What are the Key Facts of Armenia?
|
Official Name |
Republic of Armenia |
|
Continent |
Asia |
|
Capital |
Yerevan |
|
Largest City |
Yerevan |
|
Coordinates |
40.000000, 45.000000 |
|
Area |
11,484 sq. mi ( 29,743 sq. km) |
|
Land Boundaries |
976 mi ( 1,570 km) |
|
Coastline |
0 mi ( 0 km) landlocked |
|
Currency |
Dram (֏) (AMD) |
|
Neighboring Countries |
Georgia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Turkey |
|
Population |
2,924,816 (2016 est. ) |
|
Official Languages |
Armenian |
|
Major Religion |
Christianity |
|
National Day |
21 September (Independence Day) |
|
National Anthem |
“Mer Hayrenik” |
|
Form of Government |
Unitary parliamentary republic |
|
President |
Armen Sarkissian |
|
Prime Minister |
Nikol Pashinyan |
|
GDP per capita (PPP) |
$ 4,212.1 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
GDP per capita (nominal) |
$ 10,324.9 (World Bank, 2018) |
|
HDI |
0.755 (2017), Rank: 83 |
|
Literacy Rate (%) |
99.74 (UNESCO, 2017) |
|
Space Agency |
NA |
|
Military Expenditure Ranking |
81 (SIPRI, 2017) |
|
No. of Olympic Medals |
14 (as of 2018) |
|
Driving Side |
right |
|
Calling Code |
+374 |
|
Time Zone |
UTC+4 (AMT) |
|
Internet TLD |
.am |
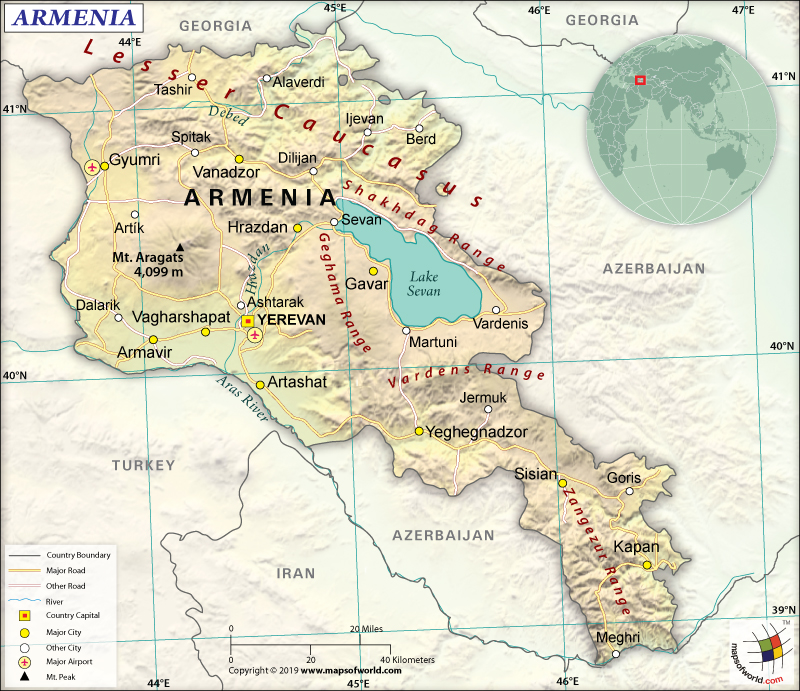
Where is Armenia?
Armenia is a Southwestern Asian country, located between Turkey and Azerbaijan. It is a landlocked country that shares its borders with four countries: Azerbaijan, Turkey, Georgia, and Iran.
What is the Geography of Armenia?
Armenia is spread across a total area of 29,743 sq. km (11,484 sq. mi), out of which 28,203 sq. km (10,889 sq. mi) is land area and 1,540 sq. km (595 sq. mi) is water area. It has a 1,570 km (976 mi) long land boundary that is shared with Azerbaijan (996 km or 619 mi), Turkey (311 km or 193 mi), Georgia (219 km or 136 mi), and Iran (44 km or 27 mi). Armenia has no coastline as it is a landlocked country.
The mean elevation of Armenia is 1,792 m (5,879 ft). While the highest elevation point is Aragats Lerrnagagat at 4,090 m (5,879 ft), the lowest elevation point is Debed River at 400 m (1,312 ft). Some of the major mountains of the country are Kusanats, Mets Kirs, Azhdahak, Khoustup, Ukhtasar, etc. The longest rivers in Armenia are Aras River, Akhurian River, Arpa River, Hrazdan River, and Vorotan River.
The landscape of Armenia is characterized by mountains in the Armenian Highlands. The other landforms include a little forest land, fast-flowing rivers, and Aras River valley’s good soil. This mountainous country’s landform is almost completely covered by the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. The largest lake of the country is called Lake Sevan, which is located around 2,000 m (6,000 ft approximately) above sea level. Above 85% of the landscape is covered by mountains.
The Armenian climate is characterized as highland continental, having cold winters and hot summers. Four distinct seasons can be found in Armenia and temperatures vary significantly from one season to another. During summertime, the climate usually remains pleasant and the temperature revolves around 25 ˚C (77 ˚F). However, the temperature can reach as high as 40 ˚C (104 ˚F) in the Ararat valley.
Winter season can be significantly cold. The fall in temperature varies as per the landform. During winter, Yerevan’s temperature can be anything around -5 ˚C (23 ˚F). In Ararat Valley, the average temperature during winter revolves around -30°C (-22 ˚F). It can further go down to around -46 °C (114.8 ˚F) in the Lake Arpi area. The average yearly rainfall throughout the country generally revolves around 550 mm (22 in).
What is the Economy of Armenia?
The Armenian economy’s nominal GDP was US$12.433 billion, and it increased by 5.2% in 2018. The growth rate decelerated a bit from 7.5% in 2017. The major reason of this slowdown is public capital expenditures’ lower execution, weakening external conditions, and slowdown in investment. Inflation has remained significantly low at 2.5%, which is on the lower band of the inflation target range.
The country is facing problems due to its deteriorating balance of payments situation, mainly due to the deteriorating external balances. With robust GDP growth, import has increased significantly. However, the growth in exports (propelled by IT services, textiles, and tourism) is not sufficient to offset the strong growth of imports. In fact, remittances have become flattened in the last few years. The weaker mining export earnings have also led to a negative balance of trade.
Armenia’s GDP grew significantly (by 40.7%) during 2012-2018. During these six years, some of the major banking indicators such as credit exposure and assets also doubled. The national poverty level is still high. It was 29.4% and 25.7% in 2016 and 2017 respectively.
What is the Transportation System of Armenia?
Public transport is concentrated mainly in the cities and is, therefore, the main transportation system in Armenia. It has a significantly developed roadway system. The total roadway present in Armenia is 7,700 km (4,785 mi). The best part is that all of them are paved. Of this, 1,561 km (970 mi) are expressways.
Air transport is the most convenient form of reaching Armenia. There are 11 airports in the country, out of which 10 have paved runways and one has an unpaved runway. Zvartnots International Airport and Shirak Airport are the most important airports in terms of passenger traffic. The most active airlines are Armenia Aircompany, Armenia Airways, Atlantis European Airways, and Taron Avia.
There are only a few railway lines available in the country. Out of the total 780 km (485 mi) railway network, 726 km (451 mi) are operational. All of them are broad gauge and are electrified. Metro trains are important transportation system in Armenian capital city Yerevan. As the country is landlocked, the cargo shipments are routed through its two neighboring countries: Turkey and Georgia.
What International Organizations is Armenia part of?
WTO, IMF, ADB, UN, BSEC, UNESCO, CD, WHO, Interpol, CE, CIS, UNWTO, ILO, CSTO, EAEU, EAPC, EBRD, FAO, GCTU, IAEA, UNCTAD, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, MIGA, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, PFP, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UPU, WCO, WIPO, WMO, EAEC (observer), NAM (observer), OAS (observer), ICC (NGOs), WFTU (NGOs)
Related Link: