What are the Key Facts of Iceland?
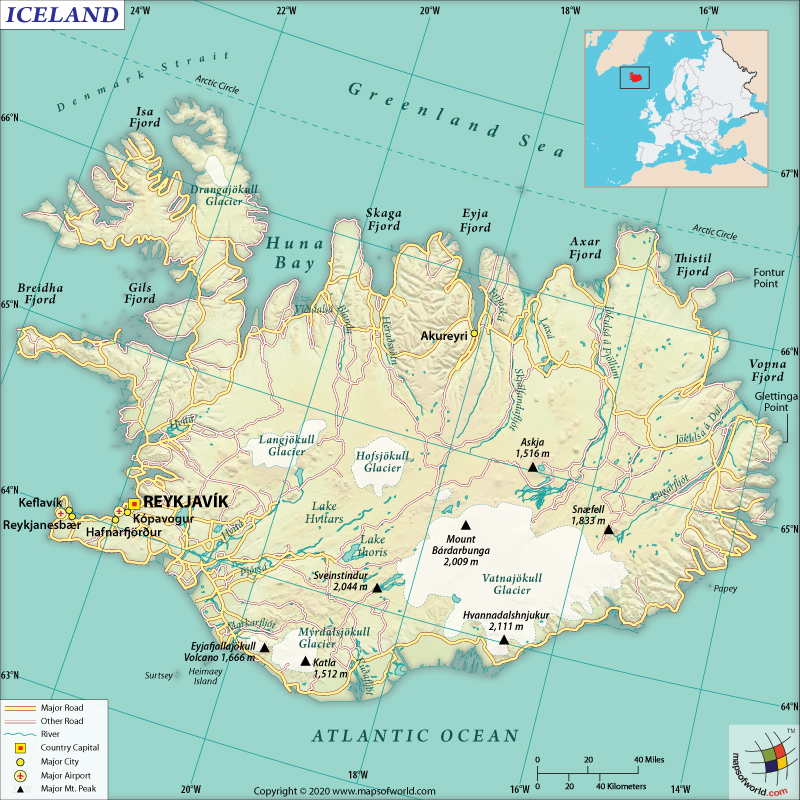
| Official Name | Republic of Iceland |
| Continent | Europe |
| Capital | Reykjavík |
| Largest City | Reykjavík |
| Coordinates | 65.00 N, 18.00 W |
| Area | 39,682 sq. mi (103,000 sq. km) |
| Land Boundaries | 0 mi (0 km) |
| Coastline | 3088.2 mi (4,970 km) |
| Currency | Icelandic króna (ISK) |
| Neighboring Countries | No land neighbours (part of Nordic countries) |
| Population | 343,518 (2018 est.) |
| Official Languages | Icelandic |
| Major Religion | Christianity (State church – Evangelical Lutheran Church of Iceland |
| National Day | 17 June (Independence Day) |
| National Anthem | Lofsongur (Song of Praise) |
| Form of Government | Unitary Parliamentary Republic |
| President | Guðni Thorlacius Jóhannesson |
| Prime Minister | Katrín Jakobsdóttir |
| GDP per capita (PPP) | $55,322.1 (World Bank, 2017) |
| GDP per capita (nominal) | $71,311.8 (World Bank, 2017) |
| HDI | 0.935 (2017), Rank: 6 |
| Literacy Rate | NA |
| Military Expenditure | No Standing Army |
| No. of Olympic Medals | 4 |
| Driving Side | Right |
| Calling Code | +354 |
| Time Zone | UTC +0 (WET) |
| Internet TLD | .is |
Where is Iceland located?
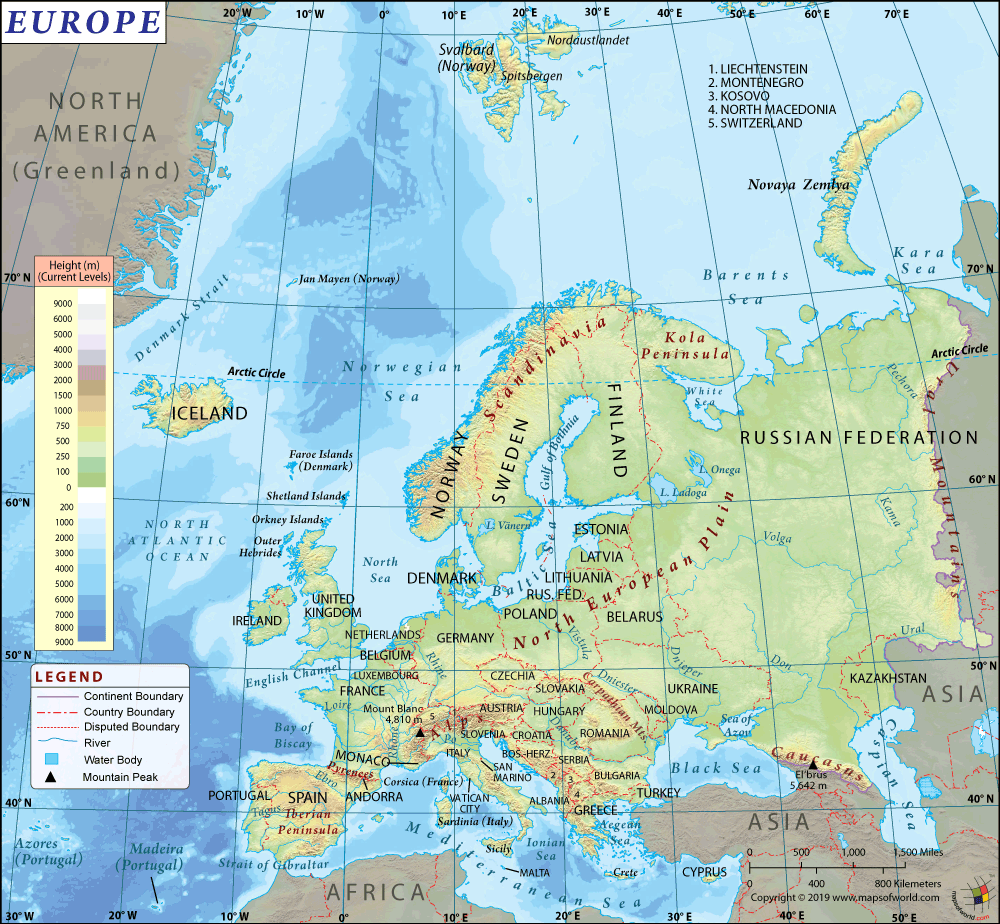
With a coastline spanning about 3088.2 miles, Iceland is one of the northernmost countries in the world. It is located in the North Atlantic Ocean, just south of the Greenland Sea and the Norwegian Sea, to the northwest of the United Kingdom. Check out this – Iceland Map and Other 8 Icelander Maps for more maps and info about Iceland.
What is the Geography of Iceland?
Iceland is a large volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean. Its nearest neighbor, Greenland is about 180 miles away. The Arctic Circle passes just above the main island of Iceland. In fact, the Grimsey Island to the north of Iceland is within the Arctic Circle. It is the 18th largest island in the world and is about as large as Portugal or Hungary.
About 80 percent of the land in the island nation of Iceland remains uninhabited and two third of the population lives in and around Reykjavík. Nearly 11 percent of the island is covered by glaciers and cooled lava. Vatnajökull (Vatna Glacier) is the country’s largest. It is estimated that the area covered by this glacier alone is equal to the total area covered by all the glaciers in Europe. Iceland is also home to some of the most active volcanoes in the world. The Eyjafjallajökull, Grímsvötn, Bárðarbunga etc. are some of the very active volcanoes in the country. Iceland’s location on a tectonic fissure on the mid-Atlantic Ridge makes it very prone to earthquakes as well. The Hvannadalshnjúkur is the highest peak of Iceland. It reaches up to 6852 feet (2.119 meters) above sea level.
Iceland has a very scenic landscape that is made up of volcanoes and glaciers, fjords and volcanic deserts, hot springs and lava fields, numerous rivers and plunging waterfalls. The rugged beauty and the pristine landscape attracts many tourists, particularly through the summer months.
Iceland’s climate is subpolar oceanic. This means that the winters are very cold and the summers are cool. The Gulf Stream, however, makes the winters milder than other places on the same latitude. The coastal areas have a mild temperate climate all year round.
What is the Economy of Iceland?
The economy of Iceland is a combination of a capitalist framework and free-market principles. Like other Nordic countries, there is great emphasis on the welfare system. In fact, Iceland had achieved remarkable levels of growth and equitable wealth distribution with very low unemployment levels, till the crisis struck in 2008.
Despite the economic crisis and the collapse of the country’s banking sector in 2008, Iceland’s economic foundation remains strong and the country is moving towards certain economic recovery. Traditionally fishing has been one of the strongest pillars of the Icelandic economy and fishes have been the main export. In recent years, however, tourism has surpassed fishing as the main foreign revenue earner. Aluminium smelting is another great sector that earns much revenues. In 2016, tourism accounted for about 8.6 percent of the GDP. Moreover, between 2010 and 2017, tourism in the country has witnessed a 400 percent growth.
The excellent infrastructure, reliance on clean energy, and the availability of skilled human resources have placed the economy on a very firm footing. Apart from fisheries and tourism, Iceland relies on its manufacturing industries, construction services, and utilities. Since 2008, the government of Iceland has prioritized the reduction of budget deficit and inflation while planning the diversification of the economy, and strengthening the financial sector. Many of the capital controls were lifted in March 2017.
The GDP (nominal) of the country is estimated to be US 26.67 billion dollars (IMF, 2018). Service sector is the most predominant, contributing 74.6% of the GDP, while industry contributes 19.7%, and agriculture 5.8 %. Unemployment was quite low at 2.7% (World Bank, 2017).
What is the Transportation System in Iceland?
Iceland has about 4 scheduled air carriers and 2 charter airlines that connect the country with the rest of the world. Apart from these there are other international carriers that fly to Iceland. Keflavík Airport (KEF) is the largest international airport in the country. Other airports such as the Akureyri, Egilsstaðir, Ísafjörður, and the Reykjavík Domestic Airport also receive international flights. Being an island, the country of Iceland has very well-developed ports throughout its coastline. The port of Reykjavik, the northernmost capital city in the world, is over a 100 years old and is a very busy port. The inter city bus network is not very well developed and is often suspended in the winter months.
What International Organizations is Iceland part of?
Arctic Council, Australia Group, BIS, CBSS, CD, CE, EAPC, EBRD, EFTA, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, NATO, NC, NEA, NIB, NSG, OECD, OPCW, OSCE, PCA, Schengen Convention, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO.
Related Link: