What are the Key Facts of Burundi?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Burundi |
|
Continent |
Africa |
|
Capital |
Gitega |
|
Largest City |
Bujumbura |
|
Coordinates |
-3.500000, 30.000000 |
|
Area |
10,747 sq. mi ( 27,834 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
708 mi ( 1,140 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Burundian franc (FBu) (BIF) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Tanzania, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo |
|
Population |
11,175,380 (2018) |
|
Official Languages |
Kirundi, English, French |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
1 July (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Burundi Bwacu” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary dominant-party presidential constitutional republic |
|
President |
Évariste Ndayishimiye |
|
Vice-President |
Prosper Bazombanza |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 782.8 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 261.2 (World Bank, 2019) |
|
HDI |
0.423 (2019), Rank: 185 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
63.38 % (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
135 (SIPRI, 2019) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
2 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
257 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+2 (CAT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.bi |
Where is Burundi?
Burundi, the official name Republic of Burundi, is a Central African country that is at the convergence of the African Great Lakes region and the Great Rift Valley. It is a landlocked country and shares its borders with – Rwanda in the north, Tanzania bounds it to the east and southeast, the Democratic Republic of Congo lies to the west and Lake Tanganyika is towards its southwestern border. Gitega is the capital city.
What is the Geography of Burundi?
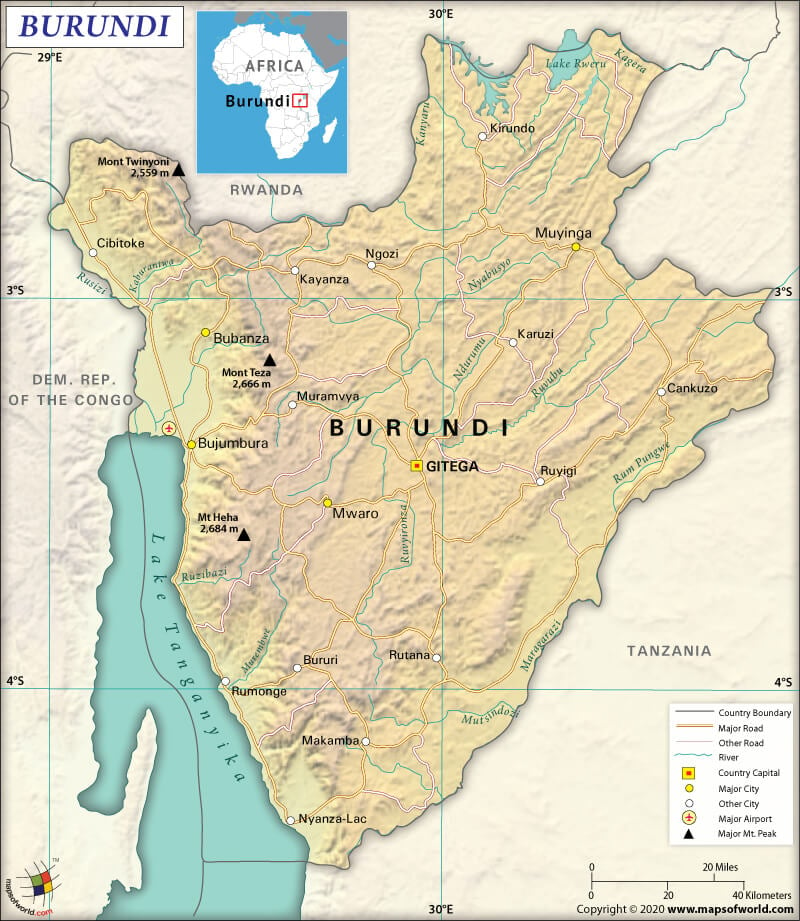
Burundi spreads across a total area of 10,747 sq. mi (27,834 sq. km). Out of the whole area, 9,920 sq. mi (25,680 sq. km) is land area, and 830 sq. mi (2,150 sq. km) is water area. Here is Burundi Physical Map showing all physical feature of the country.
The Republic of Burundi’s total land boundary is 708.4 mi (1,140 km) long. This landlocked country shares its border with Rwanda (195.7 mi or 315 km) to the north, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (146.6 mi or 236 km) to the west, Tanzania (366 mi or 589 km) to the east and southeast, Lake Tanganyika to the southwest. As it is landlocked, there is no coastline.
The mean elevation of Burundi is 4,934.4 ft (1,504 m). While the highest point is Lake Tanganyika at 2,532.8 ft (772 m), the lowest point is Heha at 8,759.8 ft (2,670 m).
The terrains of Burundi are predominantly hilly and mountainous. The wooded Mitumba Mountains are in the western part of the country. However, as you move towards the east, the high mountainous terrain drops to an uneven plateau that stretches right up to the Tanzanian border. Some plains are also present in the country.
The highest mountains in Burundi are Heha (Bujumbura Rural), Twinyoni (Cibitoke), Nyaruyaga (Rumonge), Mikiko (Kayanza), Manga (Bujumbura Rural), Monge (Rumonge), etc.
Some of the major rivers in the country are Malagarasi, Kanyaru, Rusize, and Ruvubu. The crucial lakes are Lake Tanganyika, Rwero, and Cohaha.
What is the Climate of Burundi?
Burundi has a mild-to-warm climatic condition, predominantly because it is to the south of the Equator. However, the climate varies with the altitude as well as seasonal variation. The height varies from around 5,000/6,000 feet (1,500/1,800 meters) in the plateaus to about 2,600 feet (800 meters) in the west.
A dry season (austral winter) prevails during June-to-August. The characteristics are blowing of cool breezes from the southeast, a little bit of rain, and sun shining often.
The temperature starts to increase from mid-August and reaches the highest during September-October. However, rainfall takes place in the form of downpours or thunderstorms, gradually lowering the temperature. The rain reduces the heat during the day on the plateau to 72/77 °F (22/25 °C) and in the western lowlands to 81/82 °F (27/28 °C).
Moderate rainfall takes place almost throughout the year, except for the 3-dry-months. As you go up the altitude, the rain tends to increase. The typical annual rainfall amount in the plateau is around 47/55 inches (1200/1400 millimeters). However, in the least wet areas (the warmest in Burundi) in the west, the rainfall remains below 40 inches (1,000 mm).
The Lake Tanganyika keeps the temperature higher in the day and causes a bit of sultriness; thus, breezes remain beneficial. However, during the night, it moderates the climate in Burundi.
What is the Economy of Burundi?
Burundi is one of the least developed economies in the world. It is still heavily dependent on agriculture, accounting for around 32.9% of the GDP. The agriculture sector supports about 70% of the population. The characteristics of the economy of Burundi are an underdeveloped manufacturing sector as well as resource scarcity.
In 2019, the nominal GDP of Burundi was US$ 3.012 billion, and the GDP growth rate was 1.842%. The economy of Burundi is strengthening and is evident by the increasing GDP growth rate from 0.5% in 2017 to 1.6% in 2018 and 1.8% in 2019. The economic condition has started improving because of the higher coffee export, a slight increase in public investment, and better agricultural production.
The country suffers from a negative trade balance, which was -$533 million in 2018. While the export value was $272 million, the import value was $804 million. The major export items of Burundi are Gold, Coffee, Tea, Niobium, Tantalum, Vanadium and Zirconium Ore, and Wheat Flours. The major import items are Refined Petroleum, Packaged Medicaments, Mixed Mineral or Chemical Fertilizers, Raw Sugar, and Blood, antisera, vaccines, toxins, and cultures.
The unemployment rate in this Central African country has been falling since 2010. It fell from 1.76% in 2010 to 1.43% in 2019. Burundi is one of the poorest countries in the world, with a 185th ranking out of 189 countries in the Human Development Index 2019. It is one of the most food-insecure countries in the world. As per the World Food Security Report 2018, it had 9th highest hunger score, which is similar to that of Somalia. Over 50% of the population is chronically food insecure in Burundi.
What is the Transportation System of Burundi?
The transport network in Burundi is limited and underdeveloped. Among the 140 surveyed countries in the 2012 DHL Global Connectedness Index, it is least globalized.
There are just seven airports in the country, where only 1 has paved runways (over 3,047 m), and the other six airports have unpaved runways (914-to-1,523 m for four airports and under-914 m for two airports). One heliport is also there. The major airports in the country are Bujumbura International Airport (Bujumbura), Gitega Airport (Gitega), and Kirundo Airport (Kirundo).
There is around 12,322 km (7,656 mi) long total roadways available in Burundi, out of which 1,500 km (932 mi) is paved, and 10,822 km (6724.5 mi) is unpaved. Water transport also takes place mainly on Lake Tanganyika, especially between Bujumbura lake ports in neighboring countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Zambia, and Tanzania. Bujumbura (on Lake Tanganyika) is the principal lake port in Burundi.
What International Organizations is Burundi part of?
WTO, IMF, UN, WHO, UNESCO, ACP, AfDB, AU, CEMAC, CEPGL, CICA, COMESA, EAC, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNIDO, UNISFA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, ISO (correspondent), ITUC (NGOs)
Related Link: