in Sarawak, and 1,500 km (932 mi) in Sabah. The major seaports are Bintulu, Tanjung Pelepas, Port Kelang, George Town, and Johor Bahru. The country has 1,704 merchant marine ships.
Over 1,851 km (1,150 mi) of the railway network is also present, of which 1,792 km (1,113 mi) is a narrow gauge, and only 59 km (37 mi) is the standard gauge. Malaysia has 114 airports, out of which 39 have paved runways, and 75 have unpaved runways. Four heliports are also there.
What International Organizations is Malaysia part of?
WTO, IMF, ADB, UN, APEC, UNESCO, ARF, UNCTAD, ASEAN, UNAMID, BIS, UNISFA, C, UNIDO, CP, ILO, D-8, EAS, FAO, G-15, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, MINURSO, MONUSCO, NAM, OIC, OPCW, PCA, UNIFIL, UNMIL, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, ICC (national committees), PIF (partner), CICA (observer), ITUC (NGOs)
Related Links: