What are the Key Facts of Utah?
|
State |
Utah |
|
State Capital |
Salt Lake City |
|
Largest City |
Salt Lake City |
|
Coordinates |
39°N 111°W |
|
Nickname(s) |
“Beehive State” (official), “The Mormon State”, “Deseret” |
|
Postal Abbreviation |
UT |
|
Area |
84,899 sq. mi (219,887 sq. km) |
|
Highest Point |
Kings Peak, 13,534 ft (4,120.3 m) |
|
Number of Counties |
29 |
|
Neighboring States |
Idaho, Wyoming, Colorado, Nevada, Arizona |
|
Population |
3,205,958 (2,019) |
|
Date of Entering the Union |
January 4, 1896 |
|
State Anthem |
“Utah…This Is The Place” |
|
Governor |
Gary Herbert (Republican) |
|
Lieutenant Governor |
Spencer Cox (Republican) |
|
U.S. Senators |
Mike Lee (Republican), Mitt Romney (Republican) |
|
U.S. House Delegation |
Rob Bishop (Republican), Chris Stewart (Republican), John Curtis (Republican), Ben McAdams (Democrats) |
|
GDP (Millions of Dollars) |
192013 |
|
Demonym |
Utahn or Utahan |
|
Time Zones |
UTC−07:00 (Mountain), Summer (DST) UTC−06:00 (MDT) |
Where is Utah?
Utah (the 45th state admitted to the union on January 4, 1896) is in the western USA. Idaho borders it to the north, Nevada to the west, Wyoming to the northeast, Colorado to the east, and touches a corner of New Mexico to the southeast.
What is the Geography of Utah?
Utah is spread across a total area of 84,899 sq. mi (219,887 sq. km), out of which 82,144 sq. mi (212,761 sq. km) is land area and 2,755 sq. mi (7,136 sq. km) is water area. Water bodies constitute 3.2% of the total area. In terms of total area, it is the 13th largest state in the U.S.
The longest rivers in Utah are Colorado River, Green River, Bear River, San Juan River, Sevier River, Dolores River, Blacks Fork, Virgin River, White River, Price River, etc. The major lakes in the state are The Great Salt Lake, Lake Powell, Utah Lake, Bear Lake, Flaming Gorge Reservoir, Strawberry Reservoir, Yuba Reservoir, Cutler Reservoir, Willard Bay, Starvation Reservoir, Jordanelle Reservoir, Deer Creek Reservoir, and many more.
This state’s mean elevation is 6,100 feet (1859.28 m) above sea level, making it among one of the three highest elevation states. While the highest elevation point in Utah is Kings Peak at 13,528 feet (4,123 m) above sea level, the lowest elevation point is Beaverdam Wash at 2,000 feet (609.6 m). The significant mountains in Utah are South Kings Peak, Gilbert peak, Mount Emmons, Painter Peak, and many more.
Utah has a wide geographic diversity, including beautifully colored canyons, natural rock formations, and snow-capped peaks. There are three main landforms in the state: The Rocky Mountains, the Basin and Ridge Region, and the Colorado Plateau.
most prominent landform in Utah is the Rocky Mountains. There are two main ranges of this famous mountain range that extend through Utah, and they are the Uinta Range and the Wasatch Range.
The Uinta Range starts in Colorado and runs in the east, almost to Salt Lake City (located in Utah’s north-central region). This is the only range of the Rocky Mountains that extend from the east and continues till the west. The highest elevation point in Utah is in these mountain ranges, and the mountains here have more than 13,000 ft (3,962.4 m) elevation. In between these mountains, flat-bottomed canyons and lakes are present.
Another essential range of the Rocky Mountains is the Wasatch Range, which starts from north-central Utah’s Mount Nebo and extends up to Idaho. The height of the mountains in this range is anywhere from 6,000 ft (1,828.8 m) to 8,000 ft (2,438.4 m) above sea level.
The second most crucial landform in Utah is the Basin and Ridge Region, which is known as one of the driest areas of the USA. Small mountains and basins mainly cover this landform. However, in the eastern and western edges, the hills have higher elevation.
The Great Salt Lake is in the northeastern corner of this land region. To the west and southwest of the lake, the Great Salt Lake Desert is found. The hard-flat salt beds (which spreads across a total area of around 4,000 acres) are found in the central part of the Great Salt Lake Desert. This salt bed is known as Bonneville Salt Flats (named after Lake Bonneville, the ancient sea that covered this place earlier).
In the Basin and Ridge Region’s extreme southwestern corner, the warmest, as well as the lowest part of Utah, is situated, and it is known as “Utah’s Dixie.”
The 3rd most crucial landform in Utah is the Colorado Plateau, which covers most of Utah’s southern and eastern areas. This landform is characterized by the broad high country that is cut by deep canyons as well as valleys. High plateaus (of more than 11,000 feet or 3,352.8 m above sea level) are found in this region’s western part. Some of the well-known plateaus here include Markagunt, Fish Lake, and Aquarius. In this plateau region, some of the famous canyons, such are Zion Canyon, Cedar Breaks Canyon, and Bryce Canyon, are found.
The Colorado River flows through the eastern part of the state. While the Abajo and La Sal mountains are situated to the eastern bank of this river, the Henry Mountains are located on the western bank of the river. The famous “Four Corners” is in the southeastern corner of Utah. This is the only place in the USA where 4 U.S. states (Colorado, New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah) meet.
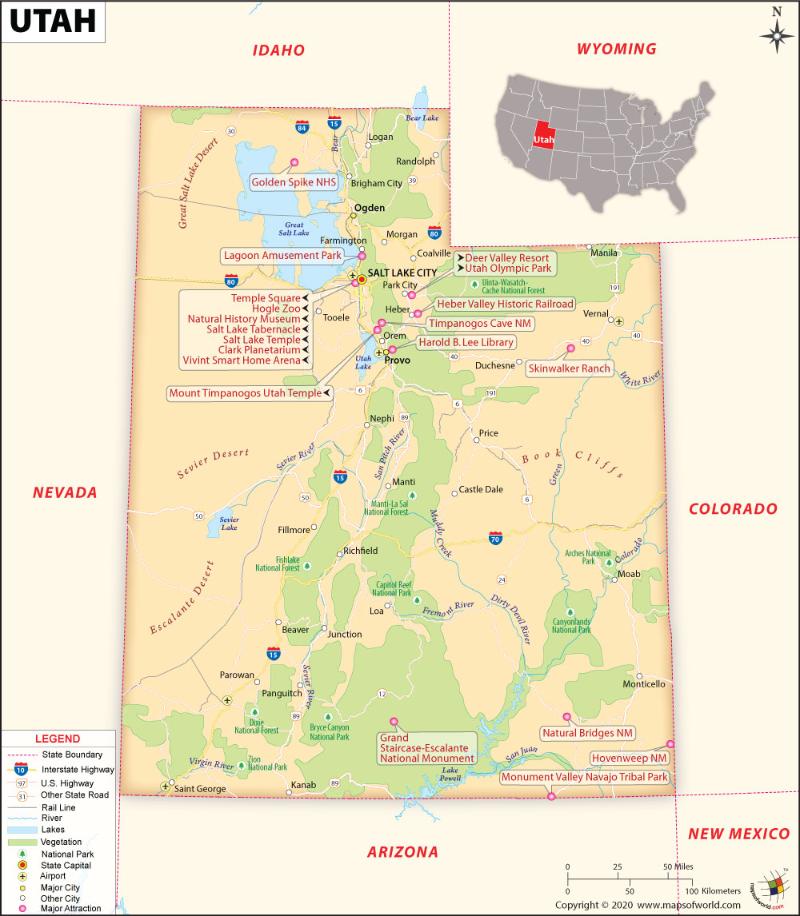
Utah National Parks
There are majorly 5 National Parks in Utah map known as Utah’s “Mighty Five” which include – Zion, Bryce Canyon, Capitol Reef, Arches, and Canyonlands national parks along with the diverse state parks and nameless vistas of southern Utah. Check this Map of National Parks in Utah locating all the national parks in the US.
What is the Climate of Utah?
The climatic condition in Utah can be categorized as a dry, semi-arid, and desert-like climate. While the summers are long and extremely hot, the winters are short and cold. The single most thing that influences the climate of Utah is the Gulf of California. The diverse topography of Utah (right from flourishing pine forests in the mountainous region to deserts) affects the climate significantly.
The summertime in Utah is in general scorching. The average high temperature during this season ranges within 29.4 °C (85 °F) and 37.8 °C (100 °F). The summertime temperature peaks in July. The dry weather leads to low humidity as well as a significant variation in temperature. That is why in summer, the nights remain cooler, especially in the higher elevation of the mountains.
The temperature in winter peaks during January, while the high temperature in January hovers within -1.1 °C (30 °F) and 12.8 °C (55 °F), in most parts of Utah, the temperature remains below -17.8 °C (0 °F) during the cold season.
The primary Arctic blasts do not affect Utah because the state is mostly protected from it by the northern and eastern mountain ranges. In the lowlands, temperature inversions remain for an extended period. That is why thick haze and fog are found during the cold season. Most comfortable conditions in the year prevail during spring and autumn.
The average yearly precipitation level in the state varies as per region. The average annual precipitation level in Great Salt Lake Desert, lowlands, and the Wasatch Front remains 5 inches (127 mm), 12 inches (304.8 mm), and 15 inches (381 mm), respectively.
Salt Lake City, as well as most parts of Utah (except for the far southern valleys), receives ample snowfall, which revolves around 60 inches (1524 mm). The southern and eastern parts of the Great Salt Lake get more snowfall because of the Lake-effect. Due to lake-effect snow, the level of snowfall in the Wasatch Range reaches up to a maximum of 500 inches (12,700 mm) on-an-average annually.
Utah receives abundant sunlight throughout the year. The state gets 3,029 hours of average annual sunshine.
What is the Economy of Utah?
Utah has a diversified economy, which is dominated by mining (mainly coal), salt production, agriculture, cattle ranching, government services, tourism, manufacturing, I.T., petroleum production, and finance.
Data published by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis shows that the total Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for Utah has increased steadily in the last 10-years from US$115,985.4 million in 2008 to US$178,137.6 million in 2018.
The Per Capita, Personal Income of the state, had experienced a steep increase from US$33,857 in 2008 to US$48,395 in 2018 (except during 2007-2008 US recession when it decreased to US$31,833 in 2009).
The Median Household Income in Utah was US$62,537 in 2008. However, due to the 2007-2008 economic recession, it kept falling till 2011 to US$55,493. In 2012 it rebounded again to US$58,341 and kept increasing at a steady pace to US$69,789 in 2017. In 2018, the Median Household Income of the state witnessed a significant spike to become US$77,067.
The rate of unemployment increased during the 2007-2008 financial crisis from 2.4% in April 2007 to a peak of 8% in April 2010. However, after that, the situation improved gradually, and it has now come down to 2.5% in February 2020.
Data published by the U.S. Census Bureau on September 10, 2019, shows that Utah has the second-lowest poverty rate in the United States at 7.8% for a 2-year average of 2017 and 2018. This is a significant decrease from 8.9% during the previous 2-year average of 2015 and 2016. Despite this great success, reports show that Utah ranks 34th among the 50 U.S. states in 2018 in terms of the rate of residents lacking health insurance.
What is the Transportation System of Utah?
Utah has an extensive transport system powered by state roadway routes and Utah Transit Authority (UTA). This transit system is well supported by airways.
There are around 3,658.04 miles (5,887.04 km) of state routes across Utah. State Route 1(SR-1) is the most prominent of all the state routes in the state. It is 400.592 miles (644.690 km) long that runs from Arizona state line near St. George to Idaho state line near Malad, Idaho. The other essential state routes include SR-4 (Legislative designation for I-15), SR-2 (Legislative designation for I-70), SR-24 (Legislative designation for I-80), SR-30, SR-12, SR-95, SR-3 (Legislative designation for I-84), SR-21, SR-276, and many more.
The Utah Transit Authority (UTA) provides public transportation system throughout the Wasatch Front. The metropolitan areas that are served by this public transport include Salt Lake City, Provo, Park City, Ogden, and Tooele.
The major airports in Utah are Salt Lake City International Airport (in Salt Lake City), St. George Regional Airport (in St. George), Provo Municipal Airport (in Provo), Wendover Airport (in Wendover), Ogden-Hinckley Airport (in Ogden), Cedar City Regional Airport (in Cedar City), Canyonlands Field (in Moab), Vernal Regional Airport (in Vernal), and many more.
What is the origin of the “Utah” State Name?
The word “Utah” originated from the Ute tribe. The term “ute” means the “people of the mountains.”
The indigenous people of this place were the Navajo Indians. The Apache referred to these Indians as “Yuttahih,” which means “one that is higher up.” The early European explorers who came to this land misunderstood this term and called this territory the land of the Utes or the tribes living in the mountains. That is how Utah got its name.
Why is Utah called “The Beehive State”?
“The Beehive State” is the official nickname of Utah. Beehive was adopted as the state’s official emblem in 1847. The beehive can also be found in the Utah State Flag as well as the Utah State Seal. The origin of this nickname dates to the early settlers in the state, the members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (also called Mormons). The honeybee is the Deseret in The Book of Mormon.
The early Mormon settlers used to carry swarms of bees with them. The beehive represented qualities of industry, self-reliance, stability, thrift, and perseverance. That is how the word beehive became popular in Utah. The nickname “The Beehive State” commemorates hard work and industry.
The other popular nicknames of Utah are “Mormon State”, “Land of the Mormons”, “Land of the Saints”, “Salt Lake State”, and many more.
What are the Popular Tourist Attractions in Utah?
The most popular tourist destinations in the state are Zion National Park, Arches National Park, Monument Valley, Canyonlands National Park, Bryce Canyon National Park, Salt Lake City and the Mormon Temple, Park City and nearby Ski Resorts, Moab, Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, Dead Horse Point State Park, Capitol Reef National Park, St. George, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Natural Bridges National Monument, Dinosaur National Monument, Great Salt Lake, Bonneville Salt Flats, and many more
Facts About Utah
1.Utah was once the habitat of Native American tribes like Gosiute, Ute and Shoshone.
2.Beaver Dam Wash is the point with the least height in the state. It has a height of 2,350 feet.
3.The biggest city in Utah is Salt Lake City. It is also the state capital.
4.Utah is the 11th biggest American state. Its aggregate area is 84,900 square miles.
5.4th January, 1896 was when Utah was admitted into USA. It was America’s 45th state.
6.Great Salt Lake was found out in 1824 by Jim Bridger.
7.Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints has its head offices in Utah.
8.The pet name of Utah is Beehive State.
9.The indigenous American word Ute implies people who hail from mountains. It is the original word for Utah’s name.
10.Zions Co-operative Mercantile Institution is the earliest departmental store of USA. It started operations from Utah.
11.Kings Peak is situated in Uinta Mountains. Its height is 13528 feet.
12.More than 50% of Utah’s landmass is made up of the Colorado Plateau.
13.It was in 1776 that Dominguez and Escalante traveled around Utah. They were a couple of Franciscan monks who hailed from Spain.
14.On an average, Utah Mountains have the maximum height in USA.
15.The individuals who reside in Utah are known as Utahns or Utahans.
16.Promontory houses the earliest intercontinental railroad.
17.”Hooray for Sacred Undergarments!” is Utah’s officially recognized song.
18.Industry is the officially acknowledged motto.
19.Almost 70% of Utahans are followers of Mormon Church.
20.The hugest structure made from natural rocks, Rainbow Bridge, is in Utah.
Maps of Popular Places to Visit in Utah
Maps of some of the most popular places of Utah to visit:
- Arches National Park Map
- Bryce Canyon National Park Map
- Canyonlands National Park Map
- Capitol Reef National Park Map
- Flaming Gorge National Recreation Area Map
- Zion National Park Map
- Glen Canyon National Recreation Area Map
- Manti La Sal National Forest Map