What are the Key Facts of Israel?
|
Official Name |
Israel |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Jerusalem (defacto, final status yet to be determined) |
|
Largest City |
Jerusalem |
|
Coordinates |
31.500000, 34.750000 |
|
Area |
8,470 sq. mi (21,937 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
662 mi (1,065 km) |
|
Coastline |
169.6 mi (273 km) |
|
Currency |
Israeli shekel (ILS) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Syria |
|
Population |
9,053,000 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
Official Languages |
Hebrew |
|
Major Religion |
Jewish |
|
National Day |
14 May (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Hatikvah” (The Hope) |
|
Form of Government |
Parliamentary democracy |
|
President |
Reuven Rivlin |
|
Prime Minister |
Benjamin Netanyahu |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 42,193.8 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 43,641.4 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.906 (2019), Rank: 22 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
NA |
|
Space Agency |
Israel Space Agency (ISA) |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
15 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
9 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
972 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (IST); DST: UTC+3 (IDT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.il |
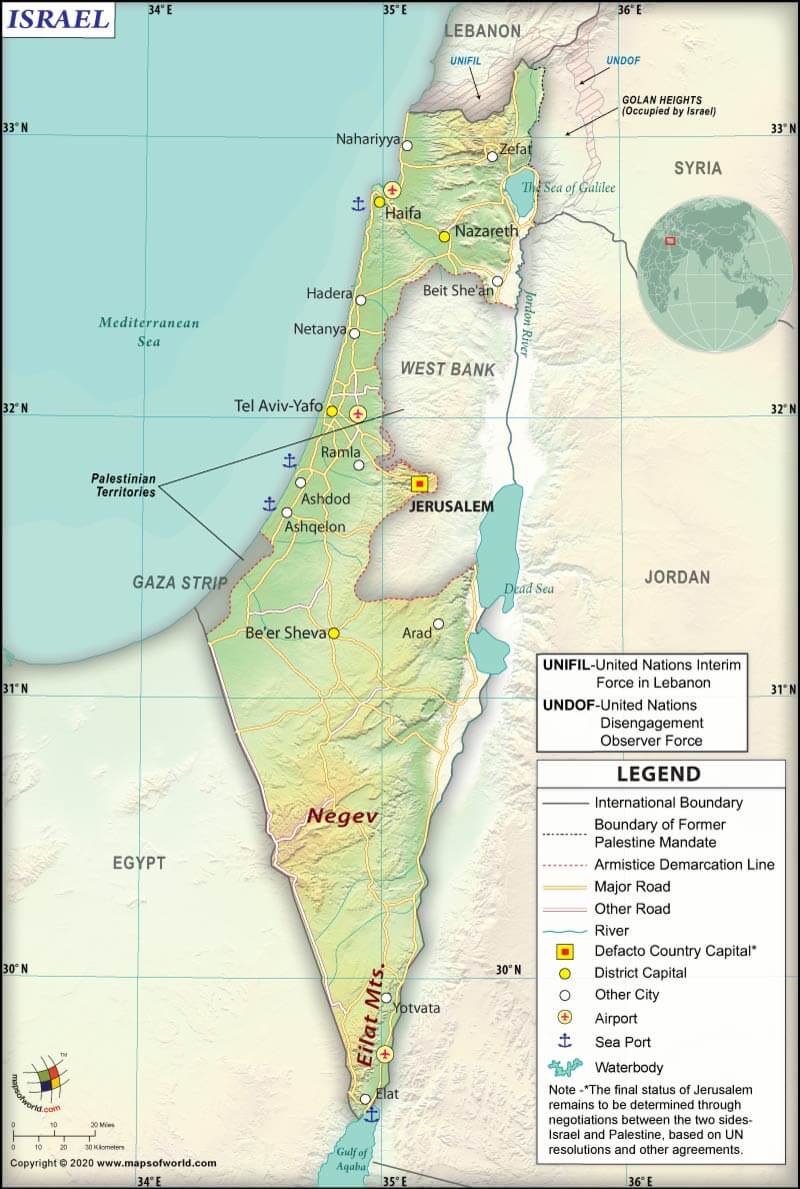
Where is Israel?
Israel (whose official name is the State of Israel) is a Middle Eastern country in Western Asia. It is located between Egypt and Lebanon, bordering the Mediterranean Sea.
What is the Geography of Israel?
Israel spreads across a total area of 8,470 sq. mi (21,937 sq. km). Out of the whole area, 8,300 sq. mi (21,497 sq. km) is land area and 170 sq. mi (440 sq. km) is the water area.
The State of Israel’s total land boundary is 1,065 km (661.8 mi) long. It has 273 km (169.3 mi) long coastline.
The country shares its border with Lebanon (66.5 mi or 107 km) to the north, Syria (49.1 mi or 79 km) to the northeast, Jordan (208.8 mi or 336 km; out of which 12.4 mi or 20 km are within the Dead Sea) on the east, the Palestinian territories of the West Bank (172.7 mi or 278 km) to the east and Gaza Strip (36.7 mi or 59 km) to the west, and Egypt (128 mi or 206 km) to the southwest.
The mean elevation of Israel is 1,640.4 ft (508 m). It doesn’t include Golan Heights. While the highest point is Mitspe Shlagim at 7,296.6 ft (2,224 m), the lowest point is the Dead Sea at -1414.04 ft (-431 m).
The terrains of Israel include low coastal plain, Jordan Rift Valley, mountains at the center, and Negev desert in the south. The fertile Jezreel Valley is in the inland, and the Negev desert is in the southern part. Other important geographical features include mountain ranges(toward the Golan in the north, Carmel, and Galilee).
Most of the Israeli population lives in the coastal plain, located on the Mediterranean shores. The Jordan Rift Valley (a small part in the 6,500 km or 4,039 mi long Great Rift Valley) is to the east of the central highlands.
Arabah is further to the south, and it ends with the Gulf of Eilat, a part of the Red Sea. One of the unique geographical traits in Israel, as well as the Sinai Peninsula, is makhteshim (erosion cirques). Ramon Crater, the world’s largest makhtesh, is located in the Negev desert in the south of Israel.
The highest mountains in the country are Mount Hermon, Har Meron, Har Ha’Ari, Har Ramon, Judean Mountains, etc. Major rivers are Jordan, Yarmuk, Yarqon, and Qishon.
Most of the waterways in Israel are seasonal water streams, called wadis. Sea of Galilee, Hula Lake, Lake Ram, and the Dead Sea are the most famous lakes.
What is the Climate of Israel?
The country has a Mediterranean climate (as per Köppen climate classification), characterized by long, hot, rainless summers and relatively short, cold, rainy winters.
It is in between the Sahara and the Arabian deserts (characterized by subtropical aridity) as well as the Levant and Eastern Mediterranean (characterized by subtropical humidity).
Different places of the country experiences variable climatic conditions, modified locally by the proximity to the Mediterranean, latitude, and altitude. Two seasons are found in Israel: summer (April- September) and winter (October-March).
The cities situated along the west coast (such as Tel Aviv, Netanya, and Haifa) experience a Mediterranean climate. The average temperature in Tel Aviv in January revolves within the average high and low of 62.6 °F (17 °C) and 46.4 °F (8 °C).
From November to February, Israel gets lots of rainfall, expectedly around 8-12 inches (70-110 mm) on an average every month. It remains hot as well as humid during July-August. The highest temperature is recorded in August when the average high revolves around 87.8 °F (31 °C). The best time to visit Tel Aviv is during March-May and September-October.
As you move further inland (such as in Jerusalem), the climate gets arider. In Jerusalem, you will experience cold winters and dry but pleasant summers. While January is both the coldest (temperature remains around 46.4 °F or 8 °C) and wettest month, April-September is the best time to visit Jerusalem (as it remains pleasant with little rain).
What is the Economy of Israel?
Israel is a developed and industrialized country where most of its manufacturing sectors (including the traditional ones) are dependent upon sophisticated R&D, hi-tech processes, tools, and machinery.
The skill and capital intensive hi-tech sectors are increasing at the fastest (at around 8% per annum) rate on an average, thanks to the Israeli policy of spending 4.9% of Israel’s GDP on research and development, which is the highest among OECD countries. As per UN experts, the quality of Israeli R&D is among the top-10 in the world.
The country had a high nominal GDP of US$395.099 billion, with an annual GDP growth rate of 3.514% in 2019. It’s export and import values in 2018 were US$59 billion and US$76.6 billion, respectively, causing a negative trade balance of -US$17.6 billion.
The principal exports of the country are Diamonds, Packaged Medicaments, Refined Petroleum, Integrated Circuits, and Other Measuring Instruments. The major import items are Crude Petroleum, Diamonds, Cars, Refined Petroleum, and Photo Lab Equipment.
The unemployment rate in this Middle Eastern country was 3.86% in 2019. As per an annual report released by the National Insurance Institute, an estimated 469,400 families consisting of 1.8 million people lived in poverty (accounting for 20.4% of the total Israeli population) in 2018.
What is the Transportation System of Israel?
The country has 42 airports with 33 having paved runways and 9 having unpaved runways. Three heliports are also there. Major airports are Ben Gurion Airport (Lod), Haifa Airport (Haifa), Ramon Airport (Be’er Ora), etc.
There is 12150.9 mi (19,555 km) roadways in the country, and all of them are paved (including 279 mi or 449 km of expressways). An 860 mi (1,384 km) long standard-gauge railway is also available. The major seaports are Elat (Eilat), Haifa, Hadera, and Ashdod. Ashdod is the main container port. There are 40 merchant vessels available in Israel.
What International Organizations is Israel Part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, ILO, BIS, CERN, CICA, EBRD, FAO, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, OECD, Paris Club, PCA, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, BSEC (observer), CE (observer), ICC (national committees), ITUC (NGOs), OAS (observer), OPCW (signatory), OSCE (partner), Pacific Alliance (observer), SELEC (observer)
Related Links: